* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Current in a Series Circuit
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Immunity-aware programming wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Fault tolerance wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Two-port network wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative circuit wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Earthing system wikipedia , lookup
Network analysis (electrical circuits) wikipedia , lookup
Circuit breaker wikipedia , lookup
RLC circuit wikipedia , lookup
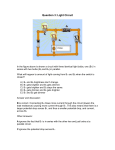
Activity 24A PS-2826 Current in a Series Circuit Electricity: current, parallel circuit Qty 1 1 1 2 Equipment and Materials PASPORT Xplorer GLX PASPORT Voltage-Current Sensor CASTLE Kit ‘D’ Cell Part Number PS-2002 PS-2115 EM-8624A PI-6602 Purpose The purpose of this activity is to determine the relationship between current and the number of light bulbs that are connected to a voltage source in a series circuit. Background Light bulbs in a series circuit are connected end-to-end like links in a chain. If light bulbs are connected in series to a voltage source, what happens to the brightness of the individual bulbs as more bulbs are added to the “chain”? What will happen to the current through the circuit as more bulbs are added to the circuit? If one bulb in a series circuit is removed, what happens to the rest of the bulbs? Preview Use a PASPORT Voltage-Current Sensor to measure the current through a series circuit that has one, two and then three light bulbs. Use the Xplorer GLX to record and display the current. Compare the current for one, two, and three light bulbs. Fig. 1: Series circuit Prediction How would the current through a series circuit change as more light bulbs are added to the circuit? Safety Precaution • Follow all directions for using the equipment. Physics with the Xplorer GLX © 2006 PASCO p. 175 Activity 24A Current in a Series Circuit PS-2826 Procedure GLX Setup 1. Connect a PASPORT Voltage-Current Sensor to a sensor port on the top of the GLX and then turn on the GLX ( ). • The GLX displays a Graph screen of Current (A) versus Time (s). 2. Press to go to the Home screen. Use the arrow keys to select Digits and press to activate your choice. 3. In the Digits screen, press to activate the measurement name. Use the arrow keys to select ‘Voltage’ and press to open the measurement name menu. 4. Select ‘Clear Input’ and press choice. Fig. 1: Select ‘Digits’ to activate your Equipment Setup 1. Put two D cells into the battery holder (from the CASTLE Kit). Put a round light bulb in each of three lamp sockets. 2. Set up a circuit with one light bulb, the Voltage-Current Sensor, and the voltage source as shown. • Be careful to connect an alligator clip to the spring as shown. 3. Leave one clip disconnected until you are ready to collect data. Fig. 2: Select ‘Clear Input’ Record Data • NOTE: The procedure is easier if one person handles the equipment and a second person handles the Xplorer GLX. Fig. 3: Equipment setup Physics with the Xplorer GLX © 2006 PASCO p. 176 Activity 24A Current in a Series Circuit PS-2826 Series Circuit: One Light Bulb 1. Connect the clip to the voltage source to complete the circuit. Observe the brightness of the bulb. 2. Press Start ( ) on the GLX to measure the signal from the Voltage-Current Sensor. 3. Record the current through the circuit in the Data Table in the Lab Report section. 4. Press to stop data recording. Disconnect the clip to the voltage source to open the circuit. Fig. 4: Record data Series Circuit: Two Light Bulbs 1. Connect a second light bulb in series with the first light bulb in the circuit. 2. Connect the clip to the voltage source to complete the circuit. Record the apparent brightness of the two bulbs. 3. Press Start ( ) on the GLX to measure the signal from the sensor. 4. Record the current through the circuit for two light bulbs in the Data Table. 5. Press to stop data recording. Disconnect the clip to the voltage source to open the circuit. Series Circuit: Three Light Bulbs 1. Connect a third light bulb in series with the other light bulbs in the circuit. 2. Connect the clip to the voltage source to complete the circuit. Record the apparent brightness of the three bulbs. 3. Press 4. Record the current through the circuit for three light bulbs in the Data Table. 5. Press to stop data recording. Disconnect the clip to the voltage source to open the circuit. Fig. 5: Two bulbs in series to measure the signal from the sensor. Analysis Examine your recorded current data and answer the questions in the Lab Report. Fig. 6: Three bulbs in series Physics with the Xplorer GLX © 2006 PASCO p. 177 Activity 24A Current in a Series Circuit PS-2826 Extension Repeat the procedure with the resistors included in the CASTLE Kit instead of light bulbs. Record your results and answer the questions in the Lab Report section. Physics with the Xplorer GLX © 2006 PASCO p. 178 Activity 24A Current in a Series Circuit PS-2826 Lab Report – Activity 24A: Current in a Series Circuit Name ________________________________ Date ___________ Prediction How would the current through a series circuit change as more light bulbs are added to the circuit? Data 1. How bright were the two light bulbs in series compared to the first light bulb? 2. How bright were the three light bulbs in series compared to the first light bulb? Data Table Item Current (A) One light bulb in series Two light bulbs in series Three light bulbs in series Questions 1. What did you notice about the brightness of each bulb in series as the second and third bulbs were added to the circuit? 2. How did the current for three light bulbs and two light bulbs in series compare to the current for one light bulb? 3. How does the current in a series circuit change as you add more light bulbs to the circuit? Physics with the Xplorer GLX © 2006 PASCO p. 179 Activity 24A 4. Current in a Series Circuit PS-2826 Do your results support your prediction? Physics with the Xplorer GLX © 2006 PASCO p. 180