* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Angles in Polygons
Tessellation wikipedia , lookup
Rotation formalisms in three dimensions wikipedia , lookup
Regular polytope wikipedia , lookup
Perceived visual angle wikipedia , lookup
Pythagorean theorem wikipedia , lookup
List of regular polytopes and compounds wikipedia , lookup
Integer triangle wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Complex polytope wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Multilateration wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
Compass-and-straightedge construction wikipedia , lookup
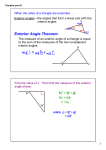
Angles in Polygons Say Thanks to the Authors Click http://www.ck12.org/saythanks (No sign in required) To access a customizable version of this book, as well as other interactive content, visit www.ck12.org CK-12 Foundation is a non-profit organization with a mission to reduce the cost of textbook materials for the K-12 market both in the U.S. and worldwide. Using an open-content, web-based collaborative model termed the FlexBook®, CK-12 intends to pioneer the generation and distribution of high-quality educational content that will serve both as core text as well as provide an adaptive environment for learning, powered through the FlexBook Platform®. Copyright © 2014 CK-12 Foundation, www.ck12.org The names “CK-12” and “CK12” and associated logos and the terms “FlexBook®” and “FlexBook Platform®” (collectively “CK-12 Marks”) are trademarks and service marks of CK-12 Foundation and are protected by federal, state, and international laws. Any form of reproduction of this book in any format or medium, in whole or in sections must include the referral attribution link http://www.ck12.org/saythanks (placed in a visible location) in addition to the following terms. Except as otherwise noted, all CK-12 Content (including CK-12 Curriculum Material) is made available to Users in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution-Non-Commercial 3.0 Unported (CC BY-NC 3.0) License (http://creativecommons.org/ licenses/by-nc/3.0/), as amended and updated by Creative Commons from time to time (the “CC License”), which is incorporated herein by this reference. Complete terms can be found at http://www.ck12.org/terms. Printed: September 7, 2014 www.ck12.org C HAPTER Chapter 1. Angles in Polygons 1 Angles in Polygons Learning Objectives • Extend the concept of interior and exterior angles from triangles to convex polygons. • Find the sums of interior angles in convex polygons. • Identify the special properties of interior angles in convex quadrilaterals. Review Queue 1. Find the measure of x and y. a. b. 2. a. b. c. d. Find w◦ , x◦ , y◦ , and z◦ . What is w◦ + y◦ + z◦ ? What two angles add up to y◦ ? What are 72◦ , 59◦ , and x◦ called? What are w◦ , y◦ , and z◦ called? Know What? Below is a picture of Devils Postpile, near Mammoth Lakes, California. These posts are cooled lava (called columnar basalt) and as the lava pools and cools, it ideally would form regular hexagonal columns. However, variations in cooling caused some columns to either not be perfect or pentagonal. First, define regular in your own words. Then, what is the sum of the angles in a regular hexagon? What would each angle be? 1 www.ck12.org Interior Angles in Convex Polygons Recall from Chapter 4, that interior angles are the angles inside a closed figure with straight sides. Even though this concept was introduced with triangles, it can be extended to any polygon. As you can see in the images below, a polygon has the same number of interior angles as it does sides. From Chapter 1, we learned that a diagonal connects two non-adjacent vertices of a convex polygon. Also, recall that the sum of the angles in a triangle is 180◦ . What about other polygons? Investigation 6-1: Polygon Sum Formula Tools Needed: paper, pencil, ruler, colored pencils (optional) 1. Draw a quadrilateral, pentagon, and hexagon. 