* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File - Lambeth academy sport
Cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
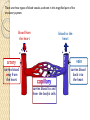
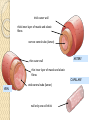
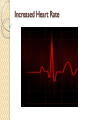
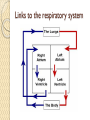
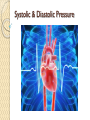
Please copy down the date, title and learning outcome and complete the starter The Cardiovascular System During Exercise Learning Objectives: Taking a look at the immediate and short-term effects of exercise on the cardiovascular system Learning Outcome: A*/A students will be able to explain in detail the immediate and shortterm effects of exercise upon the cardiovascular system. Reference will be made to blood pressure, blood vessels and the respiratory system. B/ students will be able to identify and begin to explain the immediate and short-term effects of exercise upon the CV system. C/ students will be able to list the immediate and short term effects of exercise on the body and give broad reasoning why these happens. Starter: Record your current Heart Rate - then come to the front, hi 5 Miss/Sir then return to your seat. Measure your HR again! Tricky Complete the box in the workbook on heart rates STARTER: My resting heart rate is _______ BPM After low intensity exercise (merely leaving my seat!) my HR is ________ BPM HOT EXTENSION: My HR increased because… ______________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________ ________ Trickier Complete the box in the workbook and explain why your HR increased. Apart from blood and oxygen delivery what else does our Cardiovascular system do? 1.2.2: A healthy, active lifestyle and your cardiovascular system The Cardiovascular System The cardiovascular system consists of the heart (cardio), blood and the blood vessels (vascular) The heart is a muscular pump (cardiac muscle!), which pushes blood throughout the many blood vessels in the body Blood being pushed around has 2 main functions: - to supply the body with oxygen & nutrients - to remove waste products e.g. carbon dioxide Blood vessels run throughout the body, allowing blood to travel everywhere Blood Vessels Arteries Capillaries Veins There are three types of blood vessels, as shown in this magnified part of the circulatory system. blood from the heart blood to the heart vein artery carries blood away from the heart carries blood back into the heart carries blood to and from the body’s cells thick outer wall thick inner layer of muscle and elastic fibres narrow central tube (lumen) thin outer wall ARTERY thin inner layer of muscle and elastic fibres CAPILLARY VEIN wide central tube (lumen) wall only one cell thick When blood is flowing against gravity, or when a vein is squeezed by muscle action, there is a risk that blood will flow in the wrong direction. Veins have valves to prevent backflow. vein valve open blood to the heart The valves allow blood to flow in the correct direction… backflow prevented vein valve closed …but close if blood starts to flow in the wrong direction. Comparing arteries and veins ing arteries and veins Arteries Veins Take blood away from the heart Take blood to the heart Walls are thick and elastic Walls are thin Transport oxygenated blood Transports de-oxygenated blood Has small lumen Has large lumen Has a pulse and blood travels Has no pulse and blood travels in spurts smoothly Has no valves Has valves What happens to the cardiovascular system during exercise? Immediate effects TASK… (4min discussion – think – pair – share!) What immediate effects do you think exercise has upon the cardiovascular system?! Higher Order Thinking… What happens and why do they happen? How can these immediate effects be measured? Increased Heart Rate Increased Heart Rate Heart rate is the number of times the heart Beats Per Minute (BPM) Heart rate can vary considerably from person to person, however the normal resting heart rate is between 60-80 beats per minute Exercise makes the body work harder. As a result, the muscles require more oxygen and more nutrients, such as glycogen, to function properly Increased Heart Rate Oxygen and nutrients are carried to the muscles by the blood. The heart has to work faster to pump the blood around the body, therefore the heart rate increases To bring about a change in heart rate the body releases adrenaline, which is the main cause of changes in heart rate and blood pressure. Adrenaline is a hormone Key terms Heart rate (pulse rate): the number of times the heart beats per minute Blood pressure: the force exerted by circulating blood on the walls of the blood vessels The human heart is a pump! Teacher note: The next few slides are to be quickly scanned through as they’re not essential to the unit spec… important knowledge however Links to the respiratory system Pathway of blood flow Immediate effects of exercise on the cardiovascular system 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Adrenaline released Heart rate increases and contracts more strongly Breathing becomes faster and deeper Body temperature increases Blood pressure rises Sweating starts and the body requires replacement fluids Blood Pressure Blood Pressure Blood pressure is the force exerted by circulating blood on the wall of the blood vessels. The heart makes two beating sounds Systole - made by the lower chambers contracting and pushing blood at high pressure into the arteries Diastole - made by the upper chambers contracting Increased Blood Pressure Blood pressure is the force exerted by blood on the walls of the arteries Blood pressure increases during exercise because more blood is needed to be pumped around the body, increasing pressure on the blood vessels A blood pressure metre is used to measure systolic and diastolic blood pressure Systolic & Diastolic Pressure Systolic & Diastolic Pressure Systolic pressure - the maximum pressure in the arteries when the heart contracts (beats) and pushes blood out through the aorta into the body Diastolic pressure - the pressure of the blood during the relaxation phase between heart beats (when heart is at rest) Pulse pressure - the difference between systolic and diastolic pressures Youtube support: http://www.mayoclinic.org/condition/high-blood-pressure/multimedia/what-is-bloodpressure/vid-20084747 A*/A SELECT A TASK – aim high! You are a Sports Scientist graduate and have been asked to write a report on the immediate and short term effects of physical activity upon the CV system. Evaluate the importance of the CV system and link this to the respiratory system.You must write using correct terminology. B Compose the text for an NHS booklet. This booklet is designed to inform people of the immediate and short term effects of exercise upon the CV system. Make reference to blood pressure, the heart, heart rate and the different blood vessels. C Use bullet points to recall the key pieces of information from the lesson. What is the CV system? What is it’s function? Why is it important? What are the immediate and short term effects of exercise upon the CV system? What is blood pressure? Use definitions to structure your answer. Please copy down the date, title and learning outcome and complete the starter The Cardiovascular System During Exercise Were you able to achieve the target you set for yourself? Learning Outcome: A*/A I am now able to explain in detail the short and immediate effects of exercise upon the cardiovascular system. I can make reference to the respiratory system and how efficiency improves as a result of regular exercise. I am confident when explaining blood pressure. B I am now able to identify and begin to explain the immediate and short term effects of exercise upon the CV system. C I am now able to list the immediate and short term effects of exercise on the body and give broad reasoning why these happens.