* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Examples of electric stimulators - O6U E
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Electric machine wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetic compatibility wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Pulse-width modulation wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Time-to-digital converter wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Chirp compression wikipedia , lookup
Wien bridge oscillator wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
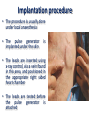
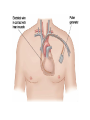
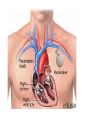
Therapeutic equipment I Lecture (5) Electric stimulator • A wide variety of electric stimulators is used in patient care and research. • They range from very low current such as the cardiac pacemaker, to high current single pulse stimulator such as defibrillators. Examples of electric stimulators • Cardiac pacemaker • Bladder stimulator • Muscle stimulator • defibrillators Cardiac pacemaker • The cardiac pacemaker is an electric stimulator that produces periodic electric pulses that are conducted to electrodes located on the surface of the heart (epicardium), within the heart muscle ( the myocardium), or within the cavity of the heart or the lining of the heart (endocardium). • The stimulus that conducted to the heart causes it to contract, this effect can be used in disease states in which the heart is not stimulated at a proper rate on its own. • The principal pathologic conditions in which cardiac pacemakers are applied are known as heart block. Types of cardiac pacemaker • 1. Asynchronous/Fixed Rate. • 2. Synchronous/Demand. • 3. Single/Dual Chamber Sequential (A & V). • 4.Programmable/nonprogrammable. Asynchronous pacemaker • Power supply: provide the energy required for the operation of the pacemaker. • Lithium-iodine cell is the current standard battery • Advantages: (1) Long life – 4 to 10 years (2) Output voltage decreases gradually with time making sudden battery failure unlikely • The oscillator establishes the pulse rate for the pacemaker, this in turn, control the pulse output circuit that provide the stimulating pulse to the heart. • This pulse is conducted along lead wires to the cardiac electrodes. • Another component of the overall construction that is the package itself. • The package should be compatible and well tolerated by the body. • It must provide the necessary protection to the circuit components, where the body is a corrosive environment, so the package must be designed to operate well in this environment, while occupying minimal volume and mass. • Titanium and stainless steel are frequently used for the package. • Timing circuit: The asynchronous pacemaker represents the simplest kind of pacemaker, because it provides a train of stimulus pulses at a constant rate regardless of the functioning of the heart. • A free running oscillator is all that is required for the timing pulse in such a system. • Output circuit: The pulse output circuit produces the actual electric stimulus that is applied to the heart. • At each trigger from the timing circuit, the output circuit generates an electric stimulus pulse that has been optimized for stimulating the myocardium through the electrode system. • Constant voltage or constant current amplitude pulses are the two usual types of stimuli produced by the output circuit. • Constant voltage amplitude pulses are typically in the range of 5.0 to 5.5V with a duration of 500 to 600 micro-sec. • Constant current amplitude pulses are typically in a range of 8 to 10 mA with pulse duration ranging from 1.0 to 1.2 mS. • Rates for asynchronous pacemaker range from 70 to 90 beats per min. whereas pacemakers that are not fixed rate typically achieve rates ranging from 60 to 150 beats per min. Implantation procedure • The procedure is usually done under local anaesthesia • The pulse generator implanted under the skin is • The leads are inserted using x-ray control, via a vein found in this area, and positioned in the appropriate right sided heart chamber • The leads are tested before the pulse generator is attached