* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Advanced Placement Chemistry Test
Physical organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Electrolysis of water wikipedia , lookup
Chemical reaction wikipedia , lookup
Acid dissociation constant wikipedia , lookup
Lewis acid catalysis wikipedia , lookup
Crystallization wikipedia , lookup
Click chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Bioorthogonal chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Chemical thermodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Ultraviolet–visible spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Thermomechanical analysis wikipedia , lookup
Thermodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Rate equation wikipedia , lookup
Thermodynamic equilibrium wikipedia , lookup
Stoichiometry wikipedia , lookup
Stability constants of complexes wikipedia , lookup
Vapor–liquid equilibrium wikipedia , lookup
Transition state theory wikipedia , lookup
Advanced Placement Chemistry Test
Unit J, v.1
Name:
February 3, 2004
Mark:
/
.
THE TEST IS IN TWO PARTS:
PART A CONTAINS TEN MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS, EACH WORTH ONE MARK.
For the Multiple Choice questions, one-quarter mark will be deducted for each incorrect answer!
PART B CONTAINS TWO ADVANCED PLACEMENT FREE RESPONSE QUESTIONS AND
IS WORTH A TOTAL OF 24 MARKS.
Answers appear below (yellow):
Part A - Multiple Choice [10 marks]
Question 1
P4(s) + 5 O2(g) <===> P4O10(s)
What is the equilibrium law expression for this reaction?
(A) Kc = [P4O10] / [P4] [O2]5
(B) Kc = [P4O10] / 5 [P4] [O2]
(C) Kc = [O2]5
(D) Kc = 1 / [O2]5
(E) Kc = [P4O10]
Question 2
Fe3O4(s) + 4 H2(g) <===> 3 Fe(s) + 4 H2O(g); ∆H > 0
For this reaction at equilibrium, which changes will increase the quantity of Fe(s)?
1. increasing temperature
2. decreasing temperature
3. adding Fe3O4(s)
(A) 1 only
(B) 2 only
(C) 1 and 2 only
(D) 2 and 3 only
(E) 1, 2 & 3
Question 3
For which one of the following will Kp = Kc?
(A) MgCO3(s) + 2HCl(g) <----> MgCl2(s) + CO2(g) + H2O(l)
(B) C(s) + O2(g) <----> CO2(g)
(C) CH4(g) + 3O2(g) <----> CO2(g) + 2H2O(g)
(D) Zn(s) + 2HCl(aq) <----> H2(g) + ZnCl2(aq)
(E) 2NO2(g) + O2(g) <----> N2O5(g)
Question 4
Consider the following chemical equilibrium inside a sealed vessel:
2 SO3(g) <----> 2 SO2(g) + O2(g)
∆Hr = +198 kJ
Which one of the following statements is false?
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
(E)
At equilibrium, the rate of the forward reaction is the same as the rate of the reverse reaction.
At equilibrium, the number of moles of SO3 present in the reaction vessel will always be the
same as the number of moles of SO2 present, regardless of the temperature.
Changing the volume of the vessel changes the amount of oxygen in the system.
Changing the temperature changes the amount of oxygen in the system.
Injecting helium gas into the vessel, but keeping the volume of the vessel unchanged, will not
"shift" the equilibrium.
Question 5
[AP, 1994]
Barium sulfate is LEAST soluble in a 0.01-molar solution of which of the following?
(A) Al2(SO4)3
(B) (NH4)2SO4
(C) Na2SO4
(D) NH3
(E) BaCl2
Question 6
[AP, Princeton Review]
Citric acid, H3C6H5O7, can give up three hydrogen ions in solution. The three dissociation reactions
are as follows:
H3C6H5O7 W H+ + H2C6H5O7-
K1 = x
H2C6H5O7- W H+ + HC6H5O72-
K2 = y
HC6H5O72- W H+ + C6H5O73-
K3 = z
Which of the following expressions gives the equilibrium constant for the reaction shown below:
H3C6H5O7 W 3 H+ + C6H5O73A) xyz
Question 7
B)
xy
z
C)
x
yz
D)
z
xy
E)
1
xyz
[AP, 1994]
4 HCl(g) + O2(g) <===> 2 Cl2(g) + 2 H2O(g)
Equal numbers of moles of HCl and O2 in a closed system are allowed to reach equilibrium as
represented by the equation above. Which of the following must be true at equilibrium?
