* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Settlement of Ancient Rome
Ancient Roman architecture wikipedia , lookup
Military of ancient Rome wikipedia , lookup
Constitutional reforms of Sulla wikipedia , lookup
Roman army of the late Republic wikipedia , lookup
Cursus honorum wikipedia , lookup
Promagistrate wikipedia , lookup
Roman economy wikipedia , lookup
Travel in Classical antiquity wikipedia , lookup
Education in ancient Rome wikipedia , lookup
Food and dining in the Roman Empire wikipedia , lookup
Roman historiography wikipedia , lookup
History of the Roman Constitution wikipedia , lookup
Roman Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Culture of ancient Rome wikipedia , lookup
Roman agriculture wikipedia , lookup
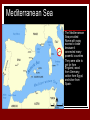
Settlement of Ancient Rome Founding The Romans had 2 different stories about how Rome was founded. It is not clear which, if either, is true. Like much of Rome’s history, the story of their settlement is laced with mythology. The Romans wrote the first history of their civilization 1000 years after the founding of the city. This document states that the date of founding was April 21, 753 B.C. Archaeological evidence supports this! The first story credits Aeneas with Rome’s founding and the second story credits Romulus and Remus. Aeneid Vergil’s Aeneid. In this epic poem, Aeneas, a Trojan prince survives the Trojan War and escapes to Italy, where he founds a new Troy, Rome. This poem is divided into XII books, telling the story of Aeneas in great detail. Romulus and Remus According to this myth, two twin boys were abandoned by their mother, thrown into the Tiber River, rescued and raised by a great she-wolf, and built opposing settlements on Rome’s hills. Remus ridiculed his brother’s work and was slain for it. Rome is named for Romulus, who became Rome’s first ruler. Why Rome? While no one knows exactly how Rome was founded or by whom, there are some environmental advantages that Rome itself has that would make it a strategic location to start a new and important city. Transportation Rome is located at the first place that people can easily cross the Tiber river, so it is the natural location of the main north-south road in Italy. The reason you can cross the Tiber at Rome is that there is an island in the river there. Salt There are also important salt flats near the city, and because salt was so valuable in the ancient world these were important to Rome’s economy. Various Environments As the Romans expanded their empire, they encountered many different environments. There were deserts, mountains, swamps, forests, and everything else. The Roman soldiers could have let this be a disadvantage because there were so many different types of terrain on which to fight. Instead, they learned how to fight in different ways in order to conquer these different areas. They had to learn to split up their big legions into small guerrilla units that would be able to get around quickly and quietly in the mountains or forest. The fact that they were able to so easily adapt to different environments was one of the reasons that the Roman Army was so successful. Mediterranean Sea The Mediterranean Sea provided Rome with easy access to trade because it connected many powerful countries They were able to get tin from England, wood from Germany, cotton from Egypt, and silver from Spain. The Great Roman Empire Rome quickly became the most powerful city of it’s time. It brought many new ideas and innovations to Law, Government, Economics, Art, Music, Literature, Military, Sports, Engineering, Architecture, Religion and Education. Even today there are Roman influences all around us