* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Biology: All Inheritance Patterns WS
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
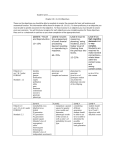
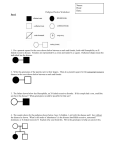
Name: _______________________________________________ Date: ______________________ Period: ________ 9) Mendel noticed that when a tall (T) plant and a short (t) plant were crossed, all the offspring were tall in height. Cross a heterozygous tall plant with a short plant. Complete the Punnett square below to support your answer. Biology: All Inheritance Patterns WS Directions: Answer the following questions and complete the Punnett Squares and Pedigree Charts. What is it? Genotypes & Phenotypes expressed Autosomal Recessive Inheritance Explains traits or disorders that are found on autosomes (chromosome pairs 1‐ 22) Ex: PKU, Cystic Fibrosis, Albinism H = Healthy = HH or Hh *Hh = Carrier (can be male or female) h = disease = hh Sex‐linked (recessive) inheritance Explains traits or disorders that are found on sex chromosomes‐ more specifically, the X (chromosome pair 23) Ex: color‐blindness, hemophilia XH = Healthy Xh = disease Males: XHY = healthy XhY = disease Females: H H X X = Healthy XHXh = Healthy (carrier) h h X X = disease Autosomal Dominant Inheritance Explains disorders that are dominant and found on autosomes (chromosome pairs 1‐ 22) Ex: Huntington’s, Achondroplasia, DMD Incomplete Dominance Explains what happens when there is a blending of traits. Ex: crossing a red flower with a white make pink. H = Disease = HH or Hh h = healthy = hh Ex: Red = RR White = WW Pink = RW Ex: Blue = BB Yellow = YY Green = BY Or you can use: D = Disease = DD or Dd D = healthy = dd *NO CARRIERS Use the following table to aid in determining genotypes for each pattern of inheritance: Autosomal Recessive Inheritance Codominance Explains what happens when neither trait is completely dominant. Ex: crossing a red flower with a white gives one with red and white spots. Ex: Blood type AB Ex: Type AB blood = AB (results from crossing Type A blood [AA or Ao] with Type B blood [BB or Bo]) a. What are the genotypes of each parent plant? ____________ b. Which trait is dominant? _____________________________ What is the probability of getting a: c. Tall pea plant? ________________ d. Hybrid pea plant? _____________ e. Purebred plant? ______________ 10) Phenylketonuria (PKU) is a recessive condition where sufferers lack an enzyme to break down phenylalanine in their diet. This condition, if left untreated, causes brain damage and retardation. Both Rita and Dexter are carriers of this disorder and do not suffer from any symptoms. Their son, however, has PKU. Complete the Punnett square and pedigree chart for all mentioned in the story). Define the following: Draw your Punnett Square below 1) Genotype: ____________________________________________________________________________________ 2) Phenotype: ___________________________________________________________________________________ 3) Punnett Square: _______________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________________ 4) Pedigree Chart: ________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________________ 5) Autosomes: ___________________________________________________________________________________ 6) Sex Chromosomes: _____________________________________________________________________________ Answer the following: b. Your father? ____________________________________________ 8) Give one example of how environment and genotype can interact. _____________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________________ Draw your pedigree chart below a. What are the phenotypes of each parent? ______________ What is the probability of getting: b. A healthy child? ________________________ c. A child who carries the disorder? ____________________ 7) a. In terms of genetic material, what do you inherit from your mother? ___________________________________ d. A child who has PKU? ____________________ e. TWO healthy children? ____________________________ f. If their child is a carrier of PKU, does this mean the child has the disorder? Explain: _____________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ Sex‐Linked Inheritance Autosomal Dominant Inheritance 11) The gene for normal blood clotting (XH) is dominant to the gene for Hemophilia (Xh), which is a sex‐linked recessive disorder found on the X‐chromosome of males and females. Marge is a healthy carrier of hemophilia and Homer is completely healthy. What would be Bart, Lisa, and Maggie’s genotypes? Complete the Punnett square and pedigree chart for all mentioned in the story. 13) Huntington’s disease (HD) is a dominant disorder where only 1 copy of a defected allele will cause the sufferer to lose brain function and eventually die. Russ and Leslie met at a HD support clinic and both contain the HD allele. However, they still want to plan a future together and what to know the chances of having a child without HD. Can you help them? Create a Punnett square and pedigree chart for all mentioned in the story. Draw your Punnett Square below Draw your pedigree chart below a. What is the genotype of Marge? ________ Homer? ________ What is the probability of getting a: b. Daughter with hemophilia? ________________________ c. Carrier? ________________________________ d. Son with hemophilia? ____________________________ e. Healthy child? ___________________________ 12) Duchene Muscular Dystrophy (DMD) is a sex‐linked recessive disorder found on the X chromosome. Sufferers with DMD (Xd) lack the protein called dystrophin. Because sufferers lack this protein, their muscle cells wear away sooner than those unaffected causing early death. Abby is homozygous recessive for DMD and Ray is healthy. They want to know, if they have a son, what his genotype will be? Create a Punnett square & pedigree chart for all mentioned in the story. Draw your Punnett Square below Draw your pedigree chart below Draw your pedigree chart below a. List the genotypes of each parent? ________________ What is the probability of getting a: b. A healthy child? _________c. A heterozygous child?________ d. A homozygous dominant child? _________ Incomplete Dominance Inheritance 14) Think about the flower color problems we previously did in class. How could one create all three flower colors at a time (red, pink, white)? Support your answer with a Punnett Square. a. What are the phenotypes of the parent flowers? __________________ What is the probability of getting: b. White flowers? __________c. Homozygous flowers? _______ d. Heterozygous flowers? ________ Codominant Inheritance a. What is the genotype of Abby? _________ Ray? _________ What is the probability of getting a: Draw your Punnett Square below b. A child with DMD? _____________ c. Girl with DMD? ____________ d. Homozygous child?_____________ e. If this couple has a boy, what are the chances that the boy will have DMD? ___________________________ 15) There are 3 alleles for blood (A, B, O). A and B are both dominant, and only O is recessive. Keva has heterozygous type B blood and Kobe has type O blood. Complete the Punnett Square below. a. What is Keva’s genotype? ____________ Kobe’s? ____________ What is the probability of getting: b. The same genotype as Keva? ______________________ c. The same phenotype as Kobe? _____________________ d. A child with codominant blood? ____________________