* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Development of the Cardiovascular System
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Turner syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Aortic stenosis wikipedia , lookup
Atrial septal defect wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
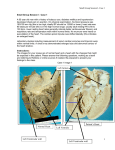
Development of the circulation system 陳建榮 http://web.nchu.edu.tw/pweb/users/chenjr/ Midgut development of animals Normal development of circulation system -Early Events -Migration of cardiogenic mesenchyme -Differentiation of mesenchyme -Chamber formation -Folding of the heart tube -Critical Changes -Vascular Changes Migration of cardiogenic mesenchyme 血管母細胞索 血管母細胞索 Differentiation of mesenchyme The early heart is a simple tube which commences beating during the third week (Day 21-22). Cardiogenic mesenchyme differentiates into three distinct cell populations: -Endocardium 心內膜 -Myocardium 心肌 -Epicardium 心外膜 Cell Population Endocardium Myocardium Epicardium Functions and Fates Endothelial lining Connective tissue precursor (Valves and fibrous skeleton) Myocytes Conduction system (Purkinje fibres) Myoendocrine cells (Atrial Natriuretic Factor production) Coronary vessel precursors Visceral pericardial lining SA node, AV node mesoderm Early heart chambers Sinus venosus (SV) 靜脈竇 This is the collecting compartment of the heart. Oxygenated blood from the placenta and deoxygenated blood from embryonic tissues are mixed in the sinus. Primitive atrium (PA) 心房原基 This is the compartment destined for further partition to the definitive atria. Primitive ventricle (PV) 心室原基 This is the compartment destined for further partition to the definitive ventricles. Bulbus cordis (BC) 心球 This will contribute to the pulmonary trunk and aorta, along with the truncus arteriosus. Truncus arteriosus (TA) 動脈幹 This will contribute to the aortic arches. Fibrous skeleton (FS) 纖維骨架 This is the area of connective tissue proliferation, site of future valves. Folding of the heart tube Apoptosis in the dorsal mesocardium will allow movement of the early heart tube within the pericardial cavity Ant. Post. Normal development of Heart -Early Events -Critical Changes -Endocardial cushion(心內墊) growth and fusion -Bulboventricular looping 動脈球心室環 -Interatrial septum(心房間隔) formation -Interventricular septum(心室間隔) formation -Aortico-pulmonary septum(主肺動脈隔) formation -Vascular Changes Endocardial cushion心內墊 fusion Endocardial cushions are areas of the fibrous skeleton forming between the atrium and ventricle. Endocardial cushions serve two important functions: -form a partition in the heart tube between the atrium (PA) and ventricle (PV) (tricuspid and bicuspid valves) -provide a "scaffold" of the interatrial septae and the interventricular septum Defects in endocardial cushion fusion are associated with trisomies 18 and 21 (Down's syndrome). Clinical problems Valvular atresia 房室瓣閉鎖 Valvular atresias arise from the uneven partition of the AV canal. Depending on the size and position of the narrowed channel, a tricuspid atresia or a biscuspid atresia results. Atresias arising from anomalous partition of the canal are referred to as congenital atresias The folding of the heart tube brings the inflow and outflow trunks in an adjacent position at the superior aspect of the developing heart. The dorsal fold forms the two pericardial sinuses and places the fibrous skeleton in a single plane Inflow and outflow trunks are positioned posteriorly as a result of the dorsal fold Bulboventricular loop動脈球心室環 Bulboventricular looping動脈球心室環 BV looping is a consequence of several changes: - Dorsal folding The first dorsal fold forms an expanded primitive ventricle, referred to as the bulboventricular loop. - Ventricular growth Differential growth of the proximal ventricular tissue causes a counter-clockwise rotation of the folded heart tube. The site of ventricular growth marks the future left ventricle. Abnormal growth of the distal primitive ventricle causes clockwise rotation, an anomaly known as dextrocardia心偏右. - AV canal房室管 partitioning The Atrio-Ventricular (AV) canal between the primitive atrium and ventricle has now been partitioned by the fusing endocardial cushions. - Shunting of venous return The development of the venous system causes an increase in right-sided venous return to the primitive atrium. Combined with the partitioning of the AV canal, the change in blood flow volume and directions assists in the outgrowth of the left ventricle. Dextrocardia 心偏右 Clinical problems Looping anomalies(dextrocardia心偏右) Bulboventricular looping動脈球心室環 BV looping is a consequence of several changes: - Dorsal folding The first dorsal fold forms an expanded primitive ventricle, referred to as the bulboventricular loop. - Ventricular growth Differential growth of the proximal ventricular tissue causes a counter-clockwise rotation of the folded heart tube. The site of ventricular growth marks the future left ventricle. Abnormal growth of the distal primitive ventricle causes clockwise rotation, an anomaly known as dextrocardia心偏右. - AV canal房室管 partitioning The Atrio-Ventricular (AV) canal between the primitive atrium and ventricle has now been partitioned by the fusing endocardial cushions. - Shunting of venous return The development of the venous system causes an increase in right-sided venous return to the primitive atrium. Combined with the partitioning of the AV canal, the change in blood flow volume and directions assists in the outgrowth of the left ventricle. Interatrial septum formation Blue arrows - direction of growth; Red arrow - direction of blood flow; ECC - endocardial cushion; RA - right atrium; LA - left atrium. 