* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download ATRIAL SEPTAL DEFECT
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Artificial heart valve wikipedia , lookup
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Atrial fibrillation wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Atrial septal defect wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
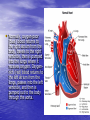
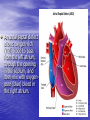
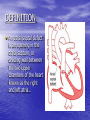
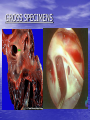
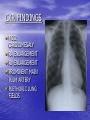
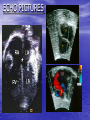
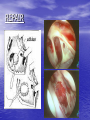
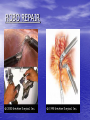
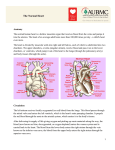
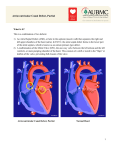
ATRIAL SEPTAL DEFECT BY DR.ANAND • Normally, oxygen-poor (blue) blood returns to the right atrium from the body, travels to the right ventricle, then is pumped into the lungs where it receives oxygen. Oxygenrich (red) blood returns to the left atrium from the lungs, passes into the left ventricle, and then is pumped out to the body through the aorta. • An atrial septal defect allows oxygen-rich (red) blood to pass from the left atrium, through the opening in the septum, and then mix with oxygenpoor (blue) blood in the right atrium. DEFINITION • An atrial septal defect is an opening in the atrial septum, or dividing wall between the two upper chambers of the heart known as the right and left atria.. GROSS SPECIMENS EMBRYOLOGY • The heart is forming during the first 8 weeks of fetal development. It begins as a hollow tube, then partitions within the tube develop that eventually become the septa (or walls) dividing the right side of the heart from the left. Atrial septal defects occur when the partitioning process does not occur completely, leaving an opening in the atrial septum. HEMODYNAMICS • RT.ATRIUM RECEIVES • RT.ATRIUM BLOOD FROM SUP. & INF.VENA CAVA & FROM LT. ATRIUM ENLARGES HEMODYNAMICS • LARGE VOL OF BLOOD FROM RT.ATRIUM PASSES THRU NORMAL TRICUSPID VALVE & PULMONARY VALVE • DELAYED DIASTOLIC • • MURMUR(LOW LT STERNAL BORDER) RT.VENTRICLE ENLARGES PULMONARY EJECTION MURMUR HEMODYNAMICS • PULM. VALVE CLOSES • WIDELY SPLIT S2 • LATE & P2 IS DELAYED RV IS FULLY LOADED,SO FURTHER RISE IN RV VOLUME CANNOT OCCUR • FIXED SPLIT S2 • ACCENTUATED S2 PRESENTATION • recurrent chest infections • fatigue • sweating • rapid breathing • shortness of breath • poor growth ON EXAMINATION • INSPECTION • PARASTRNL IMPULSE • PALPATION • SYSTOLIC THRILL AT 2ND LT SPACE AUSCULTATION • WIDE FIXED SPLIT S2 • ACCENTUATED P2 • ESM AT LT 2nd & 3rd INTERSPACES • DELAYED DIASTOLIC MURMUR AT LOW LT INTERSPACE CXR FINDINGS • MOD. • • • • CARDIOMEGALY RA ENLARGEMENT RV ENLARGEMENT PROMINENT MAIN PULM ARTERY PLETHORIC LUNG FIELDS ECG CHANGES • RT AXIS DEVIATION • RT VENT • HYPERTROPHY rsR’ PATTERN IN V1 ECHO PICTURES SEVERITY ASSESMENT • INTENSITY OF THE TWO MURMURS • THE HEART SIZE COMPLICATION • PULMONARY HYPERTENSION(ABOVE 20 YEARS) • DISAPPEARANCE OF DIASTOLIC MURMUR • APPEARANCE OF PULM EJECN CLICK • LOUD PALPABLE P2 • P2_STILL WIDELY SPLIT MANAGEMENT • MEDICAL • ANTIBIOTICS FOR CHEST INFECTIONS • DIGOXIN TO INCREASE WORK OF HEART • DIURETICS TO REDUCE PRELOAD SURGICAL REPAIR:DEVICES REPAIR ROBO REPAIR