* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Respiratory System
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
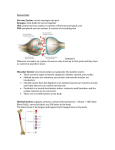
What Happens to our body when we exercise? The Respiratory System The respiratory system is one of many systems in our body. It is the first system to do with exercise. In this system is the lungs, blood and trachea. Breathing Breathing is the first process in the respiratory system. When you inhale (breathe in) oxygen enters your body, when you exhale (breathe out) carbon dioxide leaves the body. The body automatically makes us breathe all day. We breathe all day, every day for the rest of our lives. After you inhale the oxygen travels down the trachea, also known as the windpipe. Inside the trachea are tiny hairs called cilia which catch any mucus and dirt that goes down it to stop it from reaching your lungs. The diaphragm is the muscle that lets us breathe. When we inhale the diaphragm contacts and when you exhale the diaphragm relaxes. The diaphragm is placed under our lungs and if we didn’t have one we would probably die. Lungs The lungs are the main organ that helps us breathe. Our lungs are located in our chest behind the ribcage. The ribcage is connected to our spine and gives extra protection for our lungs. The lungs rest on the diaphragm. If we looked at a human lung it would be a bit squishy and would look a pinkish-red colour. Lungs are not the same size, the left lung is smaller to leave room for the heart behind it. The bronchus is where the trachea splits into two so air enters both of our lungs. The bronchus is the main tube to the lungs and the plural for bronchus is bronchi. The bronchioles are connected to the bronchus. Bronchioles are tiny hair like tubes. They get smaller and smaller as more and more bronchioles connect to each other. Inside each lung are thirty thousand bronchioles. The bronchioles allow blood to flow through our lungs. At the end of each bronchiole are tiny air sacs called alveoli. Every time you breathe in your alveoli fill with air. In both lungs the lungs are six hundred million alveoli. The alveoli lets the oxygen into the blood and carbon dioxide into the lungs. The alveoli are surrounded by capillaries. Blood Blood is the main fluid in our body and they play an important part in the respiratory system. Capillaries are tiny blood vessels that flow through your lungs. Capillaries are so thin blood needs to flow in single file through them. The oxygen from the lungs is transferred into our blood cells. Exercise When we exercise the respiratory system accelerates. The system accelerates so you get more oxygen into your body. Whilst you exercise you breathe faster and deeper. Every minute you breathe in 3 litres of air and an average amount of breaths in a minute is 50 to 100. The Circulatory System The circulatory system is the second system to do with exercise. It involves the heart, blood, blood vessels and 3 different circulatory system. Heart The heart is the main pump in the body. It is located behind the left lung and surrounded by the ribcage. The heart is located near all the main organs in our body, like our brain. The ribcage provides extra protection to our lungs & heart. It’s easier to pump blood to the upper body than it would if it was in the lower body. The size of a heart is the size of an average clenched fist. Our heart is a hollow bag so blood can go in & out of it. The heart is called the cardiac muscle and red in colour. Our heart is different to all our other muscles because the fibres in the heart have a special pattern to make the heart stronger. The heart is divided into four chambers. The left atrium receives oxygenated blood that has just been to the lungs and the right atrium receives deoxygenated blood that just went around the body and needs to go to the lungs. Our right ventricle pumps blood to the pulmonary artery and the left ventricle pumps aorta. The tricuspid valve is between the ventricle and atrium. It allows blood into the ventricle from the atrium on the right side. The valve on the left side is called the bicuspid valve. There are different types of nerves such as sympathetic nerves. Nerves can control different parts of our body. Sympathetic nerves receive impulses from the brain and tells the heart to beat. Parasympathetic nerves act as a brake for the heart and slows it down when it needs to. These nerves are part of the autonomic system which sends signals automatically. 3 Circulations There are 3 circulations in the circulatory system. There is Coronary circulation, Pulmonary circulation and systemic circulation. The coronary vessels carry our blood around the heart, it also helps with the circulation of blood around the cardiac muscle(heart). The coronary circulation helps dispose of waste. Pulmonary circulation helps get blood to and from our lungs and heart. Bronchioles circulation supplies blood to tissue of larger airways inside the lungs. Systemic circulation is the circulation of blood around the body. It supplies our bodies cells with oxygen and nutrients. It also helps take waste away. Blood Vessels There are 4 layers in arteries, the first is , The tunica adventitia. This contains blood vessels to supply oxygen and nutrients to the blood vessels. The tunica adventitia is the outer layer of the arteries and it also has nerve cells in it. The next layer is the tunica media. This is the muscular layer and it is thicker when it’s in an artery. There is higher blood pressure in arteries so there is more muscle. The tunica media is like elastic so they can pulse when the heart beats. Tunica intimia is the inner lining and made of endothial cells. The lumen has a hollow centre for the blood vessels and it is less wide than in a vein. The lumen creates a higher blood pressure. The capillaries don’t have the three layers. The capillaries have one layer of endothial cells. Veins have the same structure as arteries but still has differences. The lumen is much wider in arteries than in veins. The veins have less pressure so the tunica media is thinner. Veins also contain valves which stops blood going the wrong direction. The valves help to pool the blood and muscles help move the blood back to the heart. The veins carry deoxygenated blood into our heart. The pulmonary artery carries deoxygenated blood from the right ventricle to the lungs. The pulmonary vein carries oxygenated blood to the heart. The aorta is the largest artery in the body and it takes oxygenated blood from the right ventricle to the body. The vena cava are the largest veins in the body. The vena cava return blood from both upper & lower body to the heart. Blood Blood is an important part of the circulatory system, our blood takes heat from the busier parts of the body like our heart, brain & lungs to heat us up. The blood spreads the heat evenly around the body. There are 4 main parts in our