* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Tools of Geometry
Duality (projective geometry) wikipedia , lookup
History of geometry wikipedia , lookup
Multilateration wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Integer triangle wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
Pythagorean theorem wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Line (geometry) wikipedia , lookup
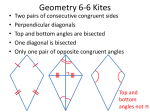
Name _______________________________________ Date ___________________ Class __________________ Tools of Geometry Module 1 Choose the best answer. Refer to the figure for Exercises 1 and 2. 1. Which represents the name of the ray whose endpoint is K and that passes through R? A RK C KS B KT D RK 2. In the diagram, how many different rays have endpoint R? F 1 H 3 G 2 J 4 8. What is the next letter in the sequence? D, H, L, P, . . . F Q H S G R J T 9. Which is the counterexample that proves the conjecture false? “If two rays have the same endpoint, then they are opposite rays.” A C B D Refer to the figure for Exercises 3 and 4. 3. What is MP? A 1 C 4 B 2 D 5 4. What is LP? F 7.5 H 2.5 G 2.5 J 7.5 5. An angle whose measure is 70° is what type of angle? A acute C obtuse B right D straight 6. GJ bisects FGH, mFGJ (7x 9)°, and mHGJ (2x 36)°. What is mFGH? F 43° H 86° G 54° J 108° 7. An angle measuring 22° is bisected. What is the measure of the angles that are formed? A 11° C 33° B 22° D 44° 10. Identify the hypothesis of the conditional statement “Two angles are complementary if the sum of their measures is 90 degrees.” F if G Two angles are complementary H the sum of their measures is 90 degrees J Two angles are complementary if the sum of their measures is 90 degrees. 11. Which conditional statement has the same truth value as this statement? “The sum of two odd numbers is even.” A If two even numbers are added, then their sum is even. B If an even and odd number are added, then their sum is even. C If two even numbers are multiplied, then their product is odd. D If two odd numbers are multiplied, then their product is even. © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company Holt McDougal Analytic Geometry Name _______________________________________ Date ___________________ Class __________________ Tools of Geometry Use the figure for Exercises 12–15. 18. Find the next item in the pattern. 2, 5, 8, 11, 14, . . . ________________________________________ 12. Name a line. 19. Show that the conjecture is false by finding a counterexample. When the letters i and e appear next to each other in a word, the letter i always comes before the letter e. ____________________________________ ________________________________________ 13. Name a segment on line n. ____________________________________ 14. Name a ray with endpoint A. 20. Identify the hypothesis and conclusion of the statement “If it is raining, then there are clouds in the sky.” ________________________________________ ____________________________________ ________________________________________ 15. Name the intersection of BC and AB. ________________________________________ ____________________________________ 16. Z is in the interior of WXY. If mWXZ 110°, and mZXY 20°, what is mWXY? 21. Given: If Lewis earns a scholarship, he can go to college. Lewis earns a scholarship. Conjecture: Lewis can go to college. Determine whether the conjecture is valid by the Law of Detachment. ____________________________________ 17. A and B are complementary. mA 29. Find mB. ________________________________________ ____________________________________ © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company Holt McDougal Analytic Geometry Name _______________________________________ Date ___________________ Class __________________ Algebraic and Geometric Proofs Module 2 Choose the best answer. 1. Consider the related biconditional statement for the conditional statement “If Shelly lives in Texas, then she lives in the United States.” Which of the following statements is true about the related biconditional statement? A The biconditional is true because the conditional is true. B The biconditional is false because the conditional and its converse are false. C The biconditional is true because the conditional and its converse are true. D The biconditional is false because the converse of the conditional is false. 