* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Biology 207 Workshop 5 1.The plant Haplopappus has only three
Skewed X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Y chromosome wikipedia , lookup
Hybrid (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
Neocentromere wikipedia , lookup
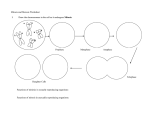
Biology 207 Workshop 5 1.The plant Haplopappus has only three chromosomes pairs. Assume they are a long metacentric pair, a medium length telocentric pair and a short acrocentric pair. Draw a cell of this organism in: a) anaphase of mitosis b) anaphaseI c) anaphase II anaphase mitosis anaphase I anaphase II 2. If a female plant of the genotype Aabb were pollinated by a plant of genotype aaBb, list all possible progeny genotypes. AaBb, aaBb, Aabb, aabb 3. In humans, the somatic cells are diploid, having 46 chromosomes. Answer the following questions with respect to a single human cell: a) How many centromeres are in a cell in late mitotic anaphase? 92 b) How many centromeres are in a cell at metaphase I? 46 c) How many chromatids are in a cell during Prophase II? 46 d) How many chromosomes are in a cell at Metaphase II? 23 e) How many chromosomes are in a cell during mitotic prophase? 46 4. For the following diagrams, identify a) whether the cell is in mitosis, meiosis I or meiosis II, or can’t tell,b) whether the cell is in interphase, prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase or can’t tell, c) what the DIPLOID chromosome number is for the organism possessing each cell. a) Meiosis I b) Metaphase c) 2n= 6 a) Mitosis b) Anaphase c) 2n=8 a) Meiosis II b) Metaphase c) 2n = 6 a) Meiosis I b) Anaphase c) 2n = 6 5. How many different types of gametes can be produced by an organism of genotype AaBbDdEEffGg? 2x2x2x1x1x2 = 16 6. Fill in the blanks with mitosis, meiosisI or meiosisII. Homologous chromosomes pair during _meiosisI_____ but not during __meiosisII____ or ___mitosis___. Crossing over occurs during __meiosisI______. Sister chromatids separate from each other during _meiosisII_____ and _mitosis______ but not during __meiosisI______. 7. Why are lethal recessive alleles much more common than lethal dominant alleles? Individuals with a dominant lethal allele will likely not make it to a reproductive age, therefore not pass the allele to future generations. However individuals who are heterozygous for a recessive lethal allele are not affected, but can pass the allele onto future generations. 8. In fruit flies, the allele for dachs (short-legged, d) is recessive to its allele for normal leg length (D) and the allele for hairy body (h) is recessive to its allele for normal body (H). Make a Punnett square for each of the following crosses: a. DdHh x Ddhh b. DDHh x Ddhh c. DdHh x ddhh. What proportion of the offspring from cross b would be expected to show the normal phenotype for both traits? a. DdHh x Ddhh b. DDHh x Ddhh DH dh Dh dH Dh dh Dh DDHh Ddhh DDhh DdHh Dh DDhh Ddhh dh DdHh ddhh Ddhh ddHh c. DdHh x ddhh DH dh Dh dH dh DdHh ddhh Ddhh ddHh DH DDHh DdHh - Half the progeny from cross b will be normal for both traits. 9. For a plant of the genotype YyRr, make a series of drawings showing the way in which the chromosomes separate in the first division of meiosis and the second division of meiosis. Label each diagram with the symbols Y, y, R, r to show how all 4 types of gametes originate. * Or you could have drawn Y and R on the same chromosome, with a crossover to generate all four gametes.