* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Reproduction in Plants - Amazing World of Science with Mr. Green
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
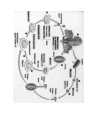
IGCSE Biology YR 10 Plant Reproduction Name: ____________________________ Prepared by William Green DBGS 2011 Glossary Nucleus Chromosomes DNA Genetic Code Inherited Gene Gametes Fertilisation Part of the cell which contains chromosomes Structures in the nucleus that are made from a chemical called DNA A chemical that contains the code for the characteristics of an organism (e.g. what that organism will look like). The coded instructions contained in DNA which give the organism its inherited characteristics Passed on from parent to offspring A section of a chromosome that codes for one characteristic. E.g. eye colour Another name for sex cells. They only contain half of the genetic code compared to normal body cells. The joining of the two gametes. This is the start of a new life. ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ Reproduction 1. What is reproduction? __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ 2. What are the two types of reproduction? ___________________________________________ ___________________________________________ 3. Asexual reproduction produces new offspring without the fusion of ______________. The offspring are _____________________ to the parent plant. 4. What are the different types of asexual reproduction? _________________________________________ ____ __________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ 5. In sexual reproduction both the _____________ and ______________ parent carry ________________. The male sex cell in plants is called the ______________ and the female sex cell is called the _______________. These two sex cells are also called ____________________. 6. Pollination occurs when the ________________ transfer to the ________________. Fertilisation occurs when a __________ is formed. The male and female sex cells are produced by ________________ in the structure of the flower. Parts of a flower Label this flower and give the definition of each part below: Stamen = _______________________________________________________________ Anther = _______________________________________________________________ Filament = ______________________________________________________________ Carpel = ________________________________________________________________ Stigma = _______________________________________________________________ Style = _________________________________________________________________ Ovary = ________________________________________________________________ Ovule = ________________________________________________________________ Pollination 1. Pollination occurs when the_________________________ is released from the _________________________ and land on the __________________ 2. What are the two methods flowers are pollinated? ____________________________________________ ____________________________________________ 3. Compare and contrast wind and insect pollinated flowers: Insect Pollinated flower Wind pollinated flower Large, coloured petals to attract insects No scent (they don’t smell!) Contain nectar to attract the insects Anthers are inside the flower where insects have to brush past them to get to the nectar inside Stigma is large and feathery and hangs outside the flower to catch pollen in the air. Flowers only appear in warm weather when there are insects around 4. True or false? Pollination is basically the same as fertilisation Write out the correct version below: __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ 5. How does cross pollination differ from self pollination? __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ 6. Why is it preferable for a plant to encourage cross-pollination rather than self pollination? __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ Fertilisation 1. Annotate this diagram to explain what happens during fertilisation. 2. Add “Zygote” and “Embryo” to your glossary list. 3. The zygote turns into the ________________ 4. The ovary turns into the __________________ 5. Water is removed from the seed in order to ______________________ activity and let the seed ________________________ Seed Dispersal 1. Any structure that contains a seed is a ____________________ 2. What is the function of fruits? __________________________________________________________ 3. Why is seed dispersal important? a. __________________________________________________________ b. __________________________________________________________ 4. What sorts of things will plants compete with each other for? List as many as you can __________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ 5. Describe in as much detail as you can how plants disperse their seeds: __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ Seed structure 1. What do seeds contain? _____________________________________________________________________ 2. What will the radicle grow in to? ________________________________________ 3. What will the plumule grow in to? ______________________________________ 4. What will the hypocotyls grow in to? ____________________________________ 5. What are the cotyledons? ______________________________________________ 6. What is the testa? _____________________________________________________ 7. What is the microyple? ________________________________________________ 8. Seeds with two cotyledons are called ____________________________. Seeds with one cotyledon are called _________________________ 9. Label these diagrams of the seed: Germination 1. What is germination? ______________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ 2. What is the first thing to happen in germination? ______________________ __________________________________________________________________ 3. Complete the germination diagram 4. Explain how these factors affect germination: Water __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ Oxygen __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ Temperature __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ Light __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________