* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 06 Intrusions
Physical oceanography wikipedia , lookup
Post-glacial rebound wikipedia , lookup
Composition of Mars wikipedia , lookup
Geochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Abyssal plain wikipedia , lookup
Algoman orogeny wikipedia , lookup
Oceanic trench wikipedia , lookup
Plate tectonics wikipedia , lookup
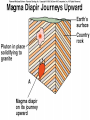
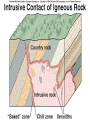
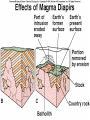
Magma & Intrusions Learning objectives: 1. Learn to interpret igneous textures. 2. Understand igneous intrusive structures. Where we are • Today: Plate Tectonics & Intrusive Rocks - Magma creation - Magma changes - Intrusive Features • Next: Volcanoes & Hazards [show pillow lava] Convergent Boundaries “Subduction Zones” • It’s all about the water! • What’s getting subducted? Convergent Plate Boundaries Convergent Plate Boundaries Heating of ocean crust releases fluids (mostly water) into mantle above. Convergent Plate Boundaries Heating of ocean crust releases fluids (mostly water) into mantle above. Added fluids produce basalt magma from melting mantle. Convergent Plate Boundaries Buoyant magma rises to base of crust. Heating of ocean crust releases fluids (mostly water) into mantle above. Added fluids produce basalt magma from melting mantle. Convergent Plate Boundaries Buoyant magma rises to base of crust. Heating of ocean crust releases fluids (mostly water) into mantle above. As basalt moves through continental crust, it melts and absorbs some crust, becoming more silica-rich. Added fluids produce basalt magma from melting mantle. Convergent Plate Boundaries Continental arc volcanoes violently erupt silica-rich magma as ash from composite volcano. Buoyant magma rises to base of crust. Heating of ocean crust releases fluids (mostly water) into mantle above. As basalt moves through continental crust, it melts and absorbs some crust, becoming more silica-rich. Added fluids produce basalt magma from melting mantle. Convergent Plate Boundaries • Continental Volcanic Arc - e.g., WA • Volcanic Island Arc - e.g., Japan A Cooperative Quiz • Where mantle convection causes rising asthenosphere: A. The mantle rock will erupt on the seafloor B. The mantle rock will melt (at least partially) producing basaltic magma C. The molten mantle will crystallize D. The subducting slab will rise Magma evolution • Magmas can change their composition. How? - assimilation (melt the rocks around them) - crystallization (crystallize Si-poor minerals) basalt andesite granite Show Fractional Crystallization animation A Cooperative Quiz • By removing early-formed crystals from a ______ magma, we can obtain a ______ magma. A. granite ... rhyolite B. basalt ... granite C. granite ... basalt D. Si-rich ... Si-poor A Cooperative Quiz A Cooperative Quiz • A magma body will rise from its point of origin until: A. Its density equals that of the surrounding rock B. Its density exceeds that of the surrounding rock C. It solidifies to the point it cannot flow D. It gets to the surface Magma density • Magmas are (usually) less dense than the rocks around them. • If they reach the surface: Volcanism! • If not... Intrusive features • Represent magma that solidified (froze) after it stopped moving - dike - sill - pluton - batholith a large body of igneous rock Show Igneous Features animation A Cooperative Quiz A Cooperative Quiz • True (A) or false (B): Igneous intrusions range in scale from a few cm3 to thousands of km3 d’Alessio, UC Berkeley • Wrong: Sketch with caption • Right: explanatory labels on sketch Isostasy Rubric • Thickness effect • Density effect • Elevation differences • Mountain roots • Crust / lithosphere “floating” on mantle / asthenosphere MOR Rubric • Lithosphere-20 • Crust-20 • Asthenosphere-20 • Asthenosphere convection-30 • Rising asthenosphere/ mantle-30 • Melting due to decompression-30 • Crustal age progression-20 • Topographic ridge-30 • Plates moving apart-30 • Thinner lithosphere near ridge-20 • Reason for ridge-20 • Shallow magma chamber-20 • Transform faults-30 • Magnetic stripes-30 • Earthquakes-10 • Rock types-10 each • Total possible: 370+ Sketch Problems • Isostasy • • Must relate water sketch to earth! Mid-ocean ridges Lithosphere is not below crust What causes the spreading? • Not rising magma • Mostly slab-pull - Magma Quiz 1. 2. 3. 4. What causes melting at mid-ocean ridges? What causes melting in Hawaii? What causes melting below Mt. Baker? What is the composition of the melt produced in each of the above locations? 5. What is the composition of the melt erupted in each of the above locations? Locale Plate Tectonic Environment Reason for Magma Production Typical Rock mid-ocean ridge divergent boundary decompression basalt wetting andesite convergent subduction boundary (w/at zone least 1 ocean plate) “hot spot” within plate basalt/ decompression rhyolite Questions to think about in video A. What volcanic hazard affects many, but kills few? B. What volcanic hazard is the most hazardous to people far from the volcano? C. What is the main volcanic hazard for Bellingham? D. What is the least important hazard for Bellingham? Turn on the International Volcanic Hazards Training Video now.