* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The War to End Slavery
First Battle of Lexington wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Malvern Hill wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Hampton Roads wikipedia , lookup
East Tennessee bridge burnings wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Fort Henry wikipedia , lookup
Kentucky in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Antietam wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Roanoke Island wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Port Royal wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Island Number Ten wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Wilson's Creek wikipedia , lookup
Fort Fisher wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Fort Donelson wikipedia , lookup
Hampton Roads Conference wikipedia , lookup
Capture of New Orleans wikipedia , lookup
Battle of New Bern wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Lewis's Farm wikipedia , lookup
Second Battle of Corinth wikipedia , lookup
Ulysses S. Grant and the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Baltimore riot of 1861 wikipedia , lookup
Commemoration of the American Civil War on postage stamps wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Namozine Church wikipedia , lookup
Issues of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Economy of the Confederate States of America wikipedia , lookup
Tennessee in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Shiloh wikipedia , lookup
South Carolina in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Opposition to the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Cedar Creek wikipedia , lookup
Western Theater of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
First Battle of Bull Run wikipedia , lookup
Virginia in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
United States presidential election, 1860 wikipedia , lookup
Anaconda Plan wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Fort Pillow wikipedia , lookup
Alabama in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Conclusion of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Seven Pines wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Gaines's Mill wikipedia , lookup
Georgia in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Border states (American Civil War) wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom and the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Military history of African Americans in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
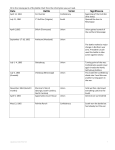
THE WAR TO END SLAVERY Learning Target: I can discuss the impact of the Civil War on Americans, including the impact based on where they live, sex, ethnicity and economic status. I-IN THE BEGINNING….. A-South said that if Abraham Lincoln won the presidential election of 1860, they would secede from the Union 1-Abraham Lincoln rand against Stephen Douglas A) Both from Illinois B) Ran against each other for US Senate in 1858 C) Had series of debates during campaign D) Put Lincoln in National spotlight eventhough Douglas won I-IN THE BEGINNING….. A-South said that if Abraham Lincoln won the presidential election of 1860, they would secede from the Union 2-Lincoln defeats Stephen Douglas Name Bell, John Breckenridge, John Douglas, Stephen Lincoln, Abraham Others Party Constitutional Union Democratic Democratic Republican Electoral Votes 39 72 12 180 0 Popular Votes 588,879 849,781 1,376,957 1,866,452 531 I-IN THE BEGINNING….. B-South Carolina secedes from the Union of Dec. 20, 1860 1-Lincoln had won the election but had not been sworn in yet, thus he was not president when S.C. secedes 2-Other states follow S.C. A) Mississippi (Jan. 9, 1861) B) Florida (Jan 10, 1861) C) Alabama (Jan 11, 1861) D) Georgia Jan. 19, 1861) E) Louisiana (Jan 26, 1861) F) Texas (Feb 23, 1861) G) Arkansas (May 6, 1861) H) North Carolina (May 20, 1861) I) Virginia (May 23, 1861) J) Tennessee (June 8, 1861) I-IN THE BEGINNING….. C-Why secede? 