原隔 原孔 次孔 次隔 Fossa ovalis卵圓窩 Clinical problems Atrial septal defects心房間隔缺損 (ASD) Atrial septal defects (ASD) are fairly common, present in 10-15% of patients with congenital cardiac anomalies. It is more commonly observed in females than males (2-3:1). Atrium septum defects (ASD) Formation of left atrium Interventricular septum formation 球狀脊 AP - aorticopulmonary主肺動脈幹; ECC - endocardial cushion心肉墊; Blue arrow - direction of bulbar ridge growth; Red arrow - direction of ventricular growth IVS Part Origin muscular ventricular wall membranous fused bulbar ridges 球狀脊 fused endocardial cushions 球狀脊 室間孔 Clinical problems Ventricular septal defects心室間隔缺損(VSD) Atrioventricular septum defect房室瓣缺損 Aortico-pulmonary septum formation The aortico-pulmonary (AP) septum主肺動脈間隔arises within the truncus arteriosus. The septum results from the downwards growth and fusion of bulbar ridges, induced by invasion of neural crest cells. The AP septum serves to divide the ventricular outflow between the pulmonary artery and the ascending aorta 球狀脊 Semilunar valve半月瓣 Clinical problems Aortic stenosis and atresia動脈瓣膜狹窄、閉鎖 Tetralogy of Fallot (法樂氏四重畸形 ) The tetralogy of Fallot results from the asymmetric division of the AP septum. The result is a stenosed pulmonary artery and a VSD. Tetralogy of fallot: -Pulmonary valve stenosis -Ventricular septal defect -Overriding aorta -Hypertrophy of right ventricle Eisenmenger's syndrome(森曼格綜合症) Characteristics of Eisenmenger's syndrome: -persistent truncus arteriosus -ventricular septal defect -left-right ventricular shunt -right ventricle hypertrophy Normal development of Heart -Early Events -Critical Changes -Vascular Changes -Overview of embryonic circulatory system -Venous development -Arterial development -Anatomical correlations Overview of embryonic circulatory system Venous system development Venous system development Clinical problems Persistent left superior vena cava Arterial system development Aortic arch derivation: -1st pair of aortic arches: maxillary a. -2nd pair of aortic arches: stapedial a. -3rd pair of aortic arches: common carotid a. and int. carotid a. -4th pair of aortic arches: -Left aortic arch -Right subclavian a. -5th pair of aortic arches: -6th pair of aortic arches: -Left left pulmonary a., ductus arteriosus -Right right pulmonary a. Aortic arch derivatives 動脈韌帶 動脈導管 Aortic arch derivatives 動脈韌帶 動脈導管 Recurrent laryngeal n. and 6th aortic arch Clinical problems Anomalies of aortic arch Double aortic arch Normal Right arch of aorta Anomalies of right subclavian artery Clinical problems Right arch of aorta Double aortic arch雙主動脈弓 Anomalies of right subclavian artery Anatomical correlations Portacaval shunt門脈分流 = portasystemic shunt Clinical problems Porto-systemic (porta-cava) shunt Intrahepatic porto-systemic shunt Extrahepatic porto-systemic shunt Ductus arteriosus動脈導管 Persistent Ductus arteriosus Patent ductus arteriosus Blue-pulmonary trunk; Red-aorta and tributaries; Green-patent ductus arteriosus PDA Closure Device Surgery Embryologic Structure Adult Equivalent Left anterior cardinal vein disappears proximally distal portion contributes to Left superior intercostal vein anastomoses with Right anterior cardinal vein distally to form Left brachiocephalic vein Left common cardinal vein oblique vein of left atrium Left posterior cardinal vein disappears Left horn of sinus venosus coronary sinus Right anterior cardinal vein superior vena cava Right common cardinal vein superior vena cava Right posterior cardinal vein azygous vein Primitive atrium right auricle Foramen ovale fossa ovalis and limbus First aortic arch maxillary artery contribution to external carotid artery Second aortic arch persists dorsally as stapedial artery Third aortic arch proximal portions form common carotid artery distal portions form internal carotid artery Fourth aortic arch left arch (with aortic sac) forms ascending aorta and arch right arch contributes to right subclavian artery Fifth aortic arch does not persist Sixth aortic arch proximal left arch - left pulmonary artery distal left arch - ligamentum arteriosum proximal right arch - right pulmonary artery distal right arch - does not persist Ductus venosus ligamentum venosum Left umbilical vein ligamentum teres distally degenerates proximally portion within septum transversum contributes to hepatic portal system Right umbilical vein degenerates proximally and distally portion within septum transversum contributes to hepatic portal system Left vitelline vein fuses with right vitelline vein to form portal vein Right vitelline vein fuses with left vitelline vein to form portal vein Development of lymphatic system Lymph sac淋巴囊 -2 jugular lymph sac頸淋巴囊 -1 retroperitoneal lymph sac腹膜後淋巴囊 -1 cisterna chyli乳糜池 -2 iliac lymph sac髂淋巴囊