* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Circulatory System - Ms Barry Home Economics
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
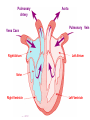
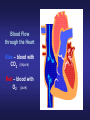
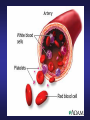
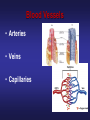
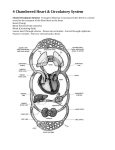
The Circulatory System Junior Certificate Home Economics Ms. Barry The Circulatory System The circulatory system transports blood around the body It is made up of three parts: 1. The Heart 2. The Blood 3. The Blood Vessels The Heart • Acts as a pump, which pumps blood around the body • Is found in the chest cavity, between the lungs • It is hollow inside and is divided in two by a wall of muscle called the septum • It has four chambers – left & right atria at the top and the left & right ventricles on the bottom • The walls of the ventricles are stronger than the atria • It contains valves to make sure the blood flows in one direction only Pulmonary Artery Vena Cava Right Atrium Aorta Pulmonary Vein Left Atrium Valve Right Ventricle Left Ventricle Blood flow through the Heart • Impure blood flows into the right atrium through the vena cavae • Flows through a valve into the right ventricle • Heart muscle contracts blood flows to the lungs carbon dioxide is exchanged for oxygen • The pure blood flows back to the heart, into the left atrium. Blood flow through the Heart • It flows through a valve into the left ventricle. • Muscle contracts blood flows through the aorta (largest artery) around the body • Blood gives out its oxygen and picks up carbon dioxide • It returns to the right atrium and the cycles begins again Blood Flow through the Heart Blue – blood with CO2 (impure) Red – blood with O2 (pure) The Blood • Adult – 4 or 5 litres of blood • Made up of plasma Plasma contains: - Red blood cells - White blood cells - Platelets Red Blood Cells • Contain a red pigment called haemoglobin • This carries oxygen around the body • Iron is needed to make haemoglobin White Blood Cells • Less white than red blood cells in blood • They attack and kill harmful germs • Prevent infection & disease Platelets • Cause blood to clot • Prevent severe blood loss Functions of Blood 1. Blood transports: – nutrients, heat and oxygen around the body – carbon dioxide to the lungs – hormones to where they are needed – waste products to the kidneys 2. Fights bacteria & infection 3. Prevents blood clotting Blood Vessels • Arteries • Veins • Capillaries Arteries • • • • Largest blood vessel Carry blood AWAY from heart Blood is usually rich in oxygen Artery walls are thick and elastic PULSE: heart forcing blood around the body can be felt in arteries under the skin Veins • Carry blood BACK to the heart • Blood is usually rich impure (high in carbon dioxide0 • Artery walls are thinner (less pressure) • Veins have VALVES to prevent backflow Capillaries • Thin walls • Allow oxygen and nutrients to pass between blood & cells • Carbon dioxide and waste from body pass into the blood to be removed • They come together to form veins