* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Sun - Hicksville Public Schools
Cygnus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Chinese astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Dyson sphere wikipedia , lookup
History of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Geocentric model wikipedia , lookup
Cassiopeia (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Astrophotography wikipedia , lookup
Perseus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
History of supernova observation wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
Planetary habitability wikipedia , lookup
Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
International Ultraviolet Explorer wikipedia , lookup
Observational astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Tropical year wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Corvus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Stellar kinematics wikipedia , lookup
Star formation wikipedia , lookup
Stellar evolution wikipedia , lookup
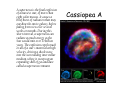
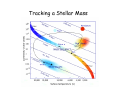
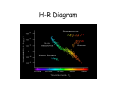
The Sun The Sun • Is by far the closest star to the Earth • Stars are luminous bodies that create their own energy through Nuclear Fusion • The Sun is an average star Nuclear Fusion • Gravity causes clouds of dust and gases in space to contract and heat until fusion begins • We use fission on earth (uranium and plutonium) which does not produce as much energy as fusion • We only can use fusion for H-bombs Sunspots • The sun contains sunspots which are temporary storms on the sun’s surface. • They provide evidence that the sun rotates once every 27 days. Before the invention of the telescope, the Sun was thought to be a perfect disk. However as soon as telescopes became available, astronomers turned them to the Sun. They discovered two things. Sunspots and blindness. Not the great scientist Galileo though, he was far too clever and sensible. He observed only at sunset and sunrise and by projecting the light onto a screen rather than trying to look through the telescope itself. He drew his results very carefully. (1612) Telescope Image of Sunspots taken from Swedish Institute of Solar Sciences Evolution of a Star Life of a Star • Stars like the sun spend most of their life on the Main Sequence. • When the Sun’s core is all fused to He, the sun will expand and become a Red Giant. • When the fuel is used up it will collapse into a White Dwarf and then a Black Dwarf • Stars more massive than the Sun will go supernova. Life Cycle of Stars Stellar Evolution A supernova is the final explosion of a massive star, of more than eight solar masses. It causes a brief burst of radiation that may outshine the entire galaxy, before fading from view over several weeks or months. During this short interval, a supernova can radiate as much energy as the Sun would emit over 10 billion years. The explosion expels much or all of a star's material at high velocity, driving a shock wave into the surrounding interstellar medium, where it sweeps up an expanding shell of gas and dust called a supernova remnant. Cassiopea A Tracking a Stellar Mass H-R Diagram Luminosity and Temperature of Stars (ESRT) Interactive HR Diagram Quesitons Questions 1. In which group are the stars most varied in both size and luminosity? • Main Sequence 2. The sun is more luminous than any stars in which group? • Dwarf 3. State one way in which the Sun and Polaris are similar and one way in which they are different. •Similar in temp. Different in luminosity 4. Why is Betelgeuse more luminous than St. Barnard’s star? •It is much larger/more massive