* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download REGENTS Review Homework
Diamond anvil cell wikipedia , lookup
Geochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Spherical Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Tectonic–climatic interaction wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Schiehallion experiment wikipedia , lookup
Milankovitch cycles wikipedia , lookup
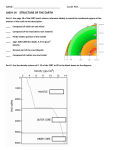
5/24/2016 Observations vs. Inferences Observations: Earth Science Regents Review seen/measured based on senses Inferences: assumption based on __________________ Density ESRT pg. ______ = mass/volume _________ density sinks ________ density floats/rises Density of water (ESRT pg. 1) = 1.0g/mL WATER IS MOST DENSE IN LIQUID FORM (4OC) Pressure ↑, Density ____ Temp. ↑, Density _____ D Earth’s Changes Cyclic Predictable Ex: 1. 2. 3. Rate of Change / Gradient Measuring Earth ESRT Earth’s RoC In pg. _____ or Gradient = Change in Values (subtract) distance or time Steep Slope/Gradient when isolines are _____________________________ shape is an ______________________ a diagram it looks like a sphere/circle ESRT pg. ____ – mass, density, & diameter Evidence of shape: sinking ships, ALTITUDE OF POLARIS = ____________________________ 1 5/24/2016 Latitude / Longitude Rotation Latitude Earth drawn left to rt.; measures above/below equator (0o) Longitude drawn up/down; join at poles; ___o each; time zones East – increase West – less ANGLE OF POLARIS = DEGREES OF LATITUDE IN NORTHERN HEMISPHERE Revolution Orbit around _________ ESRT pg. 15 Counterclockwise 365.25 days Causes __________ & seasonal constellations DO NOT CONFUSE ROTATION & REVOLUTION rotates (spins) on axis from ______ to _______ 24 hours ESRT pg. 15 Night/day; DAILY path of stars FOUCAULT PENDULUM = ROTATION CORIOLIS EFFECT = ROTATION Spheres of Earth Atmosphere – air; ESRT pages ___ & ____ – crust; ESRT pages ___, ___, & ___ Hydrosphere – water; ESRT page ___ & ___ (currents) Lithosphere Field Maps Field Map Symbols Isolines Streams – lines connection points of ____________________ Isotherm (temp.) Isobar (pressure) Contour lines (elevation) You may be asked to connect the dots & calculate the gradient (ESRT pg. 1) flow from ________ to ________; a V-shape will bend around and point in its direction Depression lines at the top of a hill, show a decrease in ________________ (volcano hole) Closer the lines = _______________________ 2 5/24/2016 Space Stars Universe _____ Solar System ______ are in the Milky Way Galaxy Sun is the ONLY STAR in our solar system ESRT pg. ____ Retrograde – planets appearing to move backwards in space when earth passes them Energy We ESRT Big Bang Theory Seasons Galaxies/planets Proof: ______ formed by an explosion Radiation Shift: moving FURTHER away _______ shift means moving closer KNOW THIS comes from ________ pg. ____; luminosity, size, color, temp. Group forms a constellation Summer Solstice: June 21st -sun rises ____ to ____; longest day Winter Solstice: December 21st -sun rises ____ to____; shortest day; closest to sun Equinoxes: March 21st & Sept. 23rd -sun rises______to _______ -equal day/night Equator always has _____ hrs. daylight KNOW THIS 3 5/24/2016 Shadows Ellipse Lower Shape altitude of sun = longer shadow shadows in __________ of earth’s _________ pg. ____ Eccentricity = dist. Btwn foci/length axis The SUN is always one foci ESRT pg. ___ Ecc. Close to ___ = circle Ecc. Close to ___ = line Longest ESRT Winds Tides Coriolis Effect: winds curve to ________ in Northern Hemisphere Winds to _______ in Southern Hemisphere Due Eclipses Insolation ________- Incoming ________ _______/rough sun, Earth, moon – sun, moon, earth to pull of ________ (earth/moon) about every ____ hours Occur Solar Radiation texture: absorbs _______/smooth: reflect 4 5/24/2016 Air Moves Air Pressure Clockwise, Pressure Out of a High Into a Low (low=left) Counterclockwise, Weather Moves to ________ in US When TEMP = ____________ Precipitation Air rises, cools, & expands Cold front: Temp. & humidity ↓, Pressure ↑ Warm front: Temp. & humidity ↑, Pressure ↓ DECREASES with increased humidity and altitude. Cool, dry = ________ Pressure Warm, humid = ________Pressure Wind results from pressure differences Named from the direction it is COMING FROM Moves from HIGH to LOW pressure ESRT pg. _____ Weather Ref. Tables ESRT pg. ____: Dew Point/Rel Humid. ****DON’T FORGET TO SUBTRACT TOP #**** ESRT pg. ___: Symbols, Thermometer, Pressure -USE a RULER to convert temp. & pressure Windward / Leeward _______________:Humid, cold, air rises, precipitation _______________:Dry, warmer air sinks Porosity Space between particles/soil porosity: -____________ Porosity -Loosely Packed -___________-Sorted SIZE DOESN’T MATTER More Particle Size 5 5/24/2016 Permeability Capillarity Ability for water to move through permeability: -_____________ particles -Unfrozen Ability for water to move ___________ capillarity: -____________ particles More Permeability More Capillarity Particle Size Particle Size Infiltration Run-Off Infiltration ________________ when: -has vegetation -unfrozen -flat ground (no slope) -unsaturated ______________ when: -no vegetation -frozen -steep slope -already saturated slope Slope vegetation Run-off Run-off Infiltration Infiltration Evapotranspiration Temp. Moderation Evaporation BODIES (water to gas/vapor) (evap. through plants) INCREASES as TEMP. ___________________ Transpiration OF WATER _____________ CLIMATE!!! Coastal cities have warmer winters & cooler summers b/c of the _____________________________________! 6 5/24/2016 Chemical Weathering Physical Weathering Changes Broken Occurs chemical make-up in _______________________climates into smaller pieces area _________, MORE WEATHERING _______________________climates FROST WEDGING -water expands when frozen and cracks rock Surface Erosion Streams Movement of weathered sediment (force) __________________- #1 AGENT OF EROSION Velocity Gravity Meanders Deposition Minerals Inside ESRT Occurs Properties stream meanders when streams meet large bodies of water -___________ particles dropped 1st -___________particles dropped LAST Water sorts particles: large on bottom/small on top ________________ with steep slope (bends) slow streams (older/flatter) Erosion on _____________ CURVES Deposition _____________ CURVES ESRT pg. ___ (particle transport & velocity) pg. ____ depend on _____________________________________ Mostly silicates (silicon & oxygen) NOT ROCKS! (they make-up rocks) 7 5/24/2016 Rocks Sedimentary ESRT Formed Igneous Metamorphic Cooling ESRT pages ___ & ___ – KNOW THESE TABLES & Solidification of ________________ Cools fast (extrusive): small/no/fine crystals -air pockets (pumice) Cools slow (intrusive): large (coarse) crystals -ex: granite MINERALS they contain are below Landscapes Arid (_____) – steep slopes & sharp angles – smooth & rounded Humid from sediments cemented together or evaporates (salts) Usually have fragments, fossils, and/or layers (_________) Change through contact metamorphism (listed on meta. Table) pg. _____ & _____ & Pressure CONTACT METAMORPHISM (bottom of table) Banded & distorted Heat Mid-Ocean Ridges New Earth being created due to convection currents in _______________________ Sea-floor spreading (Divergence) Magnetic fields reversed New – center; Old - edges ESRT pg. ____ TRENCHES are opposite – earth destroyed by subduction 8 5/24/2016 Seismic Waves P-Waves faster; travel through liquid, solid, & gas S-Waves DO NOT travel through liquid (outer core) You need _____ seismometer readings to determine epicenter ESRT pg. ____ GAP – subtract P & S arrival time & use paper to slide btwn lines for distance Plate Tectonics Convection Currents in mantle move plates 3 Types of boundaries: divergent, convergent, transform ESRT pg. ____ Mountains form by __________ Transform boundaries - earthquakes Half Life Superposition ESRT Old pg. ____ BE CHANGED – constant # Carbon-14 (5,700 yrs.) used for dating objects less than ____________ yrs. Uranium-238 for old rocks CAN’T on _________, Young on _________ of strata (layers) Intrusions & Faults are YOUNGER than the rock they cut through Contact meta. occurs w/ intrusions Index Fossils ESRT pg. ____ & _____ to date Rocks relatively Lived for _______________over a _______________________. Used 9