* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download endocrine system - Fall River Public Schools
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
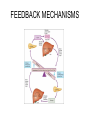
ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Honors Biology Introduction • Glands that transmit chemical messengers throughout the body • Hormones: chemical messengers – Circulate through body – Affect many body cells GLAND TYPES • Gland: organ made of cells that secrete materials – Exocrine glands: secrete nonhormonal chemicals into ducts and transport to locations inside and outside the body; i.e. sweat, mucous, saliva, digestive – Endocrine glands: ductless and throughout body; secrete hormones into bloodstream through fluid surrounding cells HORMONE TYPES • Hormones: – Compounds that are secreted into bloodstream and affect activity of distant cells – Diffuse into blood • 2 Categories – Amino acid-base hormones: derived from amino acids (epinephrine) – Steroid hormones: lipids derived from cholesterol (estrogen and testosterone) HORMONE ACTION • Each hormone only affects certain cells called target cells PROSTAGLANDINS • • • • • Group of hormone like lipids Regulate cell activities Not made by specific endocrine glands Made by cells throughout body Made and travel locally ENDOCRINE GLANDS • JIGSAW ACTIVITY – Pituitary Glands – Thyroid Gland – Adrenal Gland – Gonads – Pancreas (done for you) OTHER ENDOCRINE GLANDS • Thymus Gland: – Located beneath sternum and between lungs – Development of immune system and T cells • Pineal Gland: – Near base of brain – Secretes melatonin; cycle regulate sleep patterns OTHER ENDOCRINE GLANDS • Parathyroid Glands – 4 parathyroid glands – Back of thyroid gland – Secrete parathyroid hormone: Increase concentration of calcium ions in blood • Digestive (in walls) – Gastrin: stimulates release of digestive enzymes – Secretin: in small intestine; stimulates release of digestive enzymes from pancreas and bile from liver FEEDBACK MECHANISMS • Last step of a series controls the first step – Negative: shuts off – Positive: makes more (going into labor!) • Homeostasis – Insulin and glucagon work together to balance blood glucose – Antagonistic hormones FEEDBACK MECHANISMS NEGATIVE FEEDBACK • Final step inhibits first step; thermostat • Example: – – – – – – – – Hypothalamus secretes LH releasing hormone Stimulates LH from anterior pituitary LH released into blood and transported LH binds to target cells in tests Stimulate cAMP production Stimulate testosterone secretion Testosterone binds to target cells If high testosterone concentration; LH releasing hormone is inhibited