I. [HCl] must be less than [Cl2].
II. [O2] must be greater than [HCl].
III. [Cl2] must equal [H2O].
(A) I only
(B) II only
(C) I and III only
(D) II and III only
(E) I, II, and III
Question 8
[AP, 1984]
CuO(s) + H2(g) <===> Cu(s) + H2O(g);
∆H = - 2.0 kilojoules
When the substances in the equation above are at equilibrium at pressure P and temperature T, the
equilibrium can be shifted to favor the products by
(A) increasing the pressure by means of a moving piston at constant T
(B) increasing the pressure by adding an inert gas such as nitrogen
(C) decreasing the temperature
(D) allowing some gases to escape at constant P and T
(E) adding a catalyst
Question 9
[AP, 1984]
How many moles of NaF must be dissolved in 1.00 liter of a saturated solution of PbF2 at 25 °C to
reduce the [Pb2+] to 1 x 10¯6 molar? (Ksp of PbF2 at 25 °C = 4.0 x 10¯8)
(A) 0.020 mole
(B) 0.040 mole
(C) 0.10 mole
(D) 0.20 mole
(E) 0.40 mole
Question 10
[AP, 1994]
2 SO2(g) + O2(g) <===> 2 SO3(g)
When 0.40 mole of SO2 and 0.60 mole of O2 are placed in an evacuated 1.00-liter flask, the reaction
represented above occurs. After the reactants and the product reach equilibrium and the initial
temperature is restored, the flask is found to contain 0.30 mole of SO3. Based on these results, the
equilibrium constant, Kc for the reaction is
(A) 20.
(B) 10.
(C) 6.7
(D) 2.0
(E) 1.2
Part B - Advanced Placement Free Response Questions [24 marks]
Question 1
[AP 2003 (Form B), 13 marks]
2 HI (g) ÍÎ H2(g) + I2(g)
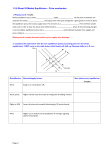
After a 1.0 mole sample of HI(g) is placed in an evacuated 1.0 L container at 700 K, the reaction
represented above occurs. The concentration of HI(g) as a function of time is shown below:
(a) Write the expression for the equilibrium constant, Kc, for the reaction. {1 mark}
(b) What is [HI] at equilibrium ?
{1 mark}
(c) Determine the equilibrium concentrations of H2(g) and I2(g).
{3 marks}
(d) On the graph above, make a sketch that shows how the concentration of H2(g) changes as a
function of time. {2 marks}
(e) Calculate the value of the following equilibrium constants at 700 K.
(i)
Kc
{3 marks}
(ii) Kp
(f) At 1000 K, the value of Kc for the reaction is 2.6 x 10-2. In an experiment, 0.75 mole of HI(g),
0.10 mole of H2(g), and 0.50 mole of I2(g) are placed in a 1.0 L container and allowed to reach
equilibrium at 1000 K. Determine whether the equilibrium concentration of HI(g) will be greater than,
equal to, or less than the initial concentration of HI(g). Justify your answer. {3 marks}
Question 2
[AP 1994, 11 marks]
MgF2(s) <===> Mg2+(aq) + 2 F¯(aq)
In a saturated solution of MgF2 at 18° C, the concentration of Mg2+ is 1.21 x 10¯3 molar. The
equilibrium is represented by the equation above.
(a)
Write the expression for the solubility-product constant, Ksp, and calculate its value at 18° C.
{3 marks}
(b)
Calculate the equilibrium concentration of Mg2+ in 1.000 liter of saturated MgF2 solution at
18°C to which 0.100 mole of solid KF has been added. The KF dissolves completely. Assume
the volume change is negligible. {3 marks}
(c)
Predict whether a precipitate of MgF2 will form when 100.0 milliliters of a 3.00 x 10¯3 molar
Mg(NO3)2 solution is mixed with 200.0 milliliters of a 2.00 x 10¯3 molar NaF solution at 18°C.
Calculations to support your prediction must be shown. {4 marks}
(d)
At 27°C the concentration of Mg2+ in a saturated solution of MgF2 is 1.17 x 10¯3 molar. Is the
dissolving of MgF2 in water an endothermic or an exothermic process? Give an explanation to
support your conclusion. {2 marks}