* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download School District of Palm Beach County World History 10th grade
Migration Period wikipedia , lookup
Muslim conquest of the Maghreb wikipedia , lookup
Late Middle Ages wikipedia , lookup
Early Muslim conquests wikipedia , lookup
Post-classical history wikipedia , lookup
Early Middle Ages wikipedia , lookup
Christianity in the 13th century wikipedia , lookup
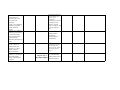
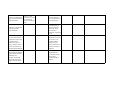
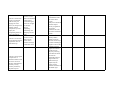
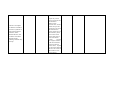
School District of Palm Beach County World History 10th grade Scope 2010-2011 1st NINE WEEKS Benchmarks Next Generation Sunshine State Standards 2008 SS.912.W.1.1 Use timelines to establish cause and effect relationships of historical events. Language Arts and Reading Standards Pacing and Topic Student Target I can LA.910.2.1.5 The student will analyze and develop an interpretation of a literary work by describing an author’s use of literary elements Aug 18 - Aug 23 Create a timeline (e.g., theme, point of Historical Inquiry listing important dates view, characterization, in chronological order. Skills setting, plot, etc.), and explain and analyze different elements of figurative language (e.g., simile, metaphor, personification, hyperbole, symbolism, allusion, imagery, etc.). Core Reading Clusters 1. Words and World History: Phrases in Context Patterns of 2. Main Idea Interaction 3. Comparisons ©2005 Cause and Effect McDougal 4. Reference and Research Littell Remediation/Enrichment LA.910.1.7.3 The student will determine the main idea or SS.912.W.1.2 Compare essential message in time measurement systems grade-level or higher used by different cultures texts through inferring, (e.g., Chinese, Gregorian, paraphrasing, and Islamic calendars, summarizing, and dynastic periods, decade, identifying relevant details. century, era) Compare time measurements systems used by different cultures. SS.912.W.1.3 Interpret and evaluate primary and secondary sources (e.g., artifacts, images, auditory and written sources). Distinguish between primary and secondary sources. Evaluate the reliability, validity, and accuracy of historical sources. Identify the point of view of these sources as well as determining bias. Identify a problem or issue and consider alternative positions and solutions. Categorize information as political, social, or economic, or as positive or negative. Compare and contrast different interpretations of key events. Construct support for a position by choosing accurate, relevant evidence. LA.910.1.6.3 The student will use context clues to determine meanings of unfamiliar words. SS.912.W.1.4 Explain how historians use historical inquiry and other sciences to understand the past (e.g., archaeology, economics, geography, forensic chemistry, political SS.912.W.1.5 Compare conflicting interpretations or schools of thought (historiography) about world events and individual contributions to history. SS.912.W.1.6 Evaluate the role of history in shaping identity and character (e.g., ethnic, cultural, personal, national, religious). SS.912.W.2.1 Locate the extent of Byzantine territory at the height of the empire. Describe the relationship between history and other sciences. Explain how archaeology, economics, geography, forensic chemistry, political science, and physics help us to learn about the past. Define and give examples of historiographical interpretation. Describe how history has helped to shape ethnic, cultural, personal, national, and religious identity of nations. Describe Byzantine Aug 24 - Sep 1 politics and the rise of Byzantine Empire Emperor Justinian. LA.910.2.1.5 The student will analyze and develop an interpretation of a literary work by describing an author’s SS.912.W.2.2 Describe the impact of Constantine use of literary the Great's establishment elements (e.g., theme, point of view, of "New Rome" (Constantinople) and his characterization, recognition of Christianity setting, plot, etc.), and explain and analyze as a legal religion. different elements of figurative language (e.g., simile, metaphor, personification, hyperbole, symbolism, Explain why Constantinople was also known as "New Rome." Describe the significance of Constantine's acceptance of Christianity to the Byzantine Empire. LA.910.1.7.3 The student will determine SS.912.W.2.3 Analyze the the main idea or extent to which the essential message in Byzantine Empire was a grade-level or higher continuation of the old