* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Controlling Overfishing
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
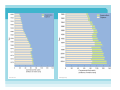
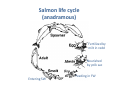
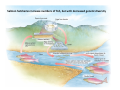
Overfishing i.e. catch exceeds replacement – changes in genetic diversity • harvesting larger specimens selective pressure for smaller animals • harvesting early in reproductive cycle selective pressure for fast maturation • surviving individuals no longer represent full genetic variability (genetic drift) increased risk of extinction Northern Elephant Seal Overfishing (continued) – changes/loss in species diversity • Extirpated (locally extinct) species cannot fulfill their ecological functions potential impact on ecosystem diversity Controlling Overfishing – Exclusive economic zones (EEZs) coastal nations control fishing within 200 miles counter-acting “Tragedy of the Commons” Controlling Overfishing (cont.) - New fisheries e.g., Alaskan Pollock (surimi) or krill as a consequence of decreasing traditional fisheries (e.g., tuna; great whales) Antarctic krill Surimi Controlling Overfishing (cont.) – Consumer education • curbing demand for endangered marine species www.oceanwise.ca • eating lower on the food chain http://www.guardian.co.uk/environment/2010/jun/ 02/un-report-meat-free-diet Other factors affecting marine fisheries – destruction/development of coastal habitats loss of feeding, breeding and nursery grounds for commercial fishes – wasteful and destructive fishing practices • inefficient use of the catch (e.g. filleting, shark finning!!) • incidental catch (a.k.a. bycatch or “trash fish”) • habitat destruction (sea floor) Trawling produces large by-catch and destroys benthic habitat Drift nets produce large by-catch and lost nets ghost fish Other factors affecting marine fisheries – aquaculture: the use of agricultural techniques to breed and raise marine organisms Aquaculture (cont.) • monoculture: only 1 species is raised • polyculture: several species are raised together • fish aquaculture: net cages vs. land-based pens • raft culture: juveniles of commercially valuable molluscs (clams, mussels, oysters) are collected and attached to ropes suspended from rafts • shrimp farming • eco-friendly aquaculture Aquaculture (cont.) Problems – Destruction of mangrove ecosystems for shrimp farms – Over-exploitation of feed fish for shrimp and salmon aquaculture – Antibiotics, pesticides, excess nutrients pollution of coastal waters – Transfer of disease (viral/bacterial)and parasites to wild stocks http://www.georgiastrait.org Case study: BC Salmon Salmon Facts • 5 species in Eastern Pacific: Chinook, Coho, Chum, Pink, Sockeye • Spawn in fresh water • Require streams that are – clear, cool, shaded, fast-running, unpolluted • One-time spawners • Spend 1-5 years in ocean • Terminal fisheries (intercepted as fish return to rivers) Salmon life cycle (anadramous) Fertilized by milt in redd Nourished by yolk sac Entering SW Feeding in FW Types of fishing vessels Purse seiner gillnetter troller BC Salmon- Issues • Overfishing • Climate change • Spawning habitat loss Bugaboo Creek clear-cut, Pt. Renfrew – Logging – Dams – Development – Pollution • Aquaculture – Introduced species – Disease transfer Sea lice Salmon hatcheries increase numbers of fish, but with decreased genetic diversity Non-Fish Marine Resources • ~ 30% world’s salt (NaCl) from ocean: evaporation ponds • Water by desalination (expensive) where necessary • Sand, gravel, chalk – dredging damages sea floor • (Minerals and methane hydrate) technological/financial/(ecological?!) restraints Not (yet) heavily exploited Methane hydrate “burning ice”