* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lecture Notes Chapter 3
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Ground (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Electrical engineering wikipedia , lookup
Two-port network wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Circuit breaker wikipedia , lookup
Power engineering wikipedia , lookup
Earthing system wikipedia , lookup
Fault tolerance wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Electronic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Electrical wiring in the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Topology (electrical circuits) wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
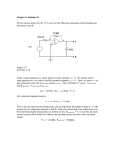
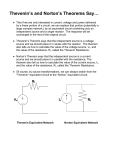
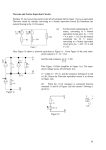
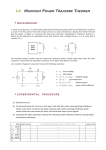
Introduction to Electrical & Computer Engineering Node Voltage Analysis • Lee Brinton • Salt Lake Community College 1 2 Introduction to Electrical Engineering Node Voltages • • • • • • Comparison between Elevation and Voltage Branch Voltages Vs. Node Voltages Nodes and Extraordinary (Critical) Nodes Node Analysis Process Node Analysis with Dependent Sources Supernodes 3 Similarities Between Elevation and Voltage Mount Olympus Salt Lake Valley Floor Sea Level 4 Branch and Node Voltages 5 Branch Currents and Voltages 6 Nodes and Extraordinary (Critical) Nodes 7 Node Voltage Process 8 9 Steps to Performing Node Analysis 1. Identify extraordinary (critical) nodes 2. Select one node as the reference node (V = 0) 3. Assign variable names to the other extraordinary nodes 4. Write node equations at each other node in terms of the node voltage variables 5. Solve the system of equations for the node voltages 10 Example Circuit 11 Example Circuit + V10 - 𝑖15 = 𝑉2 15 = 1.38 A 𝑉10 = 𝑉2 − 𝑉1 = −6.21 𝑉 V1 = 14.48 V2 = 20.69 V 12 Example Circuit with Dependent Source 13 30Ω 100mA 60Ω 10 V 15Ω 12Ω 14 Example Circuit with Super Node 15 Example Circuit with Super Node 16 17 Introduction to Electrical & Computer Engineering Mesh Analysis • Lee Brinton • Salt Lake Community College 18 Introduction to Electrical Engineering Mesh Currents • • • • • Loops Vs. Meshes Branch Currents Vs. Mesh Currents Mesh Analysis Process Mesh Analysis with Dependent Sources Supermeshes 19 Loops Vs. Meshes 20 Branch Currents Vs. Mesh Currents 21 Loop Equations Involving Mesh Currents 22 23 Steps to Performing Mesh Analysis 1. Identify meshes 2. Assign variable names to mesh currents 3. Write KVL equations around each mesh in terms of the mesh currents 4. Solve the system of equations for the mesh currents 24 25 Mesh-Current Example 26 Super Mesh 27 Super Mesh Example 15Ω 5Ω 2A + 12 V _ 3Ω 10Ω 28 Introduction to Electrical & Computer Engineering Superposition • Lee Brinton • Salt Lake Community College 29 Superposition 30 Superposition 31 Introduction to Electrical & Computer Engineering Thevenin and Norton Equivalent Circuits • Lee Brinton • Salt Lake Community College 32 Complex Circuit and Its Thevenin Equivalent a b LM324 Operational Amplifier Circuit Thevenin Equivalent Circuit Of LM324 33 Thevenin Equivalent Power at the Shaft vs. Power at the Wheels 34 Complex Circuit and Its Thevenin Equivalent a b LM324 Operational Amplifier Circuit Thevenin Equivalent Circuit Of LM324 35 Complex Circuit and Its Thevenin Equivalent 36 Open Circuit Voltage and Short Circuit Current 37 Determining the Thevenin Equivalent Circuit R1 a Vs + _ R2 b 38 Determining the Thevenin Resistance Method 1: Voc and Isc Method R1 a Vs + _ R2 b 39 Determining the Thevenin Resistance Method 2: Equivalent Resistance Method R1 a Vs + _ R2 b 40 Determining the Thevenin Resistance Method 3: Applying a Test Voltage R1 a Vs + _ R2 b 41 Example Determining Thevenin Equivalent Circuit 42 Thevenin Equivalent Circuit Example 43 Thevenin Equivalent Circuit Example 44 Introduction to Electrical & Computer Engineering Maximum Power Transfer • Lee Brinton • Salt Lake Community College 45 Power Transfer to the Load Maximize Voltage Maximize Current Maximize Power RL >> Rth RL << Rth RL ?? Rth 46 Maximum Power Transfer to the Load 47