* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit Three Worksheet – Meteorology/Oceanography – 2
Survey
Document related concepts
Lockheed WC-130 wikipedia , lookup
Tectonic–climatic interaction wikipedia , lookup
Atmosphere of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Air well (condenser) wikipedia , lookup
Severe weather wikipedia , lookup
El Niño–Southern Oscillation wikipedia , lookup
Cold-air damming wikipedia , lookup
Pangean megamonsoon wikipedia , lookup
Weather lore wikipedia , lookup
Atmospheric convection wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
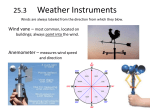
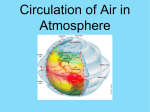
Unit Three Worksheet – Meteorology/Oceanography – 2 WS – GE – U3 – 2 Name_________________________________________________ Period__________________ Section 17.3 Multiple Choice. Select the answer that best completes the statement and write the letter for that answer in the space provided. _______1. Of the following, which is NOT a factor that controls temperature? (A) altitude (B) cloud cover (C) latitude (D) longitude (E) ocean currents _______2. The temperature differences seen between Quito, Equador and Guayaquil, Ecuador illustrate the effect of ___. (A) altitude (C) geographic position (B) cloud cover (D) ocean currents (land vs. proximity to water) _______3. The temperature differences seen between Vancouver, Canada and Winnipeg, Canada illustrate the effect of ___. (A) altitude (C) geographic position (B) cloud cover (D) ocean currents (land vs. proximity to water) _______4. The temperature differences seen between New York City, New York and Eureka, California illustrate the effect of ___. (A) altitude (C) geographic position (B) cloud cover (D) ocean currents (land vs. proximity to water) _______5. The temperature differences seen between Spokane, Washington and Seattle, Washington illustrate the effect of ___. (A) altitude (C) geographic position (B) cloud cover (D) ocean currents (land vs. proximity to water) _______6. ___ causes clouds to reflect a portion of sunlight back to space. (A) Albedo (B) Refraction (C) Solarity (D) Temperature recreation _______7. In general, temperatures at high altitudes tend to be ___ temperatures at lower altitudes if at the same latitude. (A) higher than (B) lower than (C) the same as _______8. Which of the following is a general trend on a world isothermal map? (A) Temperatures increase from the tropics toward the poles. (B) Temperatures decrease from the tropics toward the poles. (C) Temperatures decrease from east to west. (D) Temperatures increase from east to west. Short Answer. Answer the following questions. 9. How do the heating of land and water differ? page 1 – WS – GE – U3 – 2 10. Why do some coastal cities experience a moderation of temperature from water while others do not? Section 19.1 Matching. Match the definition with the term that best correlates to it. No definition will be used more than once. _____11. Air pressure A) _____12. Barometer _____13. Coriolis effect B) C) D) _____14. Jet stream E) The force exerted by the weight of a column of air above a given point Amount of pressure change occurring over a given distance Swift, high-altitude winds Apparent deflective force of Earth’s rotation on all freemoving objects, including the oceans and atmosphere Technology that measures atmospheric pressure _____15. Pressure gradient Multiple Choice. Select the answer that best completes the statement and write the letter for that answer in the space provided. _______16. In a mercury barometer, when air pressure increases, the mercury in the tube ___. (A) falls (B) falls, then rises (C) rises (D) rises, then falls _______17. Which of the following is a difference between a mercury barometer and an aneroid barometer? (A) The mercury barometer is smaller. (B) The mercury barometer can provide a continuous record of pressure changes. (C) The aneroid barometer is not as portable. (D) The aneroid barometer does not use mercury to measure pressure changes. _______18. What is the most significant source of energy for most wind? (A) air pressure (C) changes in humidity (B) air temperature (D) solar radiation _______19. Which of the following is true about air pressure acting on an object? (A) The amount pushing down on the object will gradually decrease with time. (B) The amount pushing up on the object with gradually increase with time. (C) There is more air pressure pushing up on the object than there is pushing down. (D) There is just as much air pressure pushing up as there is pushing down on the object. page 2 – WS – GE – U3 – 2 _______20. The pressure differences that make wind happen are caused ___. (A) by a sudden drop in humidity (B) when water vapor in the air rises then falls (C) by accumulations of clouds in different areas (D) by the unequal heating of Earth’s surface _______21. On a weather map, what do isobars placed close together indicate? (A) a steep pressure gradient and high winds (B) a steep pressure gradient and weak winds (C) a weak pressure gradient and high winds (D) no pressure gradient and therefore no winds _______22. What are the most prominent features of airflow above the friction layer? (A) jet streams (C) right-deflected winds (B) vertically-moving winds (D) left-deflected winds Short Answer. Answer the following question. 23. How are isobars related to pressure gradients? What three factors combine to control wind? 24. _______________________________________________________________________ 25. _______________________________________________________________________ 26. _______________________________________________________________________ Complete the following table. Factors That Affect Wind Factor Ultimate Cause Effect on Wind 28. Pressure Differences Unequal heating of Earth’s surface by the sun 29. 27. Coriolis Effect page 3 – WS – GE – U3 – 2 Factors That Affect Wind Factor Factor Factor 31. 