* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Study Guide for Week 29 CCA 1. E _v_o l_u_t i_o_n_, or change
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
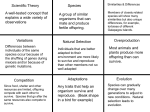
Study Guide for Week 29 CCA 1. E _v_o l_u_t i_o_n_, or change over time, is the process by which modern organisms have descended from ancient organisms 2. A scientific T h_e_o_r y_ is a well-supported, testable explanation of phenomena that have occurred in the natural world. 3. C h_a_r l_e_s __ D a_r_w i_n__ was an English naturalist who made numerous observations during his travels on the B e_a_g_l_e_ which led him to pose a hypothesis about how life changes over time. 4. F o_s_s i_l_s__ are the preserved remains of ancient organisms that provide evidence for how life has changed over time. 5. Any inherited characteristic that increases an organism’s chance of survival, like webbed feet, sharp claws, or speed, is called an _A_d a_p_t a_t_i o_n__. 6. The process whereby individuals that are better suited to their environment survive and reproduce more successfully is called N a_t_u r_a_l___ S e_l_e c_t_i o_n__ , which Darwin nicknamed S u_r_v i_v_a l__ O f__ T h_e__ F i_t_t e_s_t__. 7. Structures that have different mature forms but develop from the same embryonic tissues are called H o_m_o l_o_g o_u_s__ S t_r_u c_t_u r_e_s__. 8. Choosing to breed cows that produce the most milk or horses that are the fastest is termed S e_l_e c_t_i v_e__ B r_e_e d_i_n g__. 9. Charles Darwin’s observations of finches and turtles on the G a_l_a p_a_g o_s_ Islands led to his Theory of E v_o_l u_t_i o_n__. 10. Even though the Galapagos finches share a common ancestor, they have evolved to fit the ecosystems of their individual islands. This is an example of D a_r_w i_n_i a_n__ evolution. WORD BANK: May be used more than once Adaptation Beagle Darwinian Evolution Galapagos Homologous Structures Selective Breeding Survival of the Fittest Charles Darwin Fossils Natural Selection Theory Above is a map of the Galapagos Islands and some of the tortoises that live there. Tortoises eat plants (herbivores.) On one island, plants grow higher off the ground. Which island do you think this is? Isabela Island Hood Island EXPLAIN your answer. Why did you choose the island you did? ____ I chose Hood Island because the population of tortoises on that island have variations (better adapted) for a longer neck. The vegetation the tortoises eat on the Hood Island grows higher off the ground than the normal tortoise can reach allowing the longer necked tortoises to get all the food they need to survive and reproduce the longer necked tortoises.___ Name the steps in natural selection: __overproduction____________: far more tortoises are produced than can survive __variation_________________: members of the same species have different lengths of necks due to mutations __competition/selection_______: the longer necked (variation) tortoises are better adapted to survive to reach the more of the available food __reproduction______________: the better adapted tortoises are able to reproduce passing along to offspring the new successful longer neck trait Adaptations: Match the definition to the vocabulary term below: 1. __c___ Structural Adaptation 2. __b___ Behavioral Adaptation 3. __e___ Physiological Adaptation 4. __a___ Mimicry 5. __d___ Camouflage a. Looking like something dangerous to avoid i. being eaten b. How an organism acts that makes it better i. able to survive in its environment c. How an organism looks or is built that enables i. it to survive in its environment d. Blending into the surroundings to avoid i. detection (getting eaten!) e. A particular way an organisms’ body works i. that allows it to survive in its ii. environment Types of Adaptations: Complete the chart. Use the phrase/word list below. Structural Physiological Hollow bones Webbed feet Gills in fish Xylem in plants Body shape Birds beak shape Building a web Regulation of blood flow Regulation of body temp Bird flying Hibernation Water holding frog Producing/spitting venom Behavioral Moving in herds Migration Playing dead Nocturnal Finding shelter Squirrel gathering food PHASE/WORD LIST building a web migration squirrel gathering food body shape bird flying moving in herds playing dead webbed feet birds beak shape hibernation regulation of blood flow nocturnal gills in fish camouflage water holding frog hollow bones finding shelter xylem in plants regulation of body temperature producing/spitting venom Mendel’s Genetics: One of the traits of pea plants that Mendel observed was seed shape. The seeds were either round or wrinkled. Mendel observed that round seed shape (R) was dominate to wrinkled shape (r). Complete the punnett square to show the possible offspring of two heterozygous pea plants. Then answer the questions that follow. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. RR Rr Rr rr What two forms of the trait for seed shape did Mendel observe? __round and wrinkled________________ What was the phenotype for seed shape of both parent plants? ____Round_________________________ What percentage of the possible types of offspring had the same genotype as the parents? __50%________ What percentage of the possible types of offspring were homozygous? _____________50%_____________ What percentage of the possible types of offspring had the same phenotypes as the parents? ___75%_____ Complete the Venn Diagram for Asexual and Sexual Reproduction. Use the word list below. Asexual Reproduction Both Sexual Reproduction Diverse offspring Uniform offspring 1 parent Uniform offspring Siblings are exact copies Offspring are created DNA passes from parent(s) to offspring 2 parents Diverse offspring Siblings are not exact copies Exact copy of parent Not identical to parent No sex cells Requires sex cells (egg & sperm) Use the following ANSWER BANK to fill in Venn Diagram above: Offspring are created DNA passes from parent(s) to offspring 1 parent 2 parents Diverse offspring Uniform offspring Exact copy of parent Not identical to parent Siblings are not exact copies Siblings are exact copies Requires sex cells (egg & sperm) No sex cells (egg & sperm) Short Answer Questions: 1. What is selective breeding? __the process of selecting a few organisms with desired traits to serve as parents of the next generation__________________________________________ 2. Explain what an inherited trait is and give an example. __A physical characteristic that can be passed down from parent to child through our DNA such as our eye color_____. 3. Explain what an acquired trait is and give an example. __A physical or behavioral trait that we learn, decide to do, or a tradition we have. An example would be piercing our ears/getting a tatoo.