* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Electricity #2
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Electronic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Power inverter wikipedia , lookup
History of electromagnetic theory wikipedia , lookup
Ground loop (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Power engineering wikipedia , lookup
Electrification wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Ground (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Earthing system wikipedia , lookup
Overhead power line wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Semiconductor device wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Transmission tower wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Integrated circuit wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Network analysis (electrical circuits) wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
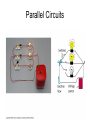
ELECTRICITY Circuits What are they? • Circuits are a path along which electricity moves Closed, series circuit Kinds of Circuits Open Closed These circuits do not have These circuits have a a complete path to follow. complete path to follow. The power cannot pass There are no openings in from the source to the the path. receiver. Light when it is turned off Light when it is turned on Kinds of Circuits Series Parallel These circuits have These circuits have more than only one path for one path for electricity to flow current to flow. through. If one light goes out If one light goes out the rest they all go out stay on Old Christmas Lights *Your house *Power lines Series Circuits Parallel Circuits Voltage • Voltage is defined as the amount of work done or the energy required in moving a unit of positive charge (1 coulomb) from a lower potential to a higher potential. Voltage is also called potential difference (PD). Current • Current is the amount of electric charge (coulombs) flowing past a specific point in a conductor over an interval of one second. 1 ampere = 1 coulomb/second = 6.24 x 1018 electrons • Electron flow is from a lower potential (voltage) to a higher potential (voltage). + e e e Wire e - Resistance Resistance •Charges passing through any conducting medium collide with the material at an extremely high rate and, thus, experience friction. Resistance •The rate at which energy is lost depends on the wire thickness (area), length and physical parameters like density and temperature as reflected through the resistively Ohm’s Law Georg Ohm • There is a simple linear relationship between voltage, current and resistance. V IR Electricity Know what it is Know the different kinds Know about the different kinds of circuits Know about conductors and insulators ElectroBoard • • • • • • Unfold and write the first matching column on the left hand side. On the right hand side, write the second matching column. Place a brad in the first hole on the left side. Locate the correct answer on the right side and place a brad in that hole. Connect the brads with a strip of aluminum foil. Tape the ENTIRE strip of foil down between each item! 9. This creates a series circuit that you can use for review. All you need to test the item is a continuity tester or a series circuit setup. SOLAR POWER