1-States’ rights, which were protected by the Constitution, were violated 2-North refused to enforce Fugitive Slave Laws 3-South denied equal land in new territories 4-North controlled the money 5-Slavery A) Note: Some historians claim the Civil War was fought over states’ rights, and slavery was just ONE of those rights II-THE NEW UNION A-Feb 1, 1861: Confederate States of America formed 1-Jefferson Davis elected the only president of the Confederacy B-Capitol: Moved 1-Montgomery, Alabama (until May 29, 1861) 2-Richmond, Virginia (until April 3, 1865) III-BATTLE BEGINS A-April 12, 1861: First “battle” of the Civil War 1-Confederates attack Fort Sumter, a Union post in S.C. and won A) Confederates fired the first shot B) Union soldiers did not have supplies C) Lincoln used this as a rallying point for Union togetherness D) no one killed at this battle III-BATTLE BEGINS B-Civil War becomes the first “modern” war 1-trench warfare 2-ironclad ships 3-railroads 4-telegraph 5-barbed wire 6-Gatlin gun III-BATTLE BEGINS D-Leaders of the war 1-North A-Lincoln asked Robert E. Lee to be the commanding General, but Lee declined, saying it was his duty to fight for his state (he was from Virginia) B-Had 9 leaders! 1-Winfield Scott A) Came up with Anaconda Plan 1) Called for naval blockade to shut out imports from the South 2) Plan to split up confederacy by Mississippi River 3) Both were eventually successful 2-Henry Halleck 3-Irvin McDowell 4-George McClellan 5-John Pope 6-George McClellan (again!) 7-Ambrose Burnside 8-Joseph Hooker 9-Ulysses S. Grant C-Other important Military Leaders 1-Gen. William T. Sherman 2-Gen. Benjamin F. Butler 3-Col. George A. Custer (Later promoted to General) III-BATTLE BEGINS 2-South: Robert E. Lee III-BATTLE BEGINS A-Lee’s main Generals 1-P.G.T. Beureguard 2-Nathan Bedford Forest 3-Thomas “Stonewall” Jackson 4-Joseph E. Johnston 5-Albert S. Johnston 6-J.E.B. Stuart 7- James Longstreet IV-STATISTICS A-Population 1-North: 21 million 2-South: 9 million A) 5 million whites B) 4 million slaves B-Economics 1-North A) War material industry B) Higher technology C) Buy way out of the army D) women worked in factories 2-South A) Relied on plantation farming 1) Problem selling cotton because of Union blockades B) Very little industry C) Rich did not have to fight D) Slave revolts V-BATTLE PLANS A-Neither side wanted people of African heritage to fight at first 1-North begins using freed people of African heritage Jan. 1, 1863 A) prior to that, used behind the lines as and other non-combat jobs cooks, 2-South began arming slaves shortly after the north because of a shortage of people V-BATTLE PLANS B-Battle Plan of the North 1-Blockade Confederate ports 2-Cut South in half by Mississippi River and later from Tennessee to Georgia 3-Capture Richmond (Capitol) 4-North had to win 5-Conscription Act of 1863 A) drafted all males 20-45 B) Ways out of draft 1) Pay Government $300 2) Get someone to take your place V-BATTLE PLANS C-Battle Plan of the South 1-Fight until the North wanted peace 2-continue to harass the North 3-had the brightest military minds in the U.S. 4-Conscription began in 1862 V-BATTLE PLANS D-Emancipation Proclamation changes the battle plan for the North 1-Lincoln writes it in September 1862 2-Says it will go into effect January 1, 1863 3-Says slaves in territories rebellious to the Union are now free 4-Did not free any slaves in slave states that did not leave the Union A) Kentucky B) Missouri C) Delaware D) Maryland E) West Virginia (joined U.S. June 20, 1863) V-BATTLE PLANS 5-Did not apply to any part of a Confederate State that was under the control of Union army/navy 6-Allows for African American to fight for the North 7-After the issuance of the Emancipation Proclamation, when the Union Army came through a town, slaves who were in the Confederate Army would turn and fight for the Union 8-Lincoln’s 10% Plan (1863) A) Lincoln believed that when 10% of the population of a seceded state take a loyalty oath to the US, the state should be re-admitted B) When 10% of 1860 registered voters took oath, can re-form government C) Set up “Malice toward none, charity toward all” concept D) rejected by Congress V-BATTLE PLANS 9-Wade-Davis Bill A) Proposal to re-unite the country B) Required 50% of states white male voters take loyalty oath C) Demanded stronger efforts by states to emancipate slaves D) Lincoln pocket vetoed this VI-BATTLES A-First conflict: Fort Sumpter B-First Manassas (First Battle of Bull Run) July 21, 1861 1-Union very confident 2-Civilians and politicians thought it would be an easy victory for the Union A) many from D.C. went to watch the battle like it was an athletic contest and they took picnic lunches 3-Both sides’ troops were poorly trained 4-Battle was so wild that the overran the spectators and some were killed 5-Confederates were said to have been standing like a stone wall A) leader: Gen. Thomas Jackson, who earned the nickname “Stonewall” because of this battle 6-Confederates, after being reinforced, did not know how to react to the success of winning 7-South is considered the winner of this battle VI-BATTLES