* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ophthalmologic Examination
Idiopathic intracranial hypertension wikipedia , lookup
Eyeglass prescription wikipedia , lookup
Vision therapy wikipedia , lookup
Photoreceptor cell wikipedia , lookup
Fundus photography wikipedia , lookup
Diabetic retinopathy wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrial optic neuropathies wikipedia , lookup
Keratoconus wikipedia , lookup
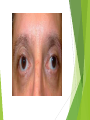
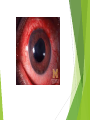
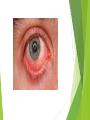
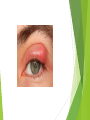
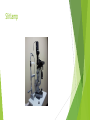
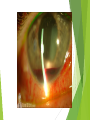
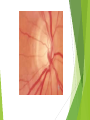
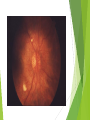
Ophthalmologic Examination Dr Amir Eftekhari Ocular History Chief complain: Abnormalities of vision Abnormalities of appearance Pain and discomfort Past medical history Family history Basic Ophthalmologic examination Vision Pupils Ocular motility External examination Slit lamp examination Tonometry Direct ophthalmoscopy Indirect ophthalmoscopy Vision Central vision : Visual Acuity ( VA ) for near from 33 cm and distance from 6 m Peripheral vision : confrontation test and perimetry Clinical assessment of VA and VF is subjective rather than objective since it requires responses on the part of the patient . Snellen chart and illiterate E charts Uncorrected VA Corrected VA : Pinhole Refraction Testing for poor vision pinhole retinoscope Pupils Basic examination : Size , shape , reactivity for both light and accommodation Pupillary abnormality may be due to : 1 ) neurologic disease 2 ) intra ocular inflammation 3 ) marked elevation of IOP 4 ) prior surgical alternation 5 ) the effect of medication 6 ) benign variation of normal Marcus Gunn Pupil Relative afferent pupillary defect ( RAPD ) Direct response to light Consensual response to light Causes of marcusgunn pupil : optic nerve lesion large retinal or severe macular lesion Ocular Motility Testing alignment 1) Light reflex on cornea 2) Cover test Testing Extra ocular movement 1 ) Ductions 2 ) Versions 3 ) vergence Ocular motility Impairment of eye movements can be due to : 1 ) neurologic problems such as cranial nerve palsy 2 ) primary extraocular muscular weakness such as myasthenia gravis 3 ) mechanical constraints within the orbit limiting rotation of the eye such as orbital floor fracture with entrapment of the inferior rectus muscle External examination Positions of eyelids Malposition of the globe such as proptosis Skin lesions and inflammatory signs such as swelling , erythema , warmth and tenderness Palpation of the bony orbital rim periocular soft tissue The general facial examination Slit lamp examination Table – mounted binocular microscope Linear slitbeam with variable angle , width , length and intensity of the light beam The magnification is normally 10 to 16 The anterior half of the eye can be visualized Slit lamp examination Lid margin and lashes Palpebral and bulbar conjunctival surface Tear film and cornea Iris Anterior chamber , aqueous Crystalline lense Anterior vitreous Slitlamp Adjunctive slitlamp techniques Lid eversion Fluorescein staining Special lenes Special attachments Tonometry Tonometry is the method of measuring intraocular pressure using calibrated instruments. The normal range is 10 to 21 mmhg. Methods of tonometry Applanation tonometry : Goldmann tonometer Perkins tonometer Tono-pen pneumatometer Indentation tonometry : Sshiotz tonometer Non contact tonometry : Air-puff tonometer Tonometery Accuracy of IOP measurement is affected by central corneal thickness If the cornea is relatively thin the actual IOP is higher than the measured value . Thus the ultrasonic measurement of corneal thickness ( pachymetry ) may be helpful in assessment of IOP . Direct Ophthalmoscopy Hand held direct ophthalmoscope Magnification : 15 in emetropic eyes The intensity of light , spot size and color of the illuminatig light can be adjusted . The ophthalmoscopes point of focus can be adjusted 60-refractive error of eye / 4 Direct ophthalmoscope Red reflex examination : at arm length from the patient Fundus examination : approximately 1-2 inches from the patients The rule of RRR and LLL Examination of optic disc and macula The green ( red free filter ) assists in the examination of the retinal vasculature and the subtle striation of the nerve fiber layer as they course toward the disc . Indirect ophthalmoscopy Comparison of indirect and direct ophthalmoscopy Direct ophthalmoscopy has greater magnification than indirect Indirect ophthalmoscopy provides much wider field of view . Indirect ophthalmoscopy is binocular and provides stereopsis Indirect ophthalmoscope has brighter light source Indirect ophthalmoscopy can be used to exam entire retina even out to ora serrata with scleral depression In indirect ophthalmoscopy the image of retina is inverted Diagnostic medications Topical anesthetics such as tetracaine and propracaine : tonometry ocular contact with diagnostic lense corneal scraping lacrimal , canalicular and punctual probing scleral depression Diagnostic medication Mydriatic drops : sympathomimetic such as 2.5% phenylefrin anticholinergic eye drops such as 0.5% or 1% tropicamide Anticholinergic drops also inhibit accommodation . Tonometry should be performed before these drops are instilled . There is small risk of acute angle closure glaucoma attack if the patient has preexisting narrow anterior chamber angle .