2. If r 14 9, what justifies r 23? F Transitive Property of Equality G Subtraction Property of Equality 4. If 5 2k, what justifies 2k 5? F Multiplication Property of Equality G Division Property of Equality H Symmetric Property of Equality J Reflexive Property of Equality 5. Which completes the statement? If 6x 5 and d 6x, then ______ by the Transitive Property of Equality. A d5 B x 5 6 C 6x d D x d 6 6. Which completes the statement? If RS GH, then ______ by the Symmetric Property of Congruence. F RS GH H GH RS G RS RS J RS GH 7. Given: L bisects KM ; M bisects LN. Prove: KL MN H Symmetric Property of Equality J Reflexive Property of Equality x 1 8, what justifies 2 x 1 16? 3. If A Subtraction Property of Equality B Division Property of Equality Proof: Since L bisects KM and M bisects LN, by definition of bisect, KL LM and LM MN. Then, by the ? , KL MN. Finally, KL MN by the definition of congruent segments.Which completes the proof? C Transitive Property of Equality A Common Segments Theorem D Multiplication Property of Equality B Transitive Property of Congruence C Segment Addition Postulate D Symmetric Property of Congruence © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company Holt McDougal Analytic Geometry Name _______________________________________ Date ___________________ Class __________________ Algebraic and Geometric Proofs 8. Given: 1 4 Prove: 2 3 Proof: 11. Complete the sentence “A _________ is any statement that you can prove.” Statements Reasons 1. 1 4 1. Given 2. 1 and 2 are supp., and 3 and 4 are supp. 2. Lin. Pairs Thm. 3. 2 3 3. ________________________________________ 12. What is the reason for Step 2? Statements Reasons 1. 1 2 and 2 3. 1. Given 2. m1 m2 and m2 m3. 2. F Transitive Property of Congruence 3. m1 m3 3. Trans. Prop. of G Vertical Angles Theorem 4. 1 3 4. Def. of s ? Which completes the proof? H Congruent Supplements Theorem J Angle Addition Postulate 9. For the following statement, what is the “Prove” statement? If ABCD is a rhombus, then it is a parallelogram. ? ________________________________________ ________________________________________ 13. The box is part of a flowchart proof. Identify the statement. A ABCD is a quadrilateral. B ABCD is a rhombus. C ABCD is a parallelogram. D ABCD is not a square. 10. Use the Reflexive Property of Congruence to complete the statement “A ________.” ________________________________________ ________________________________________ 14. Write True or False. A paragraph proof is less formal than a two-column proof, so you do not need to include every step. ________________________________________ © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company Holt McDougal Analytic Geometry Name _______________________________________ Date ___________________ Class __________________ Proving Theorems about Lines and Angles Module 3 Choose the best answer. 6. What is the value of x? Refer to the figure for Exercises 1–3. 1. Which segment is perpendicular to DE ? A AB C DF B CF D EF F 35 H 15 G 20 J 12.5 7. Which could you use to show that u || v? 2. Which segment is parallel to BE ? F AB H CF G BC J DF 3. Which segment is NOT skew to DF ? A 1 and 8 are supplementary. B 4 and 8 are supplementary. A AB C BC C 3 and 7 are congruent. B AC D BE D 7 and 8 are congruent. Refer to the figure for Exercises 4–5. 8. Why is m n? F If two coplanar lines are perpendicular to the same line, then the two lines are parallel to each other. 4. Which pair of angles are corresponding angles? F 1 and 4 H 2 and 5 G 6 and 8 J 8 and 7 5. Which pair of angles are alternate exterior angles? A 4 and 8 C 3 and 7 B 2 and 5 D 1 and 4 G If two parallel lines are cut by a transversal, then the pairs of sameside interior angles are supplementary. H In a plane, if a transversal is perpendicular to one of two parallel lines, then it is perpendicular to the other line. J If two intersecting lines form a linear pair of congruent angles, then the lines are perpendicular. Proving Theorems about Lines and Angles 9. Identify a pair of parallel segments. ________________________________________ 10. Write True or False. Parallel lines intersect. ________________________________________ 11. How many angles are formed by two lines and a transversal? ________________________________________ 15. Given r s. What is the measure of 1? ________________________________________ 16. Write True or False. You can use the measures of the angles formed by two lines and a transversal to determine whether the two lines are parallel. ________________________________________ 17. If 2 8, then r s by which theorem? 