* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Diversity And Classification of Flowering Plants:
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
History of herbalism wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
Diversity And Classification of
Flowering Plants:
Eudicots: Rosids
Michael G. Simpson
ROSIDS
• Very large, monophyletic group of Eudicots
• Linked by no clear non-molecular
apomorphies
• Ovules bitegmic (2 integuments) &
crassinucellate [contrast with Asterids]
• 13 orders
Brassicales
Glucosinolates - major plant secondary products in
the Brassicaceae and close relatives.
- deter herbivory and parasitism
- flavoring agents in the commercially important
members of the Brassicaceae, such as brocolli,
cauliflower, and mustard.
BRASSICALES
Brassicaceae (Cruciferae) — Mustard family
(name used by Pliny for cabbage-like plants).
365 genera / 3250 species.
herbs, rarely shrubs
glucosinolates (mustard oil glucosides)
perianth cruciate (petals usually clawed)
usually 2+4, tetradynamous stamens
gynoecium with a superior, 2- carpellate/loculate ovary
axile-parietal placentation
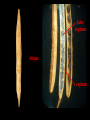
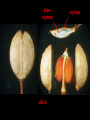
2-valved, dehiscent fruit with a replum (silique or silicle).
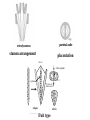
K 2+2 C 4 A 2+4 G (2), superior.
stamen arrangement
placentation
valves
replum
false septum
c.s.
replum
2 lines of
dehiscence
silique
silicle
fruit type
transverse suture
corolla
cruciate
stamens
tetradynamous
false
septum
silique
replum
false
septum
silicle
replum
The Brassicaceae have a worldwide distribution. Economic
importance includes numerous vegetable and flavoring plants
(notably the crucifers or mustard plants), including horseradish
(Armoracia rusticana), broccoli, brussels sprouts, cauliflower,
cabbage, collards, kale (all cultivars of Brassica oleracea), rutabaga
and canola oil (B. napus), mustard (B. nigra), turnip (B. rapa),
wasabi (Eutrema japonicum), radish (Raphanus sativus), and many
more; plus numerous cultivated ornamentals, dye plants (Isatis
tinctoria, woad), and some noxious weeds; Arabidopsis thalliana is
noted as a model for detailed molecular studies.
Brassica nigra
Cakile maritima
Cardamine californicum
Hirschfeldia incana
Raphanus sativus
Thysanocarpus
laciniatus
BRASSICACEAE - Mustard family
Armoracia rusticana
HORSERADISH
(L. armoracia, "horseradish" + pertaining to the country)
Part used: ROOT (more as a flavoring than a vegetable)
BRASSICACEAE - Mustard family
Brassica campestris [=B. rapa] ("of the fields")
Part used: ROOT (+ Hypocotyl)
TURNIP
[2000 BC (India); held in low esteme; turnip from English name "to
turn," appear to be turned on a lathe; First Jack O'Lantern (Irish) for All
Saints' of All Hallow's Day; Americans first used pumpkins.]
top of root somewhat flat
BRASSICACEAE - Mustard family
Brassica napus
RUTABAGA [RAPE, SWEDISH TURNIP]
(with little turnip-like root)
BRASSICACEAE - Mustard family
Brassica napus
RUTABAGA [RAPE, SWEDISH TURNIP]
Part used: ROOT (+Hypocotyl)
Pointed at upper end (but often cut off)
Cultivars selected for rape or canola oil
[Hybridization/polyploidy (2n=38) bet. cabbage (2n=18) & turnip (2n=20)]
top of root more pointed
seeds source of Canola oil
BRASSICACEAE - Mustard family
Brassica oleracea ("resembling garden cooking herbs"):
cultivated by Greeks by 650 BC; active artificial selection, many
varieties that look very different today!
BRASSICACEAE - Mustard family
Brassica oleracea v. acephala (“no head”)
Part used: LEAVES (or entire shoot)
KALE, COLLARD
BRASSICACEAE - Mustard family
Brassica oleracea v. botrytis BROCCOLI
[= B. o. v. italica] ("cluster of grapes")
Part used: FLOWERING SHOOT (flowers
fertile, can turn into inflorescence)
[Bred in Europe, mid-17th century]
BRASSICACEAE - Mustard family
Brassica oleracea v. cauliflora
CAULIFLOWER
(B. o. v. botrytis) (Gr. kaulos, "stem" + flora, flower)
Part used: FLOWERING SHOOT (Flowers abortive or immature)
[Bred by Arabians in 12th century; leaves gathered and tied around
flowers to prevent exposure to sun and therefore green color.]
BRASSICACEAE - Mustard family
Brassica oleracea v. capitata (“head”)
Part used: LEAVES (and stem of shoot)
CABBAGE
[Bred in Germany 1160 AD; both red & white (green) vars. grown.
Sauerkraut =shredded leaves & salt in earthenware crock to preserve]
BRASSICACEAE - Mustard family
Brassica oleracea v. gemmifera
BRUSSELS SPROUTS
("jewels, buds" + "bearing")
Part used: Bud-like SHOOT arising from aerial stem
BRASSICACEAE - Mustard family
Raphanus sativus
RADISH
("Greek raphanos for "quick-appearing" + "cultivated")
Part used: ROOT
In orient, long white or black-skinned forms = “DAIKONS”
[Found in Egyptian tombs, 4000 years BP]
BRASSICACEAE - Mustard family
Raphanus sativus
RADISH
Long white or black-skinned forms = DAIKONS
Daikons
Cleomaceae
K 4 C 4 A 6 G (2)
Stamens exserted, not tetradynamous
Locule 1, placentation parietal
Peritoma arborea
Cleomaceae
Cleome bassleriana