* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Science Chapter 1 Unit A
Embryonic stem cell wikipedia , lookup
Artificial cell wikipedia , lookup
Hematopoietic stem cell wikipedia , lookup
Chimera (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Dictyostelium discoideum wikipedia , lookup
Human embryogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Neuronal lineage marker wikipedia , lookup
Microbial cooperation wikipedia , lookup
Regeneration in humans wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
Cell (biology) wikipedia , lookup
State switching wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
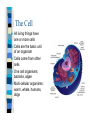
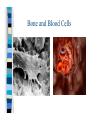
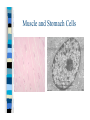
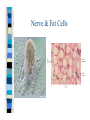
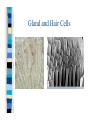
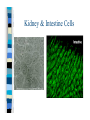
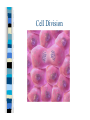
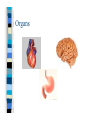
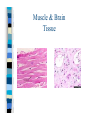
Chapter One Unit A Cells Lesson 1 What are the parts of a cell? Vocabulary Words CellCytoplasmNucleusOrganelle- Standards Students know that many multicellular organisms have specialized structures to support the transport of materials. The Cell All living things have one or more cells Cells are the basic unit of an organism Cells come from other cells One cell organisms: bacteria, algae Multi-cellular organisms: worm, whale, humans, dogs Parts of a Cell pg. 10-11 Nucleus- “brain of the cell”, control center Cell membranesurrounds cell and allows food & water to enter Cell wall (only in plant cells)- protects cell Cytoplasm- thick “jello” like fluid in cell Ribosomes- allows cell to perform functions Vacuoles- sacs that store water, food, & waste Golgi apparatus- helps cell from breaking Chloroplast (only in plant cells)- absorbs sunlight & uses energy to make food Mitochondria- “power plant” of cell, gives cell energy Endoplasmic reticulumprovides passageway for cell materials Brain Cell Bone and Blood Cells Muscle and Stomach Cells Nerve & Fat Cells Gland and Hair Cells Kidney & Intestine Cells Lesson 2 How do cells make and use energy? Vocabulary Words Cellular respiration Diffusion Osmosis- Standards Students know plant and animal cells break down sugar to obtain energy, a process resulting in carbon dioxide and water Cell Energy All organisms need energy The most important source of energy is glucose Glucose= form of sugar Animals & humans must eat glucose – Ex: bread, potatoes, rice Glucose Plants make their own glucose Plants, animals, & humans break down glucose in a process called cellular respiration Glucose + Oxygen = energy Why do cells need energy? Making protein: proteins are needed for your nails, skin, and hair Movement: muscle cells need energy to move your body Cell division: new cells form when old cells divide in two, and cells need energy for this process Transportation: cells transport water, glucose, oxygen, waste, and minerals in the body – Ex: Diffusion & osmosis are two forms of transportation Cell Division Organisms & Energy Not all organisms need the same amount of energy Who needs more energy? – – – – Warm-blooded Large body Greater speed Ex. cheetah Lesson 3 How are cells organized? Vocabulary Words Organ Organ system Tissue- Standards Students know many multicellular organisms have specialized structures to support the transport of materials Cell to Organism An organism is made up of organ systems – Ex. muscular system, digestive system, skeletal system, respiratory system Organ systems are made of organs – Ex. Brain, heart, stomach, lungs, kidneys Organs are made of tissue – Ex. Muscle tissue, brain tissue, bone tissue, nerve tissue Tissue is made of cells! Organism Organ system Organ Tissue Cells Organs Muscle & Brain Tissue