12. What is the name given to the angle pair 3 and 5? ________________________________________ ________________________________________ 13. If parallel lines are intersected by a transversal, how many pairs of corresponding angles are there? ________________________________________ 14. Complete the sentence. If a transversal intersects parallel lines and an obtuse angle is formed, all the obtuse angles are ________. 18. If two coplanar lines are cut by a transversal so that right angles are formed, how many different angle measures are there? ________________________________________ 19. Name the shortest segment from C to AB. ________________________________________ ________________________________________ Congruence and Triangles Module 4 Choose the best answer. 1. The polygon Q(3, 2), R(6, 5), S(6, 2) undergoes the transformation: (x, y) (4x, 4y). Name the coordinates of the image points. A Q'(3, 2), R'(6, 5), S'(6, 2) B Q'(7, 6), R'(10, 9), S'(10, 6) 7. What is the value of x if the acute angles of a right triangle measure 8x and 12x? A 4.5 C 9 B 5 D 10 8. In the figure, PQR UVW. What is mR? C Q'(12, 8), R'(24, 20), S'(24, 8) D Q'(–1, –2), R'(2, 1), S'(2, –2) 2. The angles of a triangle measure 4, 86, and 90. Which classification of the triangle is correct? F acute H obtuse G equiangular J right 3. Which could be the angle measures of an acute triangle? A 32-56-92 C 34-56-90 B 33-58-91 D 35-56-89 4. What is the length of the longest side of the triangle? F 8.5 H 19 G 26 J 40 F 42 H 88 G 72 J 92 9. If KMQ WJR, which segment is congruent to RW ? A KM C QK B MQ D JW 10. Which angle is congruent to Z if ZLV SPN ? F V H N G S J P 11. If ABC KJC, which statement is NOT necessarily true? 5. What is mW ? A 35 C 70 A ACB KCJ C JC BC B 40.3 D 81 B J B 6. Two angles of a triangle measure 22 and 53. What is the measure of the third angle? D JK BC 12. Suppose S N, J I, A T, JS IN, JA IT , and AS TN. Which is true? F 15 H 75 F JSA ITN H JSA INT G 25 J 105 G JSA NTI J JSA TNI Congruence and Triangles 13. The transformation M: (x, y) (0.5x, 0.5y) has been applied to the polygon KLM. If the point M had coordinates (4, 4), name the coordinates of the image of M. ________________________________________ 20. If KLM RST, what is the value of x? ________________________________________ 14. Is the polygon K(5, 4), L(5, 6), M(7, 6) congruent to the polygon N(4, 3), P(4, 5), Q(6, 5)? ________________________________________ Use the figure for Exercises 15 and 16. ________________________________________ 21. Complete the statement. Two triangles are congruent if and only if their _______ angles and sides are congruent. ________________________________________ Use the figure for Exercises 22 and 23. 15. Classify the triangle by its angle measures. ________________________________________ 22. What value of x proves ABC DEF by SAS? 16. Classify the triangle by its side lengths. ________________________________________ 17. Complete the sentence. All of the angles in an equilateral triangle measure _________. ________________________________________ 18. What is the measure of 1? _________________________________ 23. If AB DE , what additional congruence statement is needed to prove ABC DEF by SSS? _________________________________ Use the figure for Exercises 24 and 25. 24. Write True or False. You can use AAS to prove ABE CDE. ________________________________________ 19. Given: GHJ NOP. What is the value of x? ________________________________________ 25. What additional congruence statement is needed to prove ABE CDE by HL? Module 1 Quiz 1. C 2. G 3. C 4. J 5. A 6. J 7. A 8. J 9. C 10 H. 11. A 12. Possible answers: BC, CB, or line n 13. BC or CB 14. AD 15. point B 16. 130° 17. 61° 18. 17 19. Possible answer: receive 20. Hypothesis: It is raining. Conclusion: There are clouds in the sky. 21. valid Module 2 Quiz 1. D 2. G 3. D 4. H 5. A 6. H 7. B 8. H 9. C 10. ÐA 11. theorem 12. Def. of s 13. mA mB 180 14. False Module 3 Quiz 1. D 2. H 3. B 4. G 5. A 6. G 7. C 8. J 9. Sample answer: AB and DC 10. False 11. eight 12. alternate interior angles 13. four 14. congruent 15. 135° 16. True 17. Conv. of the Alt. Ext. s Thm. 18. one 19. CA Module 4 Quiz 1. C 2. J 3. D 4. J 5. D 6. J 7. A 8. G 9. C 10. G 11. D 12. H 13. M9(2,2) 14.yes 15. acute 16. isosceles 17. 60° 18. 45° 19. 35 20. 5 21. corresponding 22. 6 23. AC DF 24. True 25. EC EA