* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Human Body - Organs and Circulatory System
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
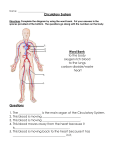
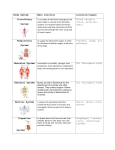
E-Day Resource E-Day Topic Resource Page Grade 2 Topic Human Body – Organs and Circulatory Systems Brief Overview/objective: To introduce the children to the intricate and amazing systems of the human body - specifically the internal organs and circulatory systems. To explore, celebrate and stand in awe of the intricate and wonderful way God created us. This unit ties to a second unit on the Human Body – the skeleton and muscles. These two units tie to a study of food, nutrition and healthy living. After completing this Enrichment Day, the students will be able to: • • • • Identify the major organs of the body and the parts of the circulatory system. Describe the skeletal system (number and makeup of bones) and list at least three major functions of the skeletal system. Describe the circulatory system of the body – Identify at least three ways to keep the heart and organs of the body healthy. Resources in workroom: • • • • • Human Body 3-ring binder- information, recipes and suggested activities ***There is a life-size skeleton for your use*** it is “stored” in a Middle School classroom… just ask… we can get it for you! The Human Body (picture cards) Human body diagram kit (located on top shelf) The human body puzzle – bones on one side, body systems on the other Posters can be found in the bottom cabinet labeled “1st-2nd Grade Resources”. Ideas to get you started: • • • • • • • • • Read and discuss the creation of Adam and Eve in Genesis 2. Read and discuss Psalm 139 and other passages about life and creation. Dissect a chicken to find skin, muscle, bones, blood vessels Outline a child on butcher paper, and add the body systems as you discuss them. Have a tasting party – divide foods into groups – salty, sweet, sour Have the class chew at least 20 times and feel the beginning process of the digestive system. Use a stethoscope to listen to the heart and lung sounds Blow into a balloon to show how lungs expand and contract Make a model of the digestive tract (1) straw for the esophagus and a balloon for the stomach, wide ribbon for the large intestines and narrow ribbon for the small intestines. (2) use food – regular and string licorice for the intestines. PERIMETER SCHOOL E-DAY RESOURCE last updated 12.4.2015 E-Day Topic Resource Page for Human Body Cardiovascular System The he cardiovascular system consists of the heart, blood vessels, and the approximately 5 liters of blood that the blood vessels transport. Responsible for transporting oxygen, nutrients, hormones, and cellular cellular waste products hardest--working organ — the heart, throughout the body, the cardiovascular system is powered by the body’s hardest which is only about the size of a closed fist. Even at rest, the average heart easily pumps over 5 liters of blood throughout the the body every minute... Cardiovascular System Anatomy The Heart The heart is a muscular pumping organ located medial to the lungs along the body’s midline in the thoracic region. The bottom tip of the heart, known as its apex, is turned to the left, so that about 2/3 of the heart is located on the body’s left side with the other 1/3 on right. The top of the heart, known as the heart’s base, connects to the great blood vessels of the body: the aorta, vena cava, pulmonary trunk, and pulmonary veins. Circulatory Loops There are 2 primary circulatory loops in the human body: the pulmonary circulation loop and the systemic circulation loop. PERIMETER SCHOOL E-DAY RESOURCE [2 of 9] last updated 12.4.2015 E-Day Topic Resource Page for Human Body 1. Pulmonary circulation transports deoxygenated blood from the right side of the heart to the lungs, where the blood picks up oxygen and returns to the left side of the heart. The pumping chambers of the heart that support the pulmonary circulation loop are the right atrium and right ventricle. 2. Systemic circulation carries highly oxygenated blood from the left side of the heart to all of the tissues of the body (with the exception of the heart and lungs). Systemic circulation removes wastes from body tissues and returns deoxygenated blood to the right side of the heart. The left atrium and left ventricle of the heart are the pumping chambers for the systemic circulation loop. Blood Vessels Blood vessels are the body’s highways that allow blood to flow quickly and efficiently from the heart to every region of the body and back again. The size of blood vessels corresponds with the amount of blood that passes through the vessel. All blood vessels contain a hollow area called the lumen through which blood is able to flow. Around the lumen is the wall of the vessel, which may be thin in the case of capillaries or very thick in the case of arteries. PERIMETER SCHOOL E-DAY RESOURCE [3 of 9] last updated 12.4.2015 E-Day Topic Resource Page for Human Body PERIMETER SCHOOL E-DAY RESOURCE [4 of 9] last updated 12.4.2015 E-Day Topic Resource Page for Human Body Organs of the Human Body There are more than 22 organs in the human body. This is a list of