* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Respiratory System
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
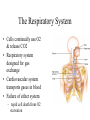
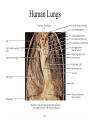
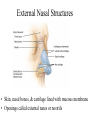
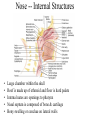
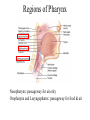
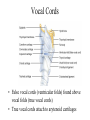
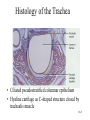
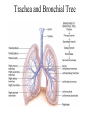
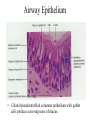
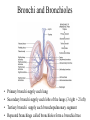
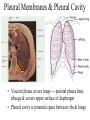
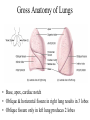
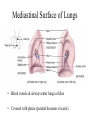
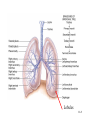
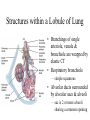
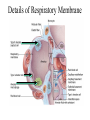
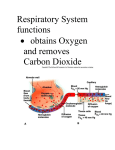
The Respiratory System • Cells continually use O2 & release CO2 • Respiratory system designed for gas exchange • Cardiovascular system transports gases in blood • Failure of either system – rapid cell death from O2 starvation Human Lungs 23-2 Respiratory System Anatomy • • • • • • • Nose Pharynx = throat Larynx = voicebox Trachea = windpipe Bronchi = airways Lungs Locations of infections – upper respiratory tract is above vocal cords – lower respiratory tract is below vocal cords External Nasal Structures • Skin, nasal bones, & cartilage lined with mucous membrane • Openings called external nares or nostrils Nose -- Internal Structures • • • • • Large chamber within the skull Roof is made up of ethmoid and floor is hard palate Internal nares are openings to pharynx Nasal septum is composed of bone & cartilage Bony swelling or conchae on lateral walls Functions of the Nasal Structures • Olfactory epithelium for sense of smell • Pseudostratified ciliated columnar with goblet cells lines nasal cavity – warms air due to high vascularity – mucous moistens air & traps dust – cilia move mucous towards pharynx • Paranasal sinuses open into nasal cavity – found in ethmoid, sphenoid, frontal & maxillary – lighten skull & resonate voice Pharynx • Muscular tube (5 inch long) hanging from skull – skeletal muscle & mucous membrane • Extends from internal nares to cricoid cartilage • Functions – passageway for food and air – resonating chamber for speech production – tonsil (lymphatic tissue) in the walls protects entryway into body • Distinct regions -- nasopharynx, oropharynx and laryngopharynx Regions of Pharynx Nasopharynx: passageway for air only Oropharynx and Laryngopharnx: passageway for food & air Cartilages of the Larynx • Thyroid cartilage forms Adam’s apple • Epiglottis---leaf-shaped piece of elastic cartilage – during swallowing, larynx moves upward – epiglottis bends to cover glottis • Cricoid cartilage---ring of cartilage attached to top of trachea • Pair of arytenoid cartilages sit upon cricoid – many muscles responsible for their movement – partially buried in vocal folds (true vocal cords) Larynx Anterior Posterior • Cartilage & connective tissue tube • Anterior to C4 to C6 • Constructed of 3 single & 3 paired cartilages Vocal Cords • False vocal cords (ventricular folds) found above vocal folds (true vocal cords) • True vocal cords attach to arytenoid cartilages Trachea • Size is 5 in long & 1in diameter • Extends from larynx to T5 anterior to the esophagus and then splits into bronchi • Layers – mucosa = pseudostratified columnar with cilia & goblet – submucosa = loose connective tissue & seromucous glands – hyaline cartilage = 16 to 20 incomplete rings • open side facing esophagus contains trachealis m. (smooth) • internal ridge on last ring called carina (cough reflex) – adventitia binds it to other organs Histology of the Trachea • Ciliated pseudostratified columnar epithelium • Hyaline cartilage as C-shaped structure closed by trachealis muscle 23-13 Trachea and Bronchial Tree Airway Epithelium • Ciliated pseudostratified columnar epithelium with goblet cells produce a moving mass of mucus. Bronchi and Bronchioles • • • • Primary bronchi supply each lung Secondary bronchi supply each lobe of the lungs (3 right + 2 left) Tertiary bronchi supply each bronchopulmonary segment Repeated branchings called bronchioles form a bronchial tree Histology of Bronchial Tree • Epithelium changes from pseudostratified ciliated columnar to nonciliated simple cuboidal, and finally to simple squamous as pass deeper into lungs • Incomplete rings of cartilage replaced by rings of smooth muscle & then connective tissue – sympathetic NS & adrenal gland release epinephrine that relaxes smooth muscle & dilates airways – asthma attack or allergic reactions constrict distal bronchiole smooth muscle Pleural Membranes & Pleural Cavity • Visceral pleura covers lungs --- parietal pleura lines ribcage & covers upper surface of diaphragm • Pleural cavity is potential space between ribs & lungs Gross Anatomy of Lungs • Base, apex, cardiac notch • Oblique & horizontal fissure in right lung results in 3 lobes • Oblique fissure only in left lung produces 2 lobes Mediastinal Surface of Lungs • Blood vessels & airways enter lungs at hilus • Covered with pleura (parietal becomes visceral) Lobules 23-21 Structures within a Lobule of Lung • Branchings of single arteriole, venule & bronchiole are wrapped by elastic CT • Respiratory bronchiole – simple squamous • Alveolar ducts surrounded by alveolar sacs & alveoli – sac is 2 or more alveoli sharing a common opening Histology of Lung Tissue Photomicrograph of lung tissue showing bronchioles, alveoli and alveolar ducts. Cells Types of the Alveoli • Type I alveolar cells – simple squamous cells where gas exchange occurs • Type II alveolar cells – free surface has microvilli – secrete alveolar fluid containing surfactant • Alveolar dust cells – wandering macrophages remove debris Alveolar-Capillary Membrane • Respiratory membrane = 1/2 micron thick • Exchange of gas from alveoli to blood • 4 Layers of membrane to cross – – – – alveolar epithelial wall of type I cells alveolar epithelial basement membrane capillary basement membrane endothelial cells of capillary • Vast surface area = handball court Details of Respiratory Membrane