* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Schematic Diagrams - Oregon State EECS
Mechanical filter wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Electrical engineering wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Signal-flow graph wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Electronic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Circuit breaker wikipedia , lookup
Flexible electronics wikipedia , lookup
Ground loop (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Earthing system wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Fault tolerance wikipedia , lookup
Integrated circuit wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
RLC circuit wikipedia , lookup
Printed circuit board wikipedia , lookup
National Electrical Code wikipedia , lookup
Electrical wiring in the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Ground (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
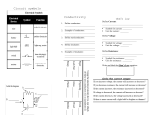
Schematic Diagrams A schematic diagram is a concise, symbolic description of an electrical circuit. It specifies the elements that make up an electrical circuit and how they are connected. Schematic diagrams form one of the basic languages of electrical engineering. On a schematic, there may be many parts which are identical in type or part number. To distinguish them, components have a reference designator or instance name which specifies each individual component. A component will also have either a part number, or value associated with it also. Some components such as transistors have no single value that can specify them, while a resistor needs only a value if its wattage rating is understood. There are no rules other than common sense that dictate what should or should not be on a schematic. component value reference designator wire1 R1 10 B1 4.5V wire2 battery symbol resistor symbol connection dot ground symbol (a) Schematic (b) Physical circuit Figure 1: Correspondance Between Schematic Diagram and Physical Circuit A document that accompanies the schematic which fully specifies the parts in a design is known as the bill of materials or BOM. The BOM contains the listing of all parts in a design. The linkage between the schematic and the BOM is via the reference designator. If the parts are on a printed circuit board, the reference designator is silk screened on the board to aid in tracing the schematic and identifying the part on the parts list. The silk screen is usually shows up as reference designators and component outlines on the top side of the printed circuit board. The Ground Symbol Since voltage is measured between two points, to simplify matters one of the points in most circuits is called the common, ground, or the reference point. The term common typically refers to the node from which all voltage measurements are made from. By convention, the voltage at the common node is considered to be zero. 1