* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Quadratic Formula
Two-body problem in general relativity wikipedia , lookup
BKL singularity wikipedia , lookup
Two-body Dirac equations wikipedia , lookup
Itô diffusion wikipedia , lookup
Differential equation wikipedia , lookup
Debye–Hückel equation wikipedia , lookup
Derivation of the Navier–Stokes equations wikipedia , lookup
Equation of state wikipedia , lookup
Partial differential equation wikipedia , lookup
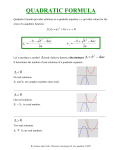
Warm-Up #50 11/1/16 1. Solve 6x2 - 24x - 36 = 0 by completing the square. 2. Write the quadratic function y = x2 + 4x - 7 in vertex form. Identify the vertex and y-intercept. Only ONE paper will be collected from each group. Solve each equation by completing the square. Completing the Square Group Practice 1. x2 + 14x = -20 2. 4x2 + 16x - 24 = 0 3. x2 + 18x - 19 = 0 Write each function in vertex form. Identify the vertex. 4. y = x2 + 6x - 7 5. y = x2 - 2x + 5 Quadratic Functions and Equations Handout Quadratic Functions and Equations Handout 1. Vertex: (2, 5); Axis of Symmetry: x = 2; Max Value at 5; 6. Vertex: (0, 0); Focus: (0, -1); Directrix: y = 1 Domain: All real numbers; Range: y ≤ 5 7. 2. 106.3 thousand units 3. Vertex: (-1, 5); Axis of Symmetry: x = -1; Max Value at 5; a. 2 Solutions: x = 0, x = 4 b. 2 Solutions: x = 3, x = -4/3 Domain: All real numbers; Range: y ≤ 5 4. y = 1.5(x - 3)2 - 9.5 5. Directrix: y = 6; y = -⅛(x + 3)2 + 4 Warm-Up #51 11/2/16 2 1. Solve 5x - 45 = 0 by finding square roots. 2. Solve x2 + 10x - 1 = 0 by completing the square. 3. Write the quadratic function y = x2 + 8x - 2 in vertex form. Identify the vertex and y-intercept. The Quadratic Formula Section 4-7 11/2/16 EQ: How can you use different ways to solve a quadratic equation 2 + + = 0, including a formula that gives values of x in terms of a, b, & c? Quadratic Equations Given ax2 + bx + c = 0, solve by completing the square. So far, we’ve talked about three different ways to solve quadratic equations. 1. Finding square roots 2. Factoring 3. Completing the square Today, we’re going to learn a fourth method: Using the Quadratic Formula Quadratic Formula The Quadratic Formula Warm-Up #52 Solve each quadratic equation using the quadratic formula. Note: One side of the equation must equal 0. Solve each quadratic equation by using the Quadratic Formula. 1. x2 - 6x - 11 = 0 4. 2x2 + 4x = 8 1. x2 + 8x + 12 = 0 2. 2x2 + 7x - 15 = 0 5. x2 + 6x = -11 2. -4x2 + 20x - 25 = 0 3. x2 + 6x + 9 = 0 6. 3n2 - 8n - 2 = 0 3. 6x2 + 3x = -10 11/3/16 Applying the Quadratic Formula: Fundraising How many solutions are there? Your school’s jazz band is selling CDs as a fundraiser. The total profit p depends on the amount x that your band charges for each CD. The equation p = -x2 + 48x - 300 models the profit of the fundraiser. What is the least amount, in dollars, you can charge for a CD to make a profit of $200? Solve your assigned problem using the Quadratic Formula. Part A has 2 real solutions A. 2x2 - 5x + 1 = 0 Part B has 1 real solution The least amount you can charge is $15.28 for each CD. The Discriminant To determine the number of real number solutions of a quadratic equation, find the value of the discriminant, b2 - 4ac, and use the following information: b2 - 4ac is positive b2 - 4ac is zero b2 - 4ac is negative 2 real solutions 1 real solution 0 real solutions Determine the number of real solutions. 7. 5x2 - 7x - 8 = 0 8. 9x2 + 24x + 16 = 0 B. x2 - 10x + 25 = 0 Part C has no real solutions C. x2 + 4x + 8 = 0 To determine the number of real number solutions, look at the discriminant: b2 - 4ac