blood. The red blood cells make our blood red and also takes up half the volume of the blood in our body. In our body there are billions of red blood cells. Our red blood cells carry oxygen to cells in our body, they also carry waste and carbon dioxide. The second cells are white blood cells. White blood cells are the biggest cell in the body, they clean our blood so we don’t get sick. The white blood cells fight diseases and germs. The third part of our blood is platelets. They are they are the smallest part in the body, but there are billions of platelets in the blood. The platelets help blood to clot so you don’t die from a little cut. Plasma is the watery substance in our blood, it makes our blood a liquid and other blood cells float in it. Plasma carries nutrients.to the bodies cells and also carries waste to the kidneys. The plasma carries body control substances like hormones, which help to regulate our bodies. Kidneys Kidneys are part of the urinary system, but are also to do with the circulatory system. The kidneys clean our blood and dispose of the waste through urine. The kidneys take physical waste from the blood and turn it to urine. Inside your body you have two kidneys, but you will survive with one. Your kidneys are located in your lower back, and if you saw kidneys they would be shaped like a bean. Inside your kidneys are one million nephrons in the cortex, they are tiny filters that clean the blood . the ureter is the tube in the kidneys that the waste trickles to the bladder. Exercise Exercise is the main thing helping our body work. When we exercise our systems accelerate and makes our heart beat faster and harder to pump blood around the body quicker. Our sympathetic nerves tells the heart to pump faster. Body cells need more oxygen and nutrients so we dispose of more waste. The Muscular System The third system to do with exercise is the muscular system. It is to do with all the muscles in our body. Types There are 3 different types of muscles voluntary, involuntary and cardiac. Voluntary or skeletal muscles are very adaptable and are used in different situations. Skeletal muscles are used for moving your body they also help to move. Skeletal muscles are connected to bones like bi-ceps, tri-ceps and our thighs and skeletal muscles move with thought. Impulses are messages that are sent from the brain to tell you to do something. Involuntary muscles or smooth muscles move without conscious thought. They are controlled by nerves which are in the autonomic system. All vital parts of our body are smooth muscles like our heart(on the inside), lungs, digesting(stomach & intestines) and we need these muscles to survive. Smooth muscles are walls of hollow structures inside the human body like our stomach. The cardiac muscle is our heart but is classified as an involuntary muscle. The heart is smooth on the inside but skeletal on the outside. Appearance Skeletal muscles take up half of the bodies weight and there are more than 640 of them in our body. They are red in colour because of all the blood in the muscle fibres. There is a layer just under the skin called the superficial layer and one deeper layer which is the second layer. Some muscles have three layers, that is called the medial layer. Skeletal muscles are different shapes and sizes but most are long and thin, some will be different shapes. Your abdominal wall is a broad and wide muscle, also shaped like flat sheets. Your gluteus maximus is the biggest muscle in our body and your thigh muscles are 30cm in length. Your smooth muscles all have smooth surfaces. Parts The skeletal muscles fibres are bundled together. Every fibre is as thin as a hair and are bound together by a connective tissue called epimysium. The fibres are divided into groups by perimysium and each fibre is made of dozens of smaller parts called fibrils. Every fibre is made of thinner threads of fibres. Each group is surrounded by blood vessels. Inside our body the big muscles have more fibres because they are bigger so they need more than the smaller muscles. The skeletal muscles are all striated or striped at a microscopic level. The tendons are the things that connect bones to muscles and there is one at the end of each muscle. Each tendon is strengthened by strong fibres of collagen. Muscles get thinner or tapers away where it is connected by a tendon and is stronger than super glue. The smooth muscles have smooth surfaces not striated. Smooth muscles are made of groups of smaller muscle cells. Smooth muscles don’t have tendons and they don’t help the body movement in our body. Smooth muscles are hollow structures of our body. The cardiac muscle has a special form of smooth and striated. It is the only place in our body with this pattern, on our heart and adjoining vessels. It is striated on the outside and smooth on the inside that helps to squeeze blood through the heart. It doesn’t use tendons because it is always moving. Movement Your skeletal muscles move with conscious thought which means it is controlled by the brain. When you think about moving, your brain sends an impulse (instruction) along nerves from the brain then the muscles moves. When muscle fibres contract, they shorten to 70% of the relaxed length. Skeletal muscles can pick up something as small as a feather to something as heavy as a table. The skeletal muscles tire easily so they need a period of rest before you use them again. The fuel it runs on is glucose or sugar so you need to keep eating sugar but not too much. Your reflexes make you react to some things nearly instantly. Our smooth muscles move without thought. They are controlled by the autonomic system. They are involved in the regulation of your internal environment. Smooth muscles contract in a gradual synchronised manner, but is much slower than skeletal muscles. They don’t tire so they work all the time. Smooth muscles are used in eyes , to make our pupils big & they regulate the size of the lumens in the blood vessels. Smooth muscles responds to stress and it changes body functions for different situations like when you’re excited. The cardiac muscle moves without thought even though it is striated. It is like a smooth muscle because it is never tired and it speeds up or down when needed. If you remove the heart it will beat for a small amount of time. Exercise When you exercise your muscles move faster. You have to think about moving faster to speed up and you would need more glucose for energy. Muscles get cramps if you use them to much. When you damage a muscle it builds because the fibres tear. When it heals it is thicker and stronger. When you exercise your heart starts to beat faster, you start to breathe faster and more blood transports around the body. Now you know how the body works with exercise. These are the main systems to do with exercise but there are other systems like the urinary system which is to do with the kidney and waste.