2. Cut each polygon into triangles by drawing all the diagonals from one vertex. Count the number of triangles. 2 www.ck12.org Chapter 1. Angles in Polygons Make sure none of the triangles overlap. 3. Make a table with the information below. TABLE 1.1: Name of Polygon Number of Sides Quadrilateral Pentagon Hexagon 4 5 6 Number of 4s from one vertex 2 3 4 (Column 3) × (◦ in a 4) 2 × 180◦ 3 × 180◦ 4 × 180◦ Total Number of Degrees 360◦ 540◦ 720◦ 4. Do you see a pattern? Notice that the total number of degrees goes up by 180◦ . So, if the number sides is n, then the number of triangles from one vertex is n − 2. Therefore, the formula would be (n − 2) × 180◦ . Polygon Sum Formula: For any n−gon, the sum of the interior angles is (n − 2) × 180◦ . Example 1: Find the sum of the interior angles of an octagon. Solution: Use the Polygon Sum Formula and set n = 8. (8 − 2) × 180◦ = 6 × 180◦ = 1080◦ Example 2: The sum of the interior angles of a polygon is 1980◦ . How many sides does this polygon have? Solution: Use the Polygon Sum Formula and solve for n. (n − 2) × 180◦ = 1980◦ 180◦ n − 360◦ = 1980◦ 180◦ n = 2340◦ n = 13 The polygon has 13 sides. Example 3: How many degrees does each angle in an equiangular nonagon have? Solution: First we need to find the sum of the interior angles in a nonagon, set n = 9. (9 − 2) × 180◦ = 7 × 180◦ = 1260◦ Second, because the nonagon is equiangular, every angle is equal. Dividing 1260◦ by 9 we get each angle is 140◦ . Equiangular Polygon Formula: For any equiangular n−gon, the measure of each angle is (n−2)×180◦ . n Regular Polygon: When a polygon is equilateral and equiangular. It is important to note that in the Equiangular Polygon Formula, the word equiangular can be substituted with regular. Example 4: Algebra Connection Find the measure of x. 3 www.ck12.org Solution: From our investigation, we found that a quadrilateral has 360◦ . We can write an equation to solve for x. 89◦ + (5x − 8)◦ + (3x + 4)◦ + 51◦ = 360◦ 8x = 224◦ x = 28◦ Exterior Angles in Convex Polygons Recall that an exterior angle is an angle on the outside of a polygon and is formed by extending a side of the polygon (Chapter 4). As you can see, there are two sets of exterior angles for any vertex on a polygon. It does not matter which set you use because one set is just the vertical angles of the other, making the measurement equal. In the picture to the left, the color-matched angles are vertical angles and congruent. In Chapter 4, we introduced the Exterior Angle Sum Theorem, which stated that the exterior angles of a triangle add up to 360◦ . Let’s extend this theorem to all polygons. Investigation 6-2: Exterior Angle Tear-Up Tools Needed: pencil, paper, colored pencils, scissors 1. Draw a hexagon like the hexagons above. Color in the exterior angles as well. 2. Cut out each exterior angle and label them 1-6. 3. Fit the six angles together by putting their vertices together. What happens? The angles all fit around a point, meaning that the exterior angles of a hexagon add up to 360◦ , just like a triangle. We can say this is true for all polygons. 4 www.ck12.org Chapter 1. Angles in Polygons Exterior Angle Sum Theorem: The sum of the exterior angles of any polygon is 360◦ . Proof of the Exterior Angle Sum Theorem Given: Any n−gon with n sides, n interior angles and n exterior angles. Prove: n exterior angles add up to 360◦ NOTE: The interior angles are x1 , x2 , . . . xn . The exterior angles are y1 , y2 , . . . yn . TABLE 1.2: Statement 1. Any n−gon with n sides, n interior angles and n exterior angles. 2. xn◦ and y◦n are a linear pair 3. xn◦ and y◦n are supplementary 4. xn◦ + y◦n = 180◦ 5. (x1◦ + x2◦ + . . . + xn◦ ) + (y◦1 + y◦2 + . . . + y◦n ) = 180◦ n 6. (n − 2)180◦ = (x1◦ + x2◦ + . . . + xn◦ ) 7. 