* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Heart - Ms. Mogck`s Classroom
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Artificial heart valve wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Atrial septal defect wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
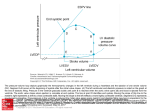
The Heart The Pathway of the Blood Through the heart, beginning at the vena cava anterior (inferior) vena cava is at the bottom superior vena cava is at the top blue blood (deoxygenated) enters the right atrium right atrium contracts blue blood is sent through the AV valve to the right ventricle right ventricle contracts sending blood through the semilunar valve out the pulmonary artery blood goes to the lungs The arteries branch into arteriolles capillaries surround the alveoli in the lungs allowing the oxygen to diffuse into the lungs red blood returns oxygenated to the heart through the pulmonary veins Oxygenated (red) blood comes from the lungs through the Pulmonary VEIN red blood enters the left atrium left atrium contracts forces blood through the AV valve into the left ventricle left ventricle is the heart’s most muscular chamber contraction of the left ventricle sends blood through the semilunar valve out the aorta the aorta is the largest ARTERY in the body it sends oxygen rich blood to the body arteries branch smaller into arterioles and eventually into capillaries capillaries transfer oxygen to tissues (greatest surface area) and extract CO2 from tissues into the blood after picking up the CO2, capillaries become venuoles and veins which lead back to the heart deoxygenated (blue) blood returns to the heart through the vena cava (main vein) Quick Question?! What is the only blood vessel in which diffusion can occur? Heartbeat Systole and Diastole phases Lub Dub of the Heart Diastole relaxation where the atria or ventricle fills with blood Systole ventricle or atrial contraction to eject blood from the chamber Lub Dub lub dub is caused by the slamming close of valves in the heart Systole ventricles contract sending blood out of the heart high pressure forces the AV valve to close AV valves closing cause the LUB semilunar valves are opened by high pressure blood leaving the ventricles Diastole atria and ventricle relax and fill with blood low pressure opens the AV valve Blood outside the heart causes high pressure and the semilunar valve slams shut Producing the DUB sound when the atria contracts (atrial systole) the blood is forced into the ventricle AV valve remains open and the semilunar remains closed Cardiac Output Cardiac output is the volume of blood pumped by the heart in one minute, which is equal to the produce of stroke volume and heart rate Example A typical human male has a stroke volume of 70mL per beat and a resting heart rate of 72 beats per minute. a. Calculate the cardiac output. Express your answer in liters per minute. b. Calculate the volume of blood that would be pumped in ONE DAY based upon the cardiac output. Work to Get Done! Complete Topic 2 Practice Questions (pg 11 booklet) Work on your lab write up!