texts through Roman Empire and in inferring, what ways it was a paraphrasing, departure. summarizing, and identifying relevant details. Describe how the Byzantine empire preserved and transmitted Greek and Roman knowledge and culture. Explain how the Byzantine church differed from the Roman church in its use of icons, language, imperial authority over the church, and marriage of priests. LA.910.1.6.3 The SS.912.W.2.4 Identify key student will use context figures associated with the clues to determine Byzantine Empire. meanings of unfamiliar Describe Justinian's achievements and life in Constantinople. words. SS.912.W.2.5 Explain the contributions of the Byzantine Empire. Explain the significance of a uniform code of laws under Justinian. Describe the major contributions in architecture, engineering and art. SS.912.W.2.6 Describe the causes and effects of the Iconoclast controversy of the 8th and 9th centuries and the 11th century Christian schism between the churches of Constantinople and Rome. Describe the disagreement over the use of icons in the Byzantine church. Explain why the Eastern and Western churches created two traditions. SS.912.W.2.7 Analyze causes (Justinian's Plague, ongoing attacks from the "barbarians," the Crusades, and internal political turmoil) of the decline of the Byzantine E i Identify political, social, and economic causes of the Byzantine Empire's collapse. Explain how military technology helped the Ottomans bring about the final collapse of the Byzantine empire. Explain how the fall of Constantinople marked a turning point in history. Identify the lands and peoples that came under Muslim rule. Describe the achievements in arts and sciences during the golden age. SS.912.W.2.8 Describe the rise of the Ottoman Turks, the conquest of Constantinople in 1453, and the subsequent growth of the Ottoman empire under the sultanate including Mehmet the Conqueror and Suleyman the Magnificent. SS.912.W.2.9 Analyze the impact of the collapse of the Western Roman Empire on Europe. LA.910.2.1.5 The student will analyze and develop an interpretation of a literary work by describing an author’s use of literary elements (e.g., theme, point of view, characterization, setting, plot, etc.), and explain and analyze different elements of figurative language (e.g., simile, metaphor, personification, hyperbole, symbolism, allusion, imagery, etc.). Identify the political, Sep 2 - Sep 13 social and economic Early Middle Ages effects of Germanic invasions. LA.910.1.7.3 The SS.912.W.2.10 Describe student will determine the orders of medieval the main idea or social hierarchy, the essential message in changing role of the grade-level or higher Church, the emergence of texts through feudalism, and the inferring, development of private paraphrasing, property as a summarizing, and distinguishing feature of identifying relevant Western Civilization. details. Explain the structure of feudalism and the role of the manor system. Analyze how medieval literature depicts chivalry, knighthood and women. Summarize the roles and status of medieval women. LA.910.1.6.3 The SS.912.W.2.11 Describe student will use the rise and achievements context clues to of significant rulers in determine meanings medieval Europe. of unfamiliar words. Identify Charles Martel's successes. Describe several ways in which Charlemagne sought to restore order to medieval Europe. SS.912.W.2.12 Recognize the importance of Christian monasteries and convents as centers of education, charitable and missionary activity, economic productivity, and political power. Explain the role that monks and nuns played in preserving Greco-Roman culture. Describe the relationship between religion and art in medieval Europe. Explain why the Church was the dominant institution of the Middle Ages. SS.912.W.2.13 Explain how Western civilization arose from a synthesis of classical Greco-Roman civilization, JudeoChristian influence, and the cultures of northern European peoples promoting a cultural unity in Europe. Explain why western nations owe much to the Greek humanist tradition, JudeoChristian ethics, and the Roman concept of law. Describe how the values that emanated from ancient cultures have set the standards by which most western nations measure their political, social and economic systems. Describe how religious traditions of the ancient Hebrews continue to influence western values. Explain how the western belief in the rule of law is built on the foundations of the ancient Romans. SS.912.W.2.17 Identify key figures, artistic, and