* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 2014 PowerPoint Template Standard
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Jatene procedure wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Atrial fibrillation wikipedia , lookup
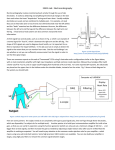
ECG Basics & Cardiac Troubleshooting Lance Lennon Product & Applications Specialist - CT March 2016 Outline 1. ECG Basics 2. Rhythms & Arrhythmias 3. Scan Techniques 4. ECG Editing Hot Cases! 3 Outline 1. ECG Basics 2. Rhythms & Arrhythmias 3. Scan Techniques 4. ECG Editing Hot Cases! 4 1. ECG Basics The heart contracts when pumping blood and rests when receiving blood. This activity and lack of activity from a cardiac cycle can be illustrated by an electrocardiogram (ECG). 5 1. ECG Basics An ECG is the recording of the electrical activity of the heart Information obtainable from an ECG includes; Heart Rate Yes Rhythm / Regularity Yes Impulse Conduction Time Intervals Yes Abnormal Conduction Pathways Yes Pumping Action No Cardiac Output No Blood Pressure No Cardiac Muscle Hypertrophy No 6 1. ECG Basics 7 1. ECG Basics P-wave SA node fires and sends electrical impulse outward to stimulate both atria and manifests as a P-wave Approximately 0.1sec in length 8 1. ECG Basics PR Interval Time in which impulse travels from the SA node to the atria and downward to the ventricles 9 1. ECG Basics QRS Complex Impulse from the bundle of HIS throughout the ventricular muscles Measures less than 0.12sec or less than three small squares on the ECG paper 10 1. ECG Basics T-wave Ventricular repolarisation meaning no associated activity of the ventricular muscle Resting phase of the cardiac cycle 11 1. ECG Basics Lazy ECG electrode setup lead to suboptimal results This is my pet peeve! Lazy setup! 12 1. ECG Basics Lazy ECG electrode setup lead to suboptimal results Exposure can interfere with ECG signal 13 1. ECG Basics Lazy ECG electrode setup lead to suboptimal results Exposure can interfere with ECG signal 14 1. ECG Basics Lazy ECG electrode setup lead to suboptimal results Leads touching gantry R peak R peak Interference Every 0.35sec 15 1. ECG Basics Lazy ECG electrode setup lead to suboptimal results Exposure can interfere with ECG signal 16 1. ECG Basics Careful patient preparation is the key to a successful cardiac scan. If the following procedure is followed for every cardiac case, abnormal ECG signals are very rare. It is critical to ensure good contact between the electrode and the skin. 17 1. ECG Basics Place the ECG electrodes on the patient’s chest using the guide below. Skin Preparation is useful to clean and abrade the skin to ensure good electrode contact. Shaving may be necessary when there is extensive chest hair. The electrodes must be outside the primary radiation beam (CABG is the only exception) 18 1. ECG Basics Perform an Impedance Test on the ECG monitor to ensure good electrode contact. Press the Measure Impedance button. The results are displayed on the monitor. Any lead with impedance that shows red (over 50kΩ) must be adjusted. Move the electrodes and clean the skin to improve contact. Only proceed when the impedance test results show blue 19 1. ECG Basics Confirm that the R-peaks are taller than the P and T waves. Adjust the lead settings on the ECG monitor to change the active lead to Lead I, II or III. Ensure the ECG cables are not touching the gantry. Move the ECG monitor away from the gantry and the injector. Confirm that a clean ECG signal is displayed before continuing! 20 1. ECG Basics 21 Outline 1. ECG Basics 2. Rhythms & Arrhythmias 3. Scan Techniques 4. ECG Editing Hot Cases! 22 2. Rhythms & Arrhythmias Types of rhythms Rate: Bradycardia = rate of <60bpm Normal = rate of 60-100bpm Tachycardia = rate of >100-160bpm Where it is coming from: Sinus = SA node Atrial = SA node fails, impulse comes from the atria (internodal or the AV node) Ventricular = SA or AV fails, ventricles will pace the heart 23 2. Rhythms & Arrhythmias Sinus rhythms Normal sinus rhythm (NSR) What is the rate? 60-100bpm What is the rhythm? Atrial or Ventricular rhythm and regular Is there a P wave before each QRS? Yes Are the P waves upright and uniform? Yes What is the length of the PR interval? 0.12-0.2sec (3-5 small squares) Do all the QRS complexes look alike? Yes The length of the QRS complexes is…? Less than 0.12sec (3 small squares) 24 2. Rhythms & Arrhythmias Sinus rhythms Sinus bradycardia rhythm What is the rate? Less than 60bpm What is the rhythm? Atrial or Ventricular rhythm and regular Is there a P wave before each QRS? Yes Are the P waves upright and uniform? Yes What is the length of the PR interval? 0.12-0.2sec (3-5 small squares) Do all the QRS complexes look alike? Yes The length of the QRS complexes is…? Less than 0.12sec (3 small squares) 25 2. Rhythms & Arrhythmias Sinus rhythms Sinus tachycardia rhythm What is the rate? 100-160bpm What is the rhythm? Atrial or Ventricular rhythm and regular Is there a P wave before each QRS? Yes Are the P waves upright and uniform? Yes What is the length of the PR interval? 