* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download i can label an atom and draw a bohr model and label
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
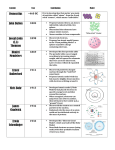
I CAN LABEL AN ATOM AND DRAW A BOHR MODEL AND LABEL THE PARTS ATOMIC THEORY The Atom ATOMS Atom comes from the Greek word atomos which means indivisible Atoms are the smallest particle that has unique properties ATOMS HAVE 3 COMPONENTS Charge Location 1. Protons p + Nucleus 2.Neutrons n 0 Nucleus 3.Electrons e - Orbit the Nucleus ATOMIC STRUCTURE Interpreting Information from the Periodic Table Atomic # Element Symbol Element Name Atomic Mass These numbers tell you a lot about atoms. Atomic number: # of protons = # of electrons # of neutrons: atomic mass – atomic number *This is the same as: # of neutrons: atomic mass – the # of protons or # of electrons Atomic # Mass Ca Ar Br p+ n0 e– Ca Atomic Atomic # Mass 20 40 p+ n0 e– 20 20 20 Ar 18 40 18 22 18 Br 35 80 35 45 35 Work on Worksheet MODELING ATOMS Bohr Diagrams Used to show electrons as they surround the nucleus of the atom STEPS TO DRAW BOHR DIAGRAM 1) Write the symbol of the element on your paper. 2) Draw in the orbits around the symbol. 3) Fill the orbits with their electrons until all of the electrons have a home. Electrons fit in orbitals 1st orbital: 2 electrons nd orbital: 8 electrons 2 3rd orbital: 8 electrons 4th & 5th orbitals: 18 electrons 6th & 7th orbitals: 32 electrons o RULES FOR BOHR DIAGRAMS lowest orbits first Put one electron on each side going clockwise before pairing Space the electrons so they are farther away from each other (equalize the force). Fill EXAMPLE 1: DRAW THE BOHR DIAGRAM FOR OXYGEN. EXAMPLE 1: DRAW THE BOHR DIAGRAM FOR OXYGEN. EXAMPLE 2: DRAW THE BOHR DIAGRAM FOR MAGNESIUM. EXAMPLE 2: DRAW THE BOHR DIAGRAM FOR MAGNESIUM. COMPLETE THE FOLLOWING 5 BOHR MODELS ON YOUR OWN TODAY’S LEARNING TARGET I can label an atom and draw a Bohr model and label the parts