intellectual achievements of the medieval period in Western Europe (e.g., Anselm of Canterbury, Chaucer, Thomas Aquinas, Roger Bacon, Hildegard of Bingen, Dante, Code of Chivalry, Gothic architecture, illumination, universities, Natural Law Philosophy, Scholasticism). SS.912.W.2.14 Describe the causes and effects of the Great Famine of 13151316, The Black Death, The Great Schism of 1378, and the Hundred Years War on Western Europe. Identify significant medieval achievements in literature, art, and architecture. LA.910.2.1.5 The student will analyze and develop an interpretation of a literary work by describing an author’s use of literary elements (e.g., theme, point of view, characterization, setting, plot, etc.), and explain and analyze different elements of figurative language (e.g., simile, metaphor, personification, hyperbole, symbolism, allusion, imagery, etc.). Sep 14 - Sep 22 Later Middle Ages SS.912.W.2.15 Determine the factors that contributed to the growth of a modern economy (e.g., growth of banking, technological and agricultural improvements, commerce, towns, guilds, rise of a merchant class). SS.912.W.2.16 Trace the growth and development of national identity in England, France, and Spain. SS.912.W.2.17 Identify key figures, artistic, and intellectual achievements of the medieval period in Western Europe (e.g., Anselm of Canterbury, Chaucer, Thomas Aquinas, Roger Bacon, Hildegard of Bingen, Dante, Code of Chivalry, Gothic architecture, illumination, universities, Natural Law Philosophy, Scholasticism). LA.910.1.7.4 The student will identify cause-and-effect relationships in text. Identify the factors that led to the Commercial Revolution. Explain how the Commercial Revolution brought new ways of doing business. LA.910.1.6.9 The student will determine the correct meaning of words with multiple meanings in context. Describe how monarchs increased their power and formed nationstates. Explain how the governments of France and England differed as they moved toward a stronger sense of nationhood. Describe the key differences between Romanesque and Gothic architecture. SS.912.W.2.18 Describe developments in medieval English legal and constitutional history and their importance to the rise of modern democratic institutions and procedures (e.g., Magna Carta, parliament, habeas corpus) SS.912.W.3.8 Identify important figures associated with the Crusades (e.g., Alexius Commenus, Pope Urban, Bernard of Clairvaux, Godfrey of Bouillon, Saladin, Richard the Lionheart, Baybars, Louis IX). SS.912.W.2.19 Describe the impact of Japan's physiography on its economic and political development. Explain how the Magna Carta limited the power of the English kings. Describe how England developed a limited monarchy. Identify the reasons why Christians and Muslims fought in the Crusades. Explain the effect of the Crusades on the economy of Europe. Describe how the Crusades affected the power of the Church and feudal lords. Analyze how the Crusades expanded European's view of the world. LA.910.1.7.4 The student will identify cause-and-effect relationships in text. Sep 23-Sep 30 Japanese Feudalism Describe how Japan's geographic setting contributed to its development. SS.912.W.2.20 Summarize the major cultural, economic, political, and religious developments in medieval Japan (e.g. Pillow Book, Tale of Genji, Shinto and Japanese Buddhism, the rise of feudalism, the development of the shogunate, samurai, and social hierarchy). LA.910.2.1.5 The student will analyze and develop an interpretation of a literary work by describing an author's use of literary elements (e.g., theme, point, of view, characterization, setting, plot), and explain and analyze different elements of figurative language (e.g., simile, metaphor, personification, hyperbole, symbolism, allusion, imagery). SS.912.W.2.21 Compare Japanese feudalism with Western European feudalism during the Middle Ages. LA.910.3.2.2 The student will draft writing by establishing a logical organizational pattern with supporting details that are substantial, specific, and relevant. SS.912.W.2.22 Describe Japan's cultural and economic relationship to China and Korea. LA.910.1.6.9 The student will determine the correct meaning of words with multiple meanings in context. Analyze the ways in which the economy and culture of Japan flourished during its later feudal age. Describe how the structure of Japanese feudalism was similar to or different from European feudalism. Analyze the influence of China and Korea on Japan. SS.912.W.3.1 