30. Friction Section 19.2 Matching. Match the definition with the term that best correlates to it. No definition will be used more than once. _____32. Anticyclone A) _____33. Cyclone _____34. Monsoon B) C) _____35. Polar easterlies D) _____36. Polar front E) _____37. Trade winds F) _____38. Westerlies G) Multiple Choice. The dominant west-to-east motion of the atmosphere that characterizes the regions on the poleward side of the subtropical highs Winds that blow from the polar high toward the subpolar low Stormy frontal zone separating cold air masses of polar origin from warm air masses of tropical origin Seasonal reversal of wind direction associated with large continents High-pressure center characterized by a clockwise flow of air in the Northern Hemisphere Low-pressure center characterizes by a counterclockwise flow of air in the Northern Hemisphere Two belts of winds that blow almost constantly from easterly directions and are located on the north and south sides of the subtropical highs Select the answer that best completes the statement and write the letter for that answer in the space provided. _______39. Pressure decreases from the outer isobars toward the center in ___. (A) anticyclones (B) cyclones (C) jet streams (D) polar fronts _______40. Because of the Coriolis effect, wind in the Southern Hemisphere ___. (A) is deflected to the left (B) is deflected to the right (C) rises higher into the atmosphere (D) sinks lower into the atmosphere _______41. In the Northern Hemisphere, pressure gradients and the Coriolis effect applied to lowpressure centers produce winds that blow ___. (A) outward and clockwise (B) outward and counterclockwise (C) inward and clockwise (D) inward and counterclockwise page 4 – WS – GE – U3 – 2 _______42. The effect of friction on the net flow of air around cyclones is that is causes air to flow ___. (A) inward in the Northern Hemisphere (B) outward in the Southern Hemisphere (C) inward in either hemisphere (D) outward in either hemisphere _______43. The atmosphere balances the unequal heating of Earth’s surface by moving ___. (A) cool air toward high latitudes and warm air toward the equator (B) warm air toward high latitudes and cool air toward the equator (C) cool air toward the east and warm air toward the west (D) warm air toward the east and cool air toward the west _______44. Weather in the United States is moved by the westerlies in a(n) ___. (A) east to west direction across the continent (B) northwest to southeast direction across the continent (C) west to east direction across the continent (D) southeast to northwest direction across the continent Matching. Match the letter in the figure at right with the corresponding part of the global circulation model. _____45. Northeast trade winds _____46. Southeast trade winds _____47. Polar easterlies _____48. Equatorial low _____49. Westerlies _____50. Subpolar low _____51. Subtropical high Short Answer. Answer the following questions. 52. How does friction control the net flow of air around a cyclone and an anticyclone? 53. Why do weather reports always emphasize cyclones and anticyclones? page 5 – WS – GE – U3 – 2 54. What must happen in the air above for divergence at the surface to be maintained, and what type of pressure center accompanies surface divergence? Section 19.3 Matching. Match the definition with the term that best correlates to it. No definition will be used more than once. _____55. Anemometer A) B) _____56. El Niño C) _____57. Prevailing wind Multiple Choice. _______58. Technology used to determine wind speed Wind that consistently blows from one direction more than from another Periodic warming of the ocean that occurs in the central and eastern Pacific and can cause extreme weather in many parts of the world Select the answer that best completes the statement and write the letter for that answer in the space provided. How often does El Niño occur? (A) about every other year (B) every 10 years (C) about every 2 to 3 years (D) about every 3 to 7 years _______59. Which of the following best describes a La Niña? (A) Unusually long El Niño event (C) Cause of an El Niño event (B) Opposite of El Niño event (D) Its effects are localized, not global. _______60. Local winds are caused by either topographic effects or by variations in ___. (A) temperature (C) air pressure (B) surface composition (D) the Coriolis effect _______61. Which of the following is the initial major effect of an El Niño? (A) Cold nutrient-rich offshore waters are replaced by warm equatorial waters. (B) Warm nutrient-rich equatorial waters are replaced by cold offshore waters. (C) Cold offshore waters are replaced by warm nutrient-rich equatorial waters. (D) Warm offshore waters are replaced by cold equatorial waters. _______62. According to researchers, how is a La Niña event triggered? (A) by warmer than average surface temperatures in the eastern Pacific (B) by colder than average surface temperatures in the eastern Pacific (C) by warmer than average coastal water temperatures in the eastern Pacific (D) by colder than average coastal water temperatures in the eastern Pacific _______63. When is a land breeze most likely to occur? (A) morning (B) noon (C) late afternoon page 6 – WS – GE – U3 – 2 (D) night _______64. A gentle wind covering less that one hundred kilometers is called ___. (A) a jet stream (C) a breeze (B) the doldrums (D) a trade wind _______65. A sea breeze is most intense ___. (A) during mid- to late-afternoon (B) in the late morning (C) late in the evening (D) at sunrise Short Answer. Answer the following questions. 66. On a camping trip on the Oregon coast, you decide to hike to the ocean, but you are not sure of the direction. The time is 4:00 P.M. How might the breeze help you find the ocean? Why? 67. Describe the general movement of weather in the United States. What two factors mainly influence global precipitation? 68. _________________________________________________________________________ 69. _________________________________________________________________________ page 7 – WS – GE – U3 – 2