* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Electric Field Lines: Rules
Earthing system wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Multiferroics wikipedia , lookup
Electrical resistivity and conductivity wikipedia , lookup
Hall effect wikipedia , lookup
Superconductivity wikipedia , lookup
Eddy current wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
History of electromagnetic theory wikipedia , lookup
History of electrochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Maxwell's equations wikipedia , lookup
Static electricity wikipedia , lookup
Faraday paradox wikipedia , lookup
Skin effect wikipedia , lookup
Insulator (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Electric machine wikipedia , lookup
Lorentz force wikipedia , lookup
Electrocommunication wikipedia , lookup
Electroactive polymers wikipedia , lookup
Electrical injury wikipedia , lookup
Electric charge wikipedia , lookup
Electric current wikipedia , lookup
Electromotive force wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetic field wikipedia , lookup
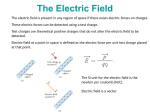
Electric Field Lines Q1 Which of the following best represents the electric field experienced at point P? -a tool used to visualize the electric field in a region of space Metal plate P q2 (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) None of the above Electric Field Lines Electric Field Lines: Rules • Field lines go away from positive charges and towards negative charges • Field is stronger where field lines are closer together • Number of lines leaving/entering a charge is proportional to magnitude of charge • Field lines don't cross Electric Field Lines For the electric field shown below, which way would a positive charge placed at the point shown move? A) up B) down C) left D) right E) it will not move Electric Dipole Two Identical Charges Parallel plates + + + + + - Electric Field Inside a Conductor: Shielding Neutral Conductor in a Field • Excess charge inside a conductor will quickly move to the conductor's surface • The charge redistributes itself so that there is no electric field inside the conductor! • If there were an electric field inside the conductor, then the charges would move until equilibrium is established • In equilibrium, the electric field inside a conductor is zero Neutral Conductor in a Field External electric field does not enter conductor Conductor shields charge inside from external fields + + + + + - + - + - + - + + + + + - For the charge distributions shown on the spherical conductors below, which field lines are most reasonable? Electric Potential Energy (19-1) • Gravity and electrical force are conservative: both forces have an associated potential energy • ∆(GPE) = mghB – mghA = GPEB – GPEA = -WAB (WAB = work done by gravity) • ∆(EPE) = EPEB – EPEA = -WAB (WAB = work done by electric force) Electric Potential V (19-2) The electric potential V at a point is the electric potential energy EPE of a charge (q0) placed there divided by the charge: V = EPE q0 Units: J/C = V (volts) V is a scalar V can be + or - Potential difference, VB – VA, between two points: V = V B V A = W AB EPE = q0 q0 ex. An electron in a TV picture tube is accelerated from rest through a potential difference of 5000V. a) What is the change in potential energy of the electron? b) What is the work done by the electric force when the electron goes from the -ve to the +ve terminal? c) What is the speed of the electron as a result of this acceleration? (m = 9.1x10-31 kg) 5000V High Voltage