* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 1.06 Guided Notes
William Flynn Martin wikipedia , lookup
Open energy system models wikipedia , lookup
Energy subsidies wikipedia , lookup
Potential energy wikipedia , lookup
100% renewable energy wikipedia , lookup
Low-Income Home Energy Assistance Program wikipedia , lookup
Energy storage wikipedia , lookup
Kinetic energy wikipedia , lookup
Public schemes for energy efficient refurbishment wikipedia , lookup
Zero-energy building wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative brake wikipedia , lookup
World energy consumption wikipedia , lookup
Low-carbon economy wikipedia , lookup
Energy Charter Treaty wikipedia , lookup
Gibbs free energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of Australia wikipedia , lookup
Alternative energy wikipedia , lookup
International Energy Agency wikipedia , lookup
Energy returned on energy invested wikipedia , lookup
Energy efficiency in transport wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Internal energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy harvesting wikipedia , lookup
Distributed generation wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of Finland wikipedia , lookup
Life-cycle greenhouse-gas emissions of energy sources wikipedia , lookup
Negawatt power wikipedia , lookup
Conservation of energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of the European Union wikipedia , lookup
Energy in the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
United States energy law wikipedia , lookup
Energy efficiency in British housing wikipedia , lookup
Energy Independence and Security Act of 2007 wikipedia , lookup
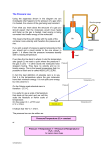
1.06 Energy and Temperature My Goals for this Lesson: Compare and contrast the various forms of energy. Identify the relationship between temperature and the movement of molecules. I’m preparing to complete a quiz on Matter and Energy Learn About different types of energy Energy is the ability to change or move matter. Energy exists in two main different forms: ____________ and _____________. _______ energy is energy of motion. _______ energy is sometimes called stored energy that can be converted to other forms of energy during chemical reactions. View the example of a ball rolling down a hill The Hoover Damm provides a real world example of both types of energy. The water that is contained behind the dam has potential energy because of its __________; it has the potential to fall. As the water flows through the dam to the lower position, the ________ energy is converted to _______ energy. Kinetic energy is the energy that a substance has because of its ________. As the water flows through the dam, its movement does work, that leads to the production of electricity. Energy conversions There are many forms of potential or kinetic energy. Energy is not __________ or __________, is only a conversion from one form to another. Water power is one of the most environmentally friendly sources of energy. Water sits above this dam as potential energy. It is drawn down a tunnel by the force of gravity. There the kinetic energy of the moving water spins blades in a turbine, which in turn spins magnets and produces electricity that is transmitted over power lines. The main forms of Energy can be classified as potential or kinetic energy. Kinetic Energy Mechanical Energy is the ______ of objects from one place to another: wheels, wind,etc. Electrical Energy is the movement of _________ charge through wires or lightning Radiant Energy is electromagnetic and travels in _____: X-rays, microwaves, etc Sound is the transfer of _______ through an object in a longitudinal wave. Thermal Energy also known as ____, due to the movement of atoms: Geothermal energy Potential Energy Stored Mechanical Energy is ______ stored in objects by the application of _____, such as a compressed spring. Chemical Energy is ______ in the bonds of atoms and molecules: Biomass, natural gas, etc. Nuclear Energy is energy stored in the _____ of an atom: fusion and fission. Gravitational Energy is the potential energy of _____: The rock resting at the top of a hill has gravitational potential energy. Measuring Energy ________ is a measure of the average kinetic energy of a substance. The _____ energy that is being measured by temperature is the ______ caused by the vibration and movement of atoms and molecules. Scientists use ___________to measure temperature, using the units _______ (also known as centigrade) or Kelvin. Converting Celsius to Kelvin If you have a temperature in Celsius (t) and need to convert it to temperature in Kelvin (T), add 273.15 to it. If you have a Kelvin temperature (T) to be changed to Celsius, subtract 273.15. T= t + 273.15 The unit for energy in the SI is Joule or Calories. 4.184 Joules = 1 Calorie