* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Evolution Slides #1
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
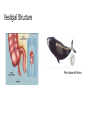
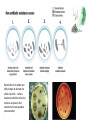
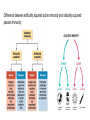
Natural Selection Variation: Heritability: Overproduction: Reproductive Advantage Driven by Environment Factors for Natural Selection: 1. Variation 2. Heritability 3. Overproduction (Overpopulation) 4. Reproductive Advantage Evidence of Evolution 1. 2. The fossil record (link between extinct and existing species… intermediates) Comparative anatomy a. Homologous structures (ancestor link) vs Analogous structures (anatomical similarity) b. Vestigial structures (kind of homologous structure… reduced forms due to lack of functional structures) 3. 4. 5. Comparative embryology (vertebrate embryos exhibit homologous structures during certain phases of development but become totally different structures in the adult forms) Comparative biochemistry (similarity of metabolic molecules and processes) Geographic distribution (similarity of species from close ancestor locations) Fossil Record Structural (anatomical) adaptation that lead to increased survival rates of species via evolution. Comparative anatomy: Homologous structures vs Analogous structures Homologous: Underlying anatomical commonalities demonstrating descent from a common ancestor. It’s when very different animals have bones that appear very similar in form or function and seem to be related. Analogous: various structures in different species having the same function but have evolved separately, thus do not share common ancestor. Homologous structures: Similar in shape and construction… example of how could be inherited form from a common ancestor with similar anatomical bone comparisons. Vestigial Structure Pelvic bone with femur Comparative embryology Comparative biochemistry Geographic Distribution Evolution intimately linked with climate and geological forces… but due to plate tectonics, species can share a close ancestor relationship from place of origin Adaptation: 1. Morphological adaptations: ● 2. Camouflage ● Mimicry Physiological adaptations: ● Antimicrobial resistance Bacteria with lots of variation and ability to adapt can decrease the effects of penicillin … bacteria resistance to antibiotics will survive, reproduce, and pass on their resistance to the next generation (natural selection) Resistance of Corn Rootworm to BT corn plants Resistance to pesticides/insecticide … Individuals with favorable variations survive and reproduce … some insects have changed genetically and are unaffected by pesticides... Origin of life on Earth Anaerobic due to lack of oxygen ➔ Prokaryotes (thought to have evolved mitochondria with oxygen use) ◆ Eukaryotes ● Invertebrates ○ Vertebrates ◆ Fishes Causes of speciation: ● ● ● ● ● Mechanical isolation… not able to sexually reproduce Behavioral isolation … ex. Mating behaviors Habitat isolation Allopatric isolation … animal populations evolved independently with unique climates/territory Changes in climate … ex. Cooler temperatures (Cretaceous period) Endangered species due to: Global warming or rapid environmental changes … not able to adapt Genetic diversity decreases Toxins (poisons) Shaping Evolutionary Theory: Evolutionary Shaping is long/slow process (due to centuries of selective changes)… With increase rate of evolutionary process in a population note signs of specific mating and eating habits. 1. Explain how some of the following evolutionary processes can occur a. Gene shuffling: b. Directional selection : increase survival rates of the animals… ex Tikaalik roseae via natural selection jointed wrists c. Natural selection (“Survival of the fittest” … ability of offspring to reproduce 1st… then amount of food an organism obtains, and ability to withstand environmental extremes) … no random mutations of genes are occurring, most members are homozygous for traits, population is above carrying capacity, little inheritable variation of traits d. Genetic drift: two new populations (wolf) … over time the presence and distribution of alleles diverge Change in allelic frequencies Directional Selection: Difference between artificially acquired active immunity and naturally acquired passive immunity: Humoral and cell mediated immunity adaptive response: Antigen = Antibody producing response 1. What are ways a thriving population of organisms are better able to survive (benefit)? 2. 3. List factors that could lead to species diversity and possibly to a new species. What is the term that is best defined as “selection of the most fit individuals based on environmental interactions?” a. Natural selection b. Artificial selection c. Selective breeding d. Acquired characteristics An increase in the rate of evolution in a population will be affected by which scenario? a. Sunlight stimulates the growth of ash leaves b. Wind blows pollen grains to nearby ash trees c. Weevils eat the larger seeds dropped by ash trees d. Migrating birds rest in ash trees on their journey south The Tiktaalik roseae fossil was recently discovered. This fossil is of a fish that lived approximately 370 million years ago. It had scales like fish. Unlike other fish fossils, this fossil has fins with jointed wrists similar to the wrist of a crocodile. Which reason is the most likely for the natural selection of this type of jointed wrist? a. Calcium buildup in bones b. Reproduction between various species c. Increased survival rates of the animals d. Sudden decreases in sea levels Scientists believe the atmosphere of early Earth was incapable of supporting aerobic organisms. Which best explains this belief? a. There was no water in the environment b. Photosynthesis was occurring too slowly c. Multicellular organisms used up the water d. Free oxygen was missing from the environment 4. 5. 6.