* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
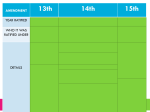
Download Name_______________________________________DUE Friday
Hampton Roads Conference wikipedia , lookup
Commemoration of the American Civil War on postage stamps wikipedia , lookup
Tennessee in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Issues of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Fourteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution wikipedia , lookup
Thirteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution wikipedia , lookup
Military history of African Americans in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Carpetbagger wikipedia , lookup
Disenfranchisement after the Reconstruction Era wikipedia , lookup
Radical Republican wikipedia , lookup
Reconstruction era wikipedia , lookup
Fifteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution wikipedia , lookup
Name_______________________________________DUE Friday May 24 Read Chapter 18, Sec 1, Rebuilding the Union pages 570 575 Answer questions on page 575 # 1, 36 1. Terms and Names: ● Radical Republican Congressman who favored using federal power to rebuild the South and promote AfricanAmerican rights. ● Reconstruction period from 18651877 in which the U.S. government attempted to rebuild Southern society and governments. ● Freedman’s Bureau federal agency set up to help former enslaved people. ● Andrew Johnson Democrat who became president after Lincoln was assassinated. ● black codes laws that limited the freedom of former enslaved people. ● Fourteenth Amendment constitutional amendment that made all people born in the U.S. (including former slaves) citizens. ● scalawag white Southerner who supported Radical Reconstruction. ● carpetbagger Northerner who went to the South after the Civil War to participate in Reconstruction. 3. How did President Andrew Johnson treat the South during Reconstruction? He believed the president (not Congress) should be in charge of Reconstruction. He believed in an “easy peace” and quick reunion with the South. He made the South ratify the 13th Amendment and recognize the authority of the federal government (pledge loyalty to the U.S. government). But..... He gave amnesty and returned property to white Southerners. Johnson did not attempt to help the formerly enslaved people of the South (for example, no land given to them, no guaranteed voting rights, no guaranteed equal protection under the law). 4. Why did Congress decide to take a larger role in Reconstruction? President Lincoln was assassinated in April of 1865 and Andrew Johnson became president. During that summer and fall, the former Confederate states held elections and prepared to send representatives to Congress; they also began passing many laws known as “black codes”. Congress did not meet for 8 months until December 1865. Many Northern representatives were outraged that former Confederate government leaders and generals were among the newly elected representatives that showed up in Washington to start serving their terms. They quickly voted to not recognize these Southern representatives. There followed a series of confrontations between President Johnson and the Republicanled Congress: Civil Rights Act of 1866 said all people born in the U.S. were citizens. 14th Amendment would guarantee citizenship to all people born or naturalized in the U.S.; had full rights; equal protection of laws. Johnson’s Response VETO Refused to support (as did all Southern states except Tennessee). Congress’ Response Voted to override his veto Outraged. Was able to it became a law. pass the amendment anyway. This helped lead to what became known as Radical Reconstruction. 5. What conditions did the Southern states meet in order to rejoin the Union? They had to approve constitutions that gave the vote to African Americans and ratify the 14th Amendment. 6. How were the black codes similar to the old slave codes? Both sets of laws heavily limited the freedoms of African Americans.