* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Battle of Tippecanoe wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Plattsburgh wikipedia , lookup
Siege of Detroit wikipedia , lookup
Siege of Fort Erie wikipedia , lookup
Army National Guard units with campaign credit for the War of 1812 wikipedia , lookup
Canadian units of the War of 1812 wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Crysler's Farm wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Frenchtown wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Lundy's Lane wikipedia , lookup
Second Battle of Sacket's Harbor wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Lake Erie wikipedia , lookup
Burning of Washington wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Stoney Creek wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Bladensburg wikipedia , lookup
Battle of York wikipedia , lookup
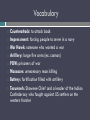
New Government in Operation: The War of 1812 Level 1 Vocabulary Counterattack: to attack back Impressment: forcing people to serve in a navy War Hawk: someone who wanted a war Artillery: large fire arms (ex. cannon) POW: prisoners of war Massacre: unnecessary mass killing Battery: fortification filled with artillery Tecumseh: Shawnee Chief and a leader of the Indian Confederacy who fought against US settlers on the western frontier Essential Questions What were the causes of the War of 1812 What were some of the major battles of the War of 1812? What were the results of the War of 1812 How do you think relations between the Native American and the US will progress in the future? Causes of the War of 1812 France and Britain hurt US trade by taking ships. Britain made US sailors join the British Navy. Britain helped Natives attack between the Appalachian Mountains and the Mississippi River. Britain wouldn’t take troops out of the Louisiana Territory. The War Hawks wanted to add Canada and Spanish Florida to the States. Events in the War of 1812 Battles and Movements of US and British troops Three Areas of Conflict Great Lakes Area Chesapeake Bay Area New Orleans Area Events in the War of 1812: Constitution “Old Ironsides” vs. Guerriere USS Constitution had more and better guns and was faster than any other ship. British fired first and did little damage. US fired on the hull and masts that destroyed the British ship. Constitution suffered little damage and had 7 killed and 7 wounded. HMS Guerriere was too damaged to keep and was burned. The victory over Guerriere showed the ability of the US Navy Game The USS Constitution captures HMS Guerriere, 19 August 1812 Events in the War of 1812: Battle of York (Toronto) 1813 Major Dearborn attacked York (modern Toronto). The Americans captured the battery after 3 hours but before the British surrendered, they destroyed the ship under construction, the naval storehouse and the magazine at the government house. The Americans were going to remove the flying British flag at the government house when it exploded and killed 38 and wounded 222. The Americans looted and destroyed the remaining government and military buildings. Later in the war Washington D.C. was burned as pay back. Events in the War of 1812: Battle of Lake Erie Sept. 10, 1813 Lawrence and 8 other American ships, 54 guns vs. Detroit and 5 other ships, 63 cannons that had a range twice as long as the Americans Lawrence suffered about 80% casualties and Commodore Perry had to abandon ship and row to Niagara to attack again. The British tried to turn their ships but hit each other and were stuck together. Perry attacked and the British surrendered. Results: American control of Lake Erie Improved American morale Fort Malden was abandoned and the British retreated up to Thames River near Detroit 6 ships were taken by the Americans Perry took Harrison’s army near Thames River to fight Events in the War of 1812: Battle of Horseshoe Bend Background: Red Sticks (followers of Tecumseh) went to Pensacola to get weapons from the Spanish and were ambushed by Americans from Fort Mims Red Sticks counterattacked & the US retreated to Fort Mims (August 30, 1813) Red Sticks made a surprise attack on 553 frontiersmen at Fort Mims Red Sticks defeated the Americans and then massacred most of the survivors including women and children As payback for the massacre, General Andrew Jackson took his militia and attacked a fortified Creek village at Horseshoe Bend Red Sticks were greatly outnumbered Big guns destroyed the defenses About 800 warriors died 500 women and children were imprisoned Andrew Jackson defeated the Creek Indians Events in the War of 1812: Battle of Horseshoe Bend Result: Treaty of Fort Jackson: (1814) Creeks gave up most of their lands in southern Alabama and Georgia to the US. Events in the War of 1812: Burning of Washington D.C. August 24, 1814 The British defeated the Americans at the Battle of Bladensburg, Maryland. The British marched into Washington, D.C. Government officials left the capital. The British army entered Washington. British troops looted and burned the White House, the Capitol building, House of Representatives and Library of Congress, a number of federal buildings, and several private homes to get revenge for York. (August 26) The British withdrew. Tom Freeman's painting of the August 24, 1814 burning of the White House by British troops during the War of 1812. Events in the War of 1812: Battle of Baltimore Sept. 12, 1814 British troops landed near Baltimore British crossed the North Point Peninsula between two rivers where the Maryland militia waited and killed the British General The British didn’t break the third American line, and their land path to Baltimore was blocked. The British tried to capture Fort McHenry to open the water route to Baltimore: The British dropped rounds all day and night When morning came and the civilians saw the American flag still flying, they were happy. Francis Scott Key wrote the first verse of the Star Spangled Banner that would later become the US national anthem. The British withdrew. It was an American victory. Events in the War of 1812: Hartford Convention 1814 New England shipping decreased because of the war. New England states sent delegates to Hartford for secret meetings. Some wanted to secede (leave the US) or at least threaten secession to get their way but most didn’t. Hartford Convention's final demands: Federal money to help New England's trade economy 7 Constitutional amendments The members of the Hartford Convention sent messengers with their demands to Washington. They arrived as news of the Treaty of Ghent and the victory in New Orleans reached the city. They were ignored. Importance: continued the idea of states' rights Federalist party began to die out The End of the War of 1812: Treaty of Ghent December 24, 1814 Ended hostilities British left Northwest Territory Restored land to prewar status Mediation for boundary disputes Events in the War of 1812: Battle of New Orleans Jan. 8, 1815 British fleet of more than 50 ships prepared to attack New Orleans General Jackson moved his army (7,000 militia) to New Orleans to help defend it. They didn’t know about the Treaty of Ghent. 7,500 British attacked Fighting lasted half an hour British withdrew U.S. victory Jackson became an American hero. Effects of the War of 1812 The British recognized US boundaries and left the Northwest Territory US gained national pride US industry increased due to the end of trade with Britain Federalist Party, which was against the war, disappeared Weakened Native resistance Essential Questions What were the causes of the War of 1812 What were some of the major battles of the War of 1812? What were the results of the War of 1812 How do you think relations between the Native American and the US will progress in the future?