0.12-0.2sec (3-5 small squares) Do all the QRS complexes look alike? Yes The length of the QRS complexes is…? Less than 0.12sec (3 small squares) 26 2. Rhythms & Arrhythmias Atrial rhythms SA node fails to generate an impulse. The atrial tissue or areas of the internodal pathways may initiate an impulse These are called atrial arrhythmias or dysrhythmias Generally not considered life threatening Careful patient management must be ongoing 27 2. Rhythms & Arrhythmias Atrial rhythms Atrial fibrillation What is the rate? Atrial 350-400bpm What is the rhythm? Irregular Is there a P wave before each QRS? Normal P waves are absent Are the P waves upright and uniform? Replaced by F waves What is the length of the PR interval? Not measurable Do all the QRS complexes look alike? Yes The length of the QRS complexes is…? Less than 0.12sec (3 small squares) 28 2. Rhythms & Arrhythmias Ventricular rhythms SA node or the AV tissue fails to initiate an impulse, ventricles will pace the heart These are called ventricular arrhythmias or dysrhythmias Electrical impulse can be initiated from any pacemaker cell in the ventricles including the bundle braches or Purkinje fibres 29 2. Rhythms & Arrhythmias Ventricular rhythms Premature ventricular complex/contraction (PVC) What is the rate? Dependent on rate and number of PVCs What is the rhythm? Regular, occasionally irregular Is there a P wave before each QRS? No P waves associated with PVC Are the P waves upright and uniform? P waves of underlying rhythm may be present What is the length of the PR interval? Not present Do all the QRS complexes look alike? Wide and bizarre The length of the QRS complexes is…? Less than 0.12sec (3 small squares) 30 2. Rhythms & Arrhythmias Asystole… quickly scan as heart is not moving! What is the rate? Absent What is the rhythm? Absent Is there a P wave before each QRS? No Are the P waves upright and uniform? Not identifiable What is the length of the PR interval? Not present Do all the QRS complexes look alike? Not present The length of the QRS complexes is…? Not present 31 2. Rhythms & Arrhythmias Artificial pacemaker What is the rate? Varies according to preset rate of pacemaker What is the rhythm? Regular if pacing fixed Irregular if demand paced Is there a P wave before each QRS? Maybe, depends on pacemaker Are the P waves upright and uniform? Maybe, depends on pacemaker What is the length of the PR interval? Variable, depends on pacemaker Do all the QRS complexes look alike? Usually The length of the QRS complexes is…? Greater than or equal to 0.12sec. Look bizarre 32 Outline 1. ECG Basics 2. Rhythms & Arrhythmias 3. Scan Techniques 4. ECG Editing Hot Cases! 33 3. Scan Techniques After Breath Exercise on Aquilion PRIME, check the following; kVp Phase selection is appropriate for HR After Breath Exercise on Aquilion ONE & ViSION, check the following; kVp Number of beats for acquisition is appropriate (can over ride) Phase selection is appropriate for HR 34 3. Scan Techniques What if this happens before Calcium Score scan? 35 3. Scan Techniques What if this happens again? 36 3. Scan Techniques If HR is high (>75bpm) and regular? Trust SURECardio settings PRIME will typically recommend Retrospective ONE & ViSION will typically recommend multiple beat scanning 37 3. Scan Techniques If HR is irregular? Trust Arrhythmia Rejection PRIME may recommend Retrospective. Can change to Prospective and trust Arrhythmia Rejection ONE & ViSION may recommend multiple beat scanning. Can force acquisition to single beat as only one good beat needed. If multiple beat scanning selected, more normal beats required… 38 3. Scan Techniques Electrophysiology (EP) planning Only interested in left atrium and pulmonary veins Not interested in coronary arteries Patients often in AF (reason for procedure) Single beat scan (force if necessary) Can use Target CTA or Prospective CTA scan mode Target phase 40% (systole) For information on the procedure and ablation; http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Electrophysiology_study 39 Outline 1. ECG Basics 2. Rhythms & Arrhythmias 3. Scan Techniques 4. ECG Editing Hot Cases! 40 4. ECG Editing Hot Cases! What if this happens after scan? 41 4. ECG Editing Hot Cases! 42 4. ECG Editing Hot Cases! ECG Save Image Aquilion PRIME Exposure Couch position HR during Breath Exercise Reconstruction Needs to fit within grey exposure window. Pitch set by Breath Exercise Where scanner has identified Rpeak. Can be moved. Cardiac Phase selected Following Breath Exercise Minimum, maximum and mean HR during actual scan eg. 60000 ÷1243=48bpm 43 4. ECG Editing Hot Cases! ECG Save Image Aquilion ONE & ViSION Number of beats selected HR during following Collimation Breath Exercise Breath Exercise Cardiac Phase selected Following Breath Exercise Exposure Reconstruction Needs to fit within grey exposure window. Where scanner has identified Rpeak. Can be moved. Minimum, maximum and mean HR during actual scan eg. 60000 ÷1398=42bpm 44 4. ECG Editing Hot Cases! Case 1 AqONE, 58-60bpm during Breath Exercise, 1 beat scan 70-80% ? Cause ? Fix 45 4. ECG Editing Hot Cases! Case 2 Aquilion PRIME ? Cause ? Fix? 46 4. ECG Editing Hot Cases! Case 2 Aquilion PRIME What about this as a fix? 47 4. ECG Editing Hot Cases! Case 2 Aquilion PRIME Don’t forget about using a R minus ms reconstruction -200ms was the money shot and revealed plaque causing stenosis 48 Outline 1. ECG Basics Get a good trace! Impedance test! Impedance test! 2. Rhythms & Arrhythmias Show off what you know! 3. Scan Techniques Think about what you need and how to achieve 4. ECG Editing Hot Cases! Work logically. Photos are very useful! 49