180◦ n = (n − 2)180◦ + (y◦1 + y◦2 + . . . + y◦n ) 8. 180◦ n = 180◦ n − 360◦ + (y◦1 + y◦2 + . . . + y◦n ) 9. 360◦ = (y◦1 + y◦2 + . . . + y◦n ) Reason Given Definition of a linear pair Linear Pair Postulate Definition of supplementary angles Sum of all interior and exterior angles in an n−gon Polygon Sum Formula Substitution PoE Distributive PoE Subtraction PoE Example 5: What is y? Solution: y is an exterior angle, as well as all the other given angle measures. Exterior angles add up to 360◦ , so set up an equation. 5 www.ck12.org 70◦ + 60◦ + 65◦ + 40◦ + y = 360◦ y = 125◦ Example 6: What is the measure of each exterior angle of a regular heptagon? Solution: Because the polygon is regular, each interior angle is equal. This also means that all the exterior angles ◦ ◦ are equal. The exterior angles add up to 360◦ , so each angle is 360 7 ≈ 51.43 . Know What? Revisited A regular polygon has congruent sides and angles. A regular hexagon has (6 − 2)180◦ = 4 · 180◦ = 720◦ total degrees. Each angle would be 720◦ divided by 6 or 120◦ . Review Questions 1. Fill in the table. TABLE 1.3: # of sides 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. # of 4s from one vertex 1 2 3 4 4s × 180◦ (sum) 180◦ 360◦ 540◦ 720◦ Sum of the exterior angles What is the sum of the angles in a 15-gon? What is the sum of the angles in a 23-gon? The sum of the interior angles of a polygon is 4320◦ . How many sides does the polygon have? The sum of the interior angles of a polygon is 3240◦ . How many sides does the polygon have? What is the measure of each angle in a regular 16-gon? What is the measure of each angle in an equiangular 24-gon? What is the measure of each exterior angle of a dodecagon? What is the measure of each exterior angle of a 36-gon? What is the sum of the exterior angles of a 27-gon? If the measure of one interior angle of a regular polygon is 160◦ , how many sides does it have? How many sides does a regular polygon have if the measure of one of its interior angles is 168◦ ? 14 ◦ If the measure of one interior angle of a regular polygon is 158 17 , how many sides does it have? How many sides does a regular polygon have if the measure of one exterior angle is 15◦ ? If the measure of one exterior angle of a regular polygon is 36◦ , how many sides does it have? 8◦ How many sides does a regular polygon have if the measure of one exterior angle is 32 11 ? For questions 17-26, find the measure of the missing variable(s). 6 Each angle in a regular n−gon 60◦ 90◦ 108◦ 120◦ www.ck12.org Chapter 1. Angles in Polygons 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 7 www.ck12.org 24. 25. 26. The interior angles of a pentagon are x◦ , x◦ , 2x◦ , 2x◦ , and 2x◦ . What is the measure of the larger angles? The exterior angles of a quadrilateral are x◦ , 2x◦ , 3x◦ , and 4x◦ . What is the measure of the smallest angle? The interior angles of a hexagon are x◦ , (x + 1)◦ , (x + 2)◦ , (x + 3)◦ , (x + 4)◦ , and (x + 5)◦ . What is x? Challenge Each interior angle forms a linear pair with an exterior angle. In a regular polygon you can use two ◦ (n−2)180◦ ◦ different formulas to find the measure of each exterior angle. One way is 360 n and the other is 180 − n (180◦ minus Equiangular Polygon Formula). Use algebra to show these two expressions are equivalent. 31. Angle Puzzle Find the measures of the lettered angles below given that m || n. 27. 28. 29. 30. Review Queue Answers 1. Answers: a. 72◦ + (7x + 3)◦ + (3x + 5)◦ = 180◦ 10x + 80◦ = 180◦ 10x = 100◦ x = 10◦ ◦ ◦ b. (5x + 17) + (3x − 5) = 180◦ 8 www.ck12.org Chapter 1. Angles in Polygons 8x + 12◦ = 180◦ 8x = 168◦ x = 21◦ 2. Answers: a. b. c. d. w = 108◦ , x = 49◦ , y = 131◦ , z = 121◦ 360◦ 59◦ + 72◦ interior angles, exterior angles 9