* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Circulatory System
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Artificial heart valve wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
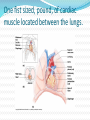
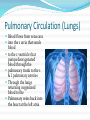
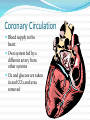
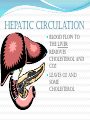
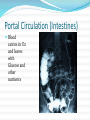
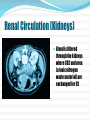
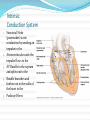
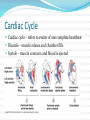
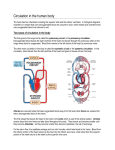
Circulatory System The heart and major blood vessels One fist sized, pound, of cardiac muscle located between the lungs. Heart walls and coverings Pericardium 2 layers of protection around the heart 1. visceral pericardium (epicardium) forms part of the wall of the heart 2. parietal pericardium loose membrane composed of dense connective tissue Heart 3 layers 1. Epicardium – connective covering 2. Myocardium - Muscle 3. Endocardium – epithelial lining Double Pump 1. Right side pumps blood to the lungs the beginning of the Pulmonary circulation 2. The left side pumps blood to the body. Systemic circulation Renal circulation Portal Circulation Hepatic Circulation Cranial Circulation Coronary Circulation Pulmonary Circulation (Lungs) Blood flows from vena cava into the r. atria that sends blood to the r. ventricle that pumps deoxygenated blood through the pulmonary trunk to the r. & l. pulmonary arteries Through the lungs returning oxygenated blood to the Pulmonary veins back into the heart at the left atria Systemic Circulation Blood flow to bones and muscles. The amount of blood depends on the need. O2 is delivered with growth hormone CO2 and urea are removed Coronary Circulation Blood supply to the heart. Own system fed by a different artery from other systems O2 and glucose are taken in and CO2 and urea removed Hepatic Circulation Blood flow to the liver Removes cholesterol and CO2 Leaves O2 and some cholesterol Portal Circulation (Intestines) Blood carries in O2 and leaves with Glucose and other nutrients Renal Circulation (Kidneys) Blood is filtered through the kidneys where CO2 and urea (a toxic nitrogen waste material) are exchanged for O2 Cranial Circulation A double system of arteries (internal carotid and vertebral) that connect to the Circle of Willis a circuit of arteries that allows blood to flow to the Dura mater in the event of a clot in any one area. Carries in O2, glucose, and cholesterol Takes out CO2 and Growth Hormone Heart Chambers 2 atria on top, thin walls, low pressure 2 ventricles below, thick walls, high pressure. Separated by the thick interartial interventricular septum The atria and ventricles separated by (AV) atrioventricular valves Inflow on the left regulated by the bicuspid (mitral) valve open during contraction Inflow on the right prevented by the tricuspid valve open during relaxation Intrinsic Conduction System 1. Sinoatrial Node 2. 3. 4. 5. (pacemaker) starts conduction by sending an impulse to the Atrioventricular node the impulse flows to the AV Bundle in the septum and splits out to the Bundle branches and further out to the walls of the heart in the Purkinje Fibers Cardiac Cycle Cardiac cycle – refers to events of one complete heartbeat Diastole – muscle relaxes and chamber fills Systole – muscle contracts and blood is ejected Heart Sounds •2 heart sounds are heard –“lub” – “dup” pause “lub” – “dup” •“lub” – is the sound of the AV valves closing •“dup” is the sound of the semilunar (mitral and tricuspid) valves closing •Abnormal sounds –Murmurs – indicate leaky valves or narrow valves –Split sounds – heart enlargement