* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Alternating Current * Learning Outcomes
Ground (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Ground loop (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Brushed DC electric motor wikipedia , lookup
Power inverter wikipedia , lookup
Power engineering wikipedia , lookup
Pulse-width modulation wikipedia , lookup
War of the currents wikipedia , lookup
Skin effect wikipedia , lookup
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
Electric machine wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Stepper motor wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Mercury-arc valve wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Voltage regulator wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Current mirror wikipedia , lookup
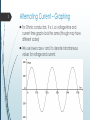
1 Alternating Current – Learning Outcomes Describe alternating current in terms of voltage and current with time. Use an oscilloscope to show a.c. Discuss the use of a.c. in the national grid. HL: Solve problems about peak and rms values of voltage and current. 2 Alternating Current While in direct current (d.c.), current always flows in the same direction (positive to negative), alternating current (a.c.) continuously changes directions. The current does not change direction abruptly – it is a gradual process of acceleration, fitting models of waves and SHM. Thus when we graph a.c. it appears as a sine wave. 3 Alternating Current – Graphing For Ohmic conductors, 𝑉 ∝ 𝐼, so voltage-time and current-time graphs look the same (though may have different scales) We use lower case v and i to denote instantaneous values for voltage and current. 4 Oscilloscopes Oscilloscopes are instruments that show the variation in electrical signals flowing through them over time. 5 National Grid As mentioned in earlier, generators generate an emf by electromagnetic induction. Due to the particular way turbines work (rotating coil in a magnetic field), the emf generated is a.c. The voltage varies from +325 V to -325 V on the mains, changing direction every 1/100 seconds (thus a full cycle takes 1/50 seconds and the frequency is 50 Hz. 6 Root-Mean-Square With d.c. we can perform calculations using a constant current and voltage. Since current and voltage vary in a.c., various formulas cannot be used normally. We use an “rms” value for a.c. voltage and current, which are given by: 𝐼𝑟𝑚𝑠 = 𝐼0 2 𝑉𝑟𝑚𝑠 = V0 2 These are effectively average values, so we can discuss average effects of a.c. over time. 7 Root-Mean-Square e.g. Domestic electricity is supplied at an rms voltage of 230 volts. Find the maximum value of the voltage in any one cycle. e.g. An alternating current flowing in a wire of resistance 10 Ω produces heat at a rate of 60 W. Find: i. the rms value of the current, ii. the peak value of the voltage across the wire. 400 turn oil has a resistance of 200 Ω and is connected to an a.c. supply. Over a 1 ms time interval the flux through the coil increases by 5 × 10-4 Wb. Find the average induced emf over the 1 ms interval. Find also the average current if the average voltage is 300 V.