* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download DISEASEDEX™ General Medicine Summary Heart failure, chronic
Survey
Document related concepts
History of invasive and interventional cardiology wikipedia , lookup
Remote ischemic conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Jatene procedure wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
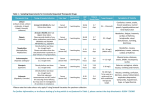
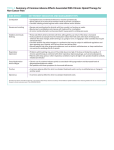
DISEASEDEX™ General Medicine Summary Heart failure, chronic; Congestive heart failure - Chronic DISEASEDEX General Medicine Clinical Review Heart failure, chronic; Congestive heart failure - Chronic (Clinical Checklist™) Definition A complex clinical syndrome resulting from any structural or functional cardiac abnormality that impairs the ability of the ventricle to fill with or eject blood Because not all patients with heart failure have volume overload at the time of the initial or subsequent evaluation, the term heart failure is preferred over the older congestive heart failure term . Medical History Infectious disease Renal failure Drug or substance use factors Coronary arteriosclerosis Hypertension [Hypertension - Chronic] Diabetes mellitus [Diabetes mellitus - Chronic] Obesity [Obesity - Chronic] Smoking Alcohol Abuse Anemia [Anemia - Chronic] Family history of Cardiomyopathy Findings Dyspnea Fatigue Peripheral edema Respiratory crackles Decreased breath sounds Orthopnea Paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea S3 gallop Jugular venous distention Hepatojugular reflux Hepatomegaly Ascites Nocturnal cough Nocturnal asthma Second heart sound split Tricuspid valve regurgitation Tachycardia Palpitations Chest pain Early satiety Nausea and vomiting Abdominal pain Cold extremities Confusion Syncope Differential Diagnosis Acute myocardial infarction - Acute Pulmonary embolism Community acquired pneumonia - Acute Asthma - Acute Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease - Chronic Pulmonary hypertension - Chronic Obstructive sleep apnea - Chronic Renal failure Liver failure - Chronic Obesity - Chronic Physical deconditioning Anemia Hypoalbuminemia Deficiency of macronutrients Anxiety Depression - Chronic Testing Suspected or known heart failure Plain chest X-ray: Radiographic findings in heart failure may include evidence of cardiac chamber enlargement, increased pulmonary venous pressure, interstitial or alveolar edema, pleural effusions, valvular or pericardial calcification, or lung disease , but a chest x-ray should not be used as a primary test for identifying the specific cardiac dysfunction associated with HF . Suspected or known heart failure 12 lead ECG: In patients with heart failure, a 12-lead ECG is frequently abnormal and may show evidence of ischemia, myocardial infarction, left ventricular hypertrophy, cardiac conduction abnormality, or cardiac arrhythmia . Suspected or known heart failure Brain natriuretic peptide measurement: Acute heart failure is likely in the presence of acute dyspnea if the B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP) level is greater than 500 picog/mL or NT-proBNP is greater than 1000 picog/mL and is unlikely if BNP is less than 100 picog/mL or NT-proBNP is less than 300 picog/mL . Although levels vary, these cut-off values may still be useful to assess decompensation of chronic heart failure . Suspected or known heart failure . Two dimensional echocardiography: All patients presenting with heart failure should receive echocardiographic evaluation of left ventricular ejection fraction, left and right ventricular size and function, ventricular wall thickness, valve function, and pericardial pathology . Suspected or known heart failure Complete blood count Magnesium measurement, serum Serum calcium measurement Blood urea nitrogen measurement Fasting blood glucose measurement Liver function tests - general Thyroid stimulating hormone measurement Fasting lipid profile Suspected or known heart failure Urinalysis: Urinalysis should be obtained in all patients presenting with acute heart failure to detect infection and assess renal function, especially if hypotension may have occurred . Suspected or known heart failure Serum potassium measurement: The target level of serum potassium in heart failure patients ranges from 4.0 to 5.5 mmol/L; hypokalemia is independently associated with increased mortality . Suspected or known heart failure Sodium measurement, serum: In heart failure, serum sodium levels below 136 mEq/L are associated with increased risk of mortality and prolonged hospitalization . Suspected or known heart failure Creatinine measurement, serum: Serum creatinine should be measured and followed closely in all patients with heart failure. Creatinine levels provide management guidance as well as prognostic information . Suspected or known heart failure Albumin measurement, serum Suspected or known acute coronary syndrome Coronary angiography: Coronary angiography assesses risk and guides therapy in high-risk acute coronary syndrome patients, especially when invasive treatment is planned . Treatment Drug Therapy First-line therapy for fluid overload and maintenance of euvolemia FUROSEMIDE Adults: Initial dose 20 to 40 mg orally daily or twice daily; up titrate as needed to obtain desired diuresis, then give determined dose daily or twice daily; maximum total daily dose 600 mg BUMETANIDE Adults: Initial dose 0.5 to 1 mg orally daily or twice daily; up titrate as needed to obtain desired diuresis, then give determined dose daily or twice daily; maximum daily dose 10 mg TORSEMIDE Adults: Initial dose 10 to 20 mg orally daily or twice daily; up titrate as needed to obtain desired diuresis, then give determined dose daily or twice daily; maximum daily dose 200 mg Heart failure with hypertension or alternative diuretic therapy for mild volume overload, or combination therapy with loop diuretics for decreased