VI-BATTLES C-Fort Henry/Fort Donelson (Feb-Apr 1862) 1-Gave U.S. Grant his first bit of national fame 2-took place in Tennessee 3-Easily overran Fort Henry 4-Moved to Fort Donelson A) Confederates stopped initial attack B) Grant knew they were low on supplies so he waited them out C) Grant demands Unconditional Surrender 1) Many people said the “U.S.” in U.S. Grant’s name stood for “Unconditional Surrender” VI-BATTLES D-Monitor vs. Merrimac/Virginia: March 8-9, 1862 1-First battle between ironclad ships 2-battle was a draw E-Shiloh (April 6-7, 1862) 1-begins the bloody battles the war is known for 2-Casulties A) North: 13,047 B) South: 10,699 VI-BATTLES F-Battles of the Seven Days (outside of Richmond, VA) 1-McClellan waiting to attack Lee 2-McClellan thinks he does not have enough troops to attack and defeat Lee A) McClellan had three times as many troops as Lee 3-Lee chases McClellan and the Union Army around for one week from town to town A) Fair Oaks (6/24/1862) B) Oak Grove (6/25/1862) C) Mechanicsville (6/26/1862) D) Gaine’s Mill (6/27/1862) E) Savage Station (6/29/1862) F) Glendale/Frayser’s Farm (6/30/1862) G) Malvern Hill (7/1/1862) 4-Causes Lincoln to remove McClellan as lead of the Union Arm (first time) VI-BATTLES G-Gettysburg (June 3-July 24, 1863) 1-Farthest north Confederates attacked during the Civil War A) Gettysburg is in Pennsylvania 2-South tried to stop raids on Richmond by attacking first A) felt the North would move armies from west to help out. 1) this would slow Grant down in the west 2) get reinforcements & supplies to forces in the west 3-marked the beginning of the end for the Confederacy 4-Union had better advantage because of where they were positioned A) Had positions on top of hills, which actually looked like cliffs when you are close by, but looked relatively flat from a distance B) Terrain was loaded with rocks C) As confederates got closer, there were many who were shocked at the Union’s advantage 5-Casulties A) North: 30, 100 B) South: 27,000 VI-BATTLES G-Gettysburg (June 3-July 24, 1863) 6-After the battle, the field is turned into a National Cemetery (and much later a National Park) A) Edward Everett gave the main dedication speech, Nov. 19, 1962 1) Speech lasted TWO HOURS B) Lincoln gives another speech 1) Speech lasts FOUR MINUTES 2) He felt his speech was an insult and apologized 3) Newspapers also insulted his speech 4) Today, considered one of the greatest speeches of all Time VI-BATTLES H-Antietam (Sept. 16, 1982) 1-Bloodiest one day of the Civil War 2-Casulties A) North: 12, 401 B) South: 10, 316 3-McClellan again in charge of the Army 4-Lincoln has a habit of visiting the battles close to D.C. VI-BATTLES I-Vicksburg (Dec. 26, 1862-July 4, 1863) 1-Grant tries to take Vicksburg head on and fails 2-Develops plan which could get his whole army captured A) However, plan works perfectly 3-Travels south past Vicksburg, the crosses the river 4-Takes Vicksburg from the backside 5-Has help from the Navy and Admiral David Farragut 6-Grant wins and is named General of all Union armies VI-BATTLES J-Wilderness (May 5-7, 1864) 1-First battle in the East under Gen. Grant 2-Union soldiers in the East were used to retreating under previous generals 3-Grant would not let them retreat 4-area was dense forest and think underbrush 5-casulties A) North: 17,666 B) South: 11, 125 6-showed both Lincoln, the soldiers and the North that he was there to win A) War ends 11 months later VI-BATTLES K-Sherman’s March to the Sea (Nov. 15, 1984-Dec. 21, 1864) 1-Led by Gen. William T. Sherman A) Grant’s right-hand man 2-destroyed everything from Atlanta, GA to Savannah, GA A) burned buildings B) ripped up railroad tracks and melted them until they could be bent 3-After taking Savannah, he turned north into the Carolinas to meet up with Grant A) Sent telegram to Lincoln giving him a Christmas gift of Savannah VI-BATTLES L-Surrender (April 9, 1965) 1-Lee surrenders to Grant at Appomattox Courthouse, VA 2-Conditions A) me got to keep their arms 1) Why: many were hunters B) Soldiers to go home C) Officers got to keep their swords and horses M-War still wages in small pockets in the deep South until June, 1865 N-Interesting Tidbit: The war began in the front yard of Wilbur McClean and the Surrender was signed in McClean’s home (McClean moved to get away from the war!!) VII-ARLINGTON NATIONAL CEMETERY VII-ARLINGTON NATIONAL CEMETERY VII-ARLINGTON NATIONAL CEMETERY VII-ARLINGTON NATIONAL CEMETERY VII-ARLINGTON NATIONAL CEMETERY VII-ARLINGTON NATIONAL CEMETERY VII-ARLINGTON NATIONAL CEMETERY VII-ARLINGTON NATIONAL CEMETERY