the ten most vital organs which is usually taught about in elementary school: Brain The brain is the controller of your body, and stores information, allows you to think and learn, as well as controls vital daily functions, like digestion, heart rate, and breathing. The brain receives impulses from your nerves, which are located throughout your body and respond to pain and other stimulation. Even though the brain is so important, it is also very delicate. The brain is PERIMETER SCHOOL E-DAY RESOURCE [5 of 9] last updated 12.4.2015 E-Day Topic Resource Page for Human Body made of soft tissue and is protected only by the skull, which is why head injuries can be so serious. The average adult brain weighs 3 pounds. Heart The heart is another vital organ. The heart's job is to pump oxygenated blood throughout your body and receive deoxygenated blood back in return. Without your heart, your other organs would not receive oxygen or have carbon dioxide removed. In an average lifetime, the heart beats more than 2.5 million times! Kidneys The kidneys are located under the ribcage in your lower back. The job of the kidneys is to filter things like water and salts out of your blood and to produce urine. The kidneys also produce an enzyme called renin. This enzyme plays a big role in regulating your blood pressure. Did you know that a healthy person is able to live with only kidney? Liver The liver is located in the upper abdomen, slightly more to the left side. The main job of the liver is to produce bile, which it sends to the stomach for digestion. The liver also filters out toxins and regulates blood sugar. Blood sugar is regulated because the liver converts sugars and stores them, releasing them when more sugar is needed in the blood. The liver is also in charge of releasing cholesterol, breaking down fats, and producing blood proteins. It is the largest internal organ! PERIMETER SCHOOL E-DAY RESOURCE [6 of 9] last updated 12.4.2015 E-Day Topic Resource Page for Human Body Pancreas The pancreas is located in the abdomen, behind the stomach. The job of the pancreas is to produce enzymes necessary for digestion and send them to the stomach. The pancreas also regulates blood sugar and does this through its process of creating insulin. The pancreas also creates glucagon which has the opposite effect of insulin and also helps to maintain blood sugar levels. Stomach The stomach receives food from the esophagus and sends it into the small intenstine. The stomach's role in digestion is to break down food and mix it with digestive juices or enzymes. Small Intenstine The job of the small intenstine is to digest food. It does this using chemicals, such as emzymes. The small intenstine also absorbs nutrients from the food through villi and gives these nutrients to your blood. The small intenstine is 5 meters long! The food moves from your small intenstine to your large intenstine with a series of muscle contractions. Large Intestine The large intenstine is located in your abdomen and is 1.5 meters in length! The large intenstine is involved in digestion, and receives undigested food from the small intenstine. The large intenstine then absorbs as much water as possible and then expels the waste and any excess fiber. Lungs The lungs are located in your chest and are protected by your rib cage. The lungs take in oxygen which goes into the blood through the heart, and expels carbon dioxide as the heart receives unoxygenated blood. PERIMETER SCHOOL E-DAY RESOURCE [7 of 9] last updated 12.4.2015 E-Day Topic Resource Page for Human Body Skin The skin is the largest organ in the human body. Its main job is to maintain the body's temperature, which means that sweat is created to cool the body, and goosebumps or raised hair occur to trap heat in the body. Along with sweat glands, the skin contains oil glands. The oil your skin releases helps to keep your skin from drying out and your hair from becoming brittle. The skin also regularly sheds cells to maintain its effectiveness. If you can imagine, there are about 19 million skin cells in every square inch of the human body! PERIMETER SCHOOL E-DAY RESOURCE [8 of 9] last updated 12.4.2015 E-Day Topic Resource Page for Human Body Websites for Practice There are lots of great websites on the Internet to help increase your understanding of the body's organs, as well as help you to practice learning and remembering them. These are my favorites: BBC Science Interactive Body: This game is like a giant jigsaw puzzle of the organs in the human body. It has a list of organs in the human body which you click on and drag it to the right place in the body, rotating if necessary. There are also a number of interesting facts for each organ. All Systems Go!: This game is a puzzle as well. A picture of a character named Arnold is shown, along with his missing organs. You have to place the organs back in his body in the correct place. If you put an organ in the wrong place, all of the organs fall out of his body and you have to start again! This list of organs in the human body and these practice sites will help you learn how your body works and help you ace your test at the same time. PERIMETER SCHOOL E-DAY RESOURCE [9 of 9] last updated 12.4.2015