* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Endocrine System
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
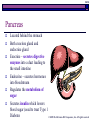
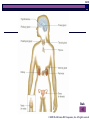
The Endocrine System © 2009 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved 34-2 How are the endocrine and nervous systems similar? The Endocrine System and the Nervous System are two communication systems for sending information to and from the brain They operate differently of course © 2009 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved 34-3 Introduction The endocrine system includes the organs of the body that secrete hormones directly into body fluids such as blood Regulates chemical reaction in cells and therefore control functions of the organs, tissues, and other cells bloodstream to Glands into secrete hormones target tissues © 2009 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved 34-4 What are hormones? 1 2 3 4 5 Chemicals secreted by a cell that affect the functions of other cells How do they affect behavior? Hormones affect the growth of bodily structures (muscles and bones), affecting what you can do physically They affect metabolic processes, influencing the amount of energy you have Certain hormones cause the differences between boys and girls Other hormones prepare the body for action during stress Hormones also act in the brain to directly influence moods and drives © 2009 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved 34-5 Hormones work like neurotransmitters in that they have a special molecular structure that match the structure of a receptor © 2009 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved 34-6 Hypothalamus Controls the pituitary gland It monitors the amount of hormones in the blood Sends out messages to correct hormonal imbalances © 2009 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved 34-7 Pituitary Gland Controlled by the hypothalamus Located at the base of the brain How does the pituitary gland act as the “Master Gland?” It secretes a large number of hormones, many of which control the output of hormones by other endocrine glands – it’s the boss of other glands Secretes the growth hormone - GH © 2009 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved 34-8 Thyroid Gland Located below the larynx (voice box) Controls how fast your body uses energy with controls your weight…metabolism Secretes the hormone thyroxine which controls the rate at which your body burns and uses energy © 2009 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved 34-9 Thyroid Gland What happens if there’s too much or too little thyroxine? Hypothyroidism – too little; become tired Hyperthyroidism – too much; overactive, lose weight and sleep © 2009 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved 34-10 Extra Parathyroid Glands Four located on the posterior surface of the thyroid gland Secrete parathyroid hormone (PTH) It’s responsible for bone growth and for regulating the calcium level in body © 2009 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved 34-11 Adrenal Glands Located on top of each kidney Becomes active when angry or scared Secretes the hormones… Epinephrine (adrenaline) Norepinephrine (noradrenaline) Same effects as sympathetic nervous system © 2009 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved 34-12 Adrenal Glands epinephrine (adrenaline) increases blood pressure, breathing rate and energy level norepinephrine (nonadrenaline) causes the heartbeat and breathing to increase; raises blood pressure Both generate the extra energy needed to handle a difficult situation Both can heighten emotions such as fear and anxiety Norepinephrine sends out a chemical that will clot blood faster just in case we get cut Glands also secrete cortical steroids – help muscles develop and cause the liver to release stored sugar when the body requires extra energy for emergencies © 2009 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved 34-13 Extra Other Hormone-Producing Organs Pineal gland Small gland Located between cerebral hemispheres Melatonin Regulates circadian rhythms May play a role in onset of puberty Thymus gland Located between lungs Thymosin Helps with immunity © 2009 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved 34-14 Pancreas Located behind the stomach Both exocrine gland and endocrine gland Exocrine – secretes digestive enzymes into a duct leading to the small intestine Endocrine – secretes hormones into bloodstream Regulates the metabolism of sugar Secretes insulin which lowers blood sugar (used to treat Type 1 Diabetes © 2009 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved 34-15 The Gonads The Ovaries Reproduction in females Secrete estrogen and progesterone Their levels vary…PMS Responsible for female sex characteristics © 2009 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved 34-16 The Gonads Testes Testosterone important in physical development of male In prenatal period, it helps decide the sex of a fetus In adolescence, it’s important for growth of muscle and bone along with the growth of male sex characteristics © 2009 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved 34-17 Hormone versus a Neurotransmitter When a chemical is used as a neurotransmitter, it is released right beside the cell that it is to excite or inhibit When a chemical is used as a hormone, it is released into the blood, which diffuses it throughout the body © 2009 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved 34-18 © 2009 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved 34-19 Back © 2009 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved