* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Concept Questions with Answers
Anti-gravity wikipedia , lookup
Mass versus weight wikipedia , lookup
Aristotelian physics wikipedia , lookup
Newton's laws of motion wikipedia , lookup
Weightlessness wikipedia , lookup
Length contraction wikipedia , lookup
Work (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Lorentz force wikipedia , lookup
Aharonov–Bohm effect wikipedia , lookup
Potential energy wikipedia , lookup
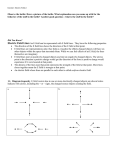
W03D2 Work, Potential Energy and Electric Potential Concept Questions with Answers 8.02 W03D2 2 Concept Question: Sign of W Concept Question Ans.: Sign of W Suppose a fixed positively charged object (charge qs > 0) is at the origin and we move a negatively charged object (charge q1 < 0) from A to B with rA < rB , where r is the distance from the origin. The work done on the negatively charged object is 1. 2. 3. 4. Answer 3: W is negative and we do a positive amount of work W is the work done by the electrical force. This is the opposite of the work that we must do in order to move a charged object in an electric field due to source. The electrical force is attractive and we are moving the positively charged object away from the source (opposite the direction of the electric field). is positive and we do a positive amount of work is positive and the electrical force does a positive amount of work is negative and we do a positive amount of work is negative and electrical force does a positive amount of work 3 4 1 Concept Question: Motion of Charged Objects Two oppositely charged are released from rest in an electric field. 1. 2. 3. 4. Concept Q. Ans.: Motion of Charged Objects 2. Both charged objects will move from higher to lower potential energy so that Both charged objects will move from lower to higher potential energy. Both charged objects will move from higher to lower potential energy. The positively charged object will move from higher to lower potential energy; the negatively charged object will move from lower to higher potential energy. The positively charged object will move from higher to lower potential energy; the negatively charged object will move from lower to higher potential energy. ΔU < 0 5 Concept Question: Motion of Charged Objects Two oppositely charged are released from rest in an electric field. 1. 2. 3. 4. 6 Concept Q. Ans.: Motion of Charged Objects Two oppositely charged are released from rest in an electric field. Both charged objects will move from lower to higher electric potential. Both charged objects will move from higher to lower electric potential. The positively charged object will move from higher to lower electric potential; the negatively charged object will move from lower to higher electric potential. The positively charged object will move from higher to lower electric potential; the negatively charged object will move from lower to higher electric potential. 3. The positively charged object will move from higher to lower electric potential; the negatively charged object will move from lower to higher electric potential. For the positively charged object: ΔV < 0 ⇒ ΔU = qΔV < 0 For the negatively charged object: ΔV > 0 ⇒ ΔU = qΔV < 0 7 8 2 Concept Question: Two Point Charges Concept Question Answer: Two Point Charges The work done in moving a positively charged object that starts from rest at infinity and ends at rest at the point P midway between two charges of magnitude +Q and –Q 1. 2. 3. 4. 3. Work from ∞ to P is zero. is positive. is negative. is zero. can not be determined – not enough info is given. 9 The potential at ∞ is zero. The potential at P is zero because equal and opposite potentials are superimposed from the two point charges (remember: V is a scalar, not a vector) 10 3