diuretic response CHLOROTHIAZIDE Adults: Initial dose 250 mg to 500 mg orally once or twice daily; maximum total daily dose 1000 mg CHLORTHALIDONE Adults: Initial dose 12.5 to 25 mg orally daily; maximum daily dose 100 mg HYDROCHLOROTHIAZIDE Adults: Initial dose 25 mg orally daily or twice daily; maximum total daily dose 200 mg METOLAZONE Adults: Initial dose 2.5 mg orally once daily; maximum daily dose 20 mg INDAPAMIDE Adults: Initial dose 2.5 mg orally once daily; maximum daily dose 5 mg Heart failure with reduced left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) or with preserved LVEF and increased cardiovascular risk CAPTOPRIL Adults: 6.25 mg orally 3 times daily; maximum 50 mg orally 3 times daily ENALAPRIL MALEATE Adults: 2.5 mg orally twice daily; maximum 10 to 20 mg twice daily LISINOPRIL Adults: 2.5 to 5 mg orally once daily; maximum 20 to 40 mg once daily PERINDOPRIL ERBUMINE Adults: Initial dose 2 mg orally once daily; maximum 8 to 16 mg once daily RAMIPRIL Adults: Initial dose 1.25 to 2.5 mg orally once daily; maximum 10 mg once daily TRANDOLAPRIL Adults: Initial dose 1 mg orally once daily; maximum 4 mg once daily FOSINOPRIL SODIUM Adults: Initial dose 5 to 10 mg orally once daily; maximum 40 mg once daily QUINAPRIL HYDROCHLORIDE Adults: Initial dose 5 mg orally twice daily; maximum 20 mg twice daily Intolerance to ACE inhibitors or in combination with ACE inhibitors for persistent symptoms CANDESARTAN CILEXETIL Adults: 4 to 8 mg orally once daily; maximum 32 mg once daily VALSARTAN Adults: 20 to 40 mg orally twice daily; maximum 160 mg twice daily LOSARTAN POTASSIUM Adults: 25 to 50 mg orally once daily; maximum 50 to 100 mg once daily Clinically stable heart failure due to reduced left ventricular systolic ejection fraction BISOPROLOL FUMARATE Adults: 1.25 mg orally once daily; maximum 10 mg once daily CARVEDILOL (Related toxicological information in CARVEDILOL) Adults: Initial dose 3.125 mg orally twice daily; maximum 25 mg twice daily (50 mg twice daily for patients over 85 kg) METOPROLOL SUCCINATE Adults (extended release tablets): Initial dose 12.5 to 25 mg orally once daily; maximum 200 mg once daily Selective use for moderate to severe symptoms of HF and decreased left ventricular ejection fraction with recent decompensation, or LV dysfunction after myocardial infarction SPIRONOLACTONE Adults: Initial dose 12.5 to 25 mg orally once daily; maximum 25 mg once or twice daily EPLERENONE Adults: Initial dose 25 mg orally once daily; maximum 50 mg once daily Mild to moderate heart failure with decreased left ventricular ejection fraction and persistent symptoms despite standard therapies or atrial fibrillation, or severe heart failure while awaiting response to standard therapies DIGOXIN (Related toxicological information in CARDIAC GLYCOSIDES) Adults: 0.125 mg to 0.25 mg orally daily; target plasma concentration 0.5 to 1 nanogram/mL Adults (over 70 years, lean body mass, or renal dysfunction): Initial dose 0.125 mg orally daily or every other day Blacks with symptomatic heart failure with decreased left ventricular ejection fraction, and consideration for non-blacks with persistent symptoms despite standard therapies Isosorbide Dinitrate / Hydralazine Adults: Initial dose 1 tablet orally three times daily; titrate upward as tolerated to maximum 2 tablets three times daily Prevention of ischemic stroke in heart failure complicated by atrial fibrillation WARFARIN SODIUM Adults: Initial dose not to exceed 5 mg orally daily ; adjust subsequent doses to achieve a target INR of 2.5 (range, 2 to 3) Procedural Therapy Acute coronary syndrome Percutaneous coronary intervention: Coronary revascularization with percutaneous coronary intervention is suitable for most high-risk patients with ST-segment elevation MI, non-ST-segment elevation MI, and unstable angina . Dyssynchronous ventricular contraction Implantation of biventricular cardiac pacemaker system Coronary artery disease Coronary artery bypass graft: CABG is the preferred revascularization strategy for most patients with significant left main coronary artery stenosis, 3-vessel coronary artery disease, and multivessel disease with treated diabetes or left ventricular dysfunction . It is appropriate in high-risk acute coronary syndrome when fibrinolysis or catheter-based treatment fails or is not indicated . Severe refractory heart failure Transplantation of heart: Although heart transplantation is the only established surgical treatment for refractory heart failure, the procedure is available to only a limited number of patients . Non-Procedural Therapy Chronic heart failure Education and Counseling Lifestyle Modification Ongoing Assessment Clinical Evaluation Laboratory Assessment and Testing Suspected or known coronary artery disease and evaluation of functional impairment Cardiovascular stress test using treadmill Coronary angiography Coronary arteriosclerosis Suspected or known coronary artery disease Radionuclide study of heart Stress echocardiography Evaluation of nutritional status Serum prealbumin level Nitrogen balance test Reassessment Laboratory Reassessment Suspected or known heart failure Serum potassium measurement: The target level of serum potassium in heart failure patients ranges from 4.0 to 5.5 mmol/L; hypokalemia is independently associated with increased mortality . Suspected or known heart failure Creatinine measurement, serum: Serum creatinine should be measured and followed closely in all patients with heart failure. Creatinine levels provide management guidance as well as prognostic information . Suspected or known heart failure . Two dimensional echocardiography: All patients presenting with heart failure should receive echocardiographic evaluation of left ventricular ejection fraction, left and right ventricular size and function, ventricular wall thickness, valve function, and pericardial pathology . Last Modified: October 27, 2010