* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Grammar and Punctuation
Georgian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Symbol grounding problem wikipedia , lookup
Preposition and postposition wikipedia , lookup
Agglutination wikipedia , lookup
Kannada grammar wikipedia , lookup
Zulu grammar wikipedia , lookup
Old Irish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Arabic grammar wikipedia , lookup
Portuguese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Ojibwe grammar wikipedia , lookup
Lithuanian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Old English grammar wikipedia , lookup
Lexical semantics wikipedia , lookup
Untranslatability wikipedia , lookup
Japanese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Swedish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Modern Hebrew grammar wikipedia , lookup
Compound (linguistics) wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek grammar wikipedia , lookup
Macedonian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Chinese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Morphology (linguistics) wikipedia , lookup
Contraction (grammar) wikipedia , lookup
Sotho parts of speech wikipedia , lookup
Italian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Icelandic grammar wikipedia , lookup
French grammar wikipedia , lookup
Scottish Gaelic grammar wikipedia , lookup
Serbo-Croatian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Yiddish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Esperanto grammar wikipedia , lookup
Spanish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Latin syntax wikipedia , lookup
Polish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Pipil grammar wikipedia , lookup
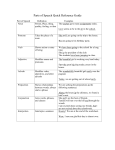
Grammar and Punctuation Grammar Adjective - A describing word that gives more meaning to a noun, e.g. two dogs, best dress. Adverb - A word that tells how, when, where or why something happened. Adverbs add meaning to verbs, adjectives and other adverbs, e.g. Daren ran quickly. She walked uphill. He will arrive soon. Antonym - A word that means the opposite of another word, e.g. hot – cold, quiet – noisy. Clause - The group of words involved with a verb. A clause is a complete message or thought. It has a subject and a verb or verb group, e.g. She played the drums. A clause may stand alone as a sentence. Compound word - A word made up of two or more words, e.g. football = foot + ball. Conjunctions and connectives - Words that join words, phrases and clauses to make more complex sentences, e.g. and, but, or, so, if, as, well, meanwhile, on the other hand Homonym - A word that has the same sound and often the same spelling as another word, but a different meaning, e.g. weak – week, no - know Nouns and noun groups - A noun is a naming word. It is the name of a person, place, feeling or thing, e.g. house, Michael, happiness, Darwin. A noun group is a group of words including noun that describes a person, place or thing, e.g. The bicycle with the rusty wheels is for sale. Object - The thing that is acted on, e.g. The man painted the chair. In some sentences, there is more than one object, e.g. She gave Jack the book. Phrase - A small group of words in a sentence or clause, e.g. She put her lunch on the bench. A phrase does not contain a verb. Preposition - A word that relates one thing or another, e.g. in, on, under, over, with, after, before, by, of. A preposition is often followed by a noun or pronoun, e.g. The box is under the bed. Pronoun - A word that stands in place of a noun, e.g. The film was long. It was boring, so we left early. Sentence - A sentence can be a question (e.g. Are you ready?), statement (e.g. I am ready.) exclamation (e.g. We are ready!) or command (e.g. Get ready.). A sentence makes sense on its own. It begins with a capital letter and ends with a full stop, question mark or exclamation mark. Speech - Direct or quoted speech uses quotation marks to show exactly what someone has said e.g., “It’s hot for sport today.” Indirect or reported speech reports what someone has sad without repeating the exact words, e.g. She said it was too hot to play sport. Subject - The thing that acts, e.g. The dog chased the stick. Syllable - A unit of sound within a word, e.g. a-maz-ing. Synonym - A word with the same or similar meaning as another word, e.g. want – desire, small – little Tense - Verbs have tense. This means they show wether something happens in the past (e.g., He ate peas), present (e.g. He is eating peas. or future (e.g. He will eat peas) Verbs and verb groups - A verb is a doing, thinking, feeling or saying word, e.g. They ran all day. She thought it might rain. He said it was ready. Verbs also describe a state of being or having, e.g. The bucket is full. Amelie had a fever. A verb is a group of words that describes something happening and includes the main verb, e.g. He is going now. She should leave now. Sue is going to leave the house. Punctuation Apostrophe (‘) - Apostrophes can show possession, e.g. Rover’s bowl. Possessive pronouns (her, his, its, theirs, ours) don’t need apostrophes. Apostrophes can also show that letters have been left out, e.g. hasn’t = has not, it’s = it is, we’ll = we will Comma (,) - Commas show short pauses in writing. They separate a string of nouns (e.g., They ate apples, oranges, pears and grapes), adjective and adverbs, (e.g., It was red, yellow, blue and gold) and different parts of speech (e.g., I meet Doug, the new boy, by the gym). Commas are also used after introductory words (e.g., By the way, it is no longer possible). Exclamation mark (!) - Exclamation marks end sentences that show a strong emotion or reaction, e.g. Wow! You really did that! Full Stop (.) - Full stops show the end of a statement or command sentence, e.g. Sam walked around the corner. Question mark (?) - A question mark is needed at the end of a question, e.g. When will his dog stop? Quotation marks (“…” or ‘…’) - Quotation marks show the exact words of a speaker (eg”I am ready now,” he said) and the title of something (e.g. He sang ‘Waltzing Matilda’). Quotation marks are sometimes called speech mark or inverted commas.