Discuss significant people and beliefs associated with Islam (e.g., the prophet Muhammad, the early caliphs, the Pillars of Islam, Islamic law, the relationship between government and religion in Islam). LA.910.2.1.5 The student will analyze and develop an interpretation of a literary work by describing an author's use of literary elements (e.g., theme, point, of view, characterization, setting, plot), and explain and analyze different elements of figurative language (e.g., simile, metaphor, personification, hyperbole, symbolism, allusion, imagery). SS.912.W.3.2 Compare the major beliefs and principles of Judaism, Christianity, and Islam. LA.910.1.7.4 The student will identify cause-and-effect relationships in text. SS.912.W.3.3 Determine the causes, effects, and extent of Islamic military expansion through Central Asia, North Africa, and the Iberian Peninsula. SS.912.W.3.4 Describe the expansion of Islam into India and the relationship between Muslims and Hindus. LA.910.1.6.9 The student will determine the correct meaning of words with multiple meanings in context. Oct 1 - Oct 12 Rise and Spread of Islam Explain how Muhammad began to unify the Arabian Peninsula under Islam. Describe how Muhammad's successors spread Islam. Describe Muslim attitudes toward philosophy and religion. Explain the similarities and differences between Judaism, Christianity, and Islam. SS.912.W.3.5 Describe the achievements, contributions and key figures associated with the Islamic Golden Age (e.g., Al-Ma'mun, Avicenna, Averroes, Algebra, AlRazi, Alhambra, The Thousand and One Nights). SS.912.W.3.6 Describe key economic, political, and social developments in Islamic history (e.g., growth of the caliphate, division of Sunni and Shi'a, role of trade, dhimmitude, Islamic slave trade). SS.912.W.3.7 Analyze the causes, key events, and effects of the European response to Islamic expansion beginning in the 7th century (e.g., growth of the caliphate, division of Sunni and Shi'a, role of trade, dhimmitude, Islamic slave trade). Identify Muslim accomplishments in art, literature, mathematics, and science. Describe the importance of trade in the Muslim empires. Explain the source of the disagreement between the Sunni and Shi'a. Week of October 11, 2010 -- Comprehension Check SS.912.W.3.9 Trace the growth of major subSaharan African kingdoms and empires (e.g., Ghana, Mali, Songhai). LA.910.2.1.7 The student will analyze, interpret, and evaluate an author's use of descriptive language (e.g., tone, irony, mood, imagery, pun, alliteration, onomatopoeia, allusion), figurative language (e.g., symbolism, metaphor, personification, hyperbole), common idioms, and mythological and literary allusions, and explain how they impact meaning in a variety of texts. SS.912.W.3.10 Identify key significant economic, political and social characteristics of Ghana (e.g., salt and gold trade, taxation system, gold monopoly, matrilineal inheritance, griots, ancestral worship, rise of Islam, slavery). LA.910.1.7.7 The student will compare and contrast elements in multiple texts. Oct 13 - Oct 22 Empires of Africa Describe how the geography of Africa encouraged the development of diverse civilizations. Identify the forces that contributed to the rise and fall of the kingdoms of Ghana, Mali, and Songhai. Explain how the goldsalt trade led to the rise of Ghana. SS.912.W.3.11 Identify key figures and significant economic, political, and social characteristics associated with Mali (e.g., Sundiata, Epic of Sundiata, Mansa Musa, Ibn Battuta, gold mining and salt trade, slavery). SS.912.W.3.12 Identify key figures and significant economic, political, and social characteristics associated with Songhai (e.g., Sunni Ali, Askia Mohammad the Great, gold, salt trade, cowries as a medium of exchange, Sankore University, slavery, professional army, provincial political structure). SS.912.W.3.13 Compare economic, political, and social developments in East, West, and South Africa. LA.910.3.2.1 The student will draft writing by developing ideas from the prewriting plan using primary and secondary sources appropriate to purpose and audience. LA.910.1.6.8 The student will identify advanced word/phrase relationships and their meanings. Describe how Mansa Musa and Sundiata advanced Mali. Evaluate the cultural impact of Mansa Musa's pilgrimage on Mali. SS.912.W.3.14 Examine the internal and external factors that led to the fall of the empires of Ghana, Mali, and Songhai (e.g., disruption of trade, internal political struggles, Islamic invasions).