* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Recognizing Bias and Persuasive Techniques
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
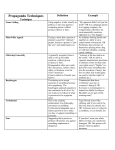
Recognizing Bias and Persuasive Techniques Have you ever tried to get someone to do something for you??? What was the situation? How did you try to get what you wanted? How did it work out for you? Did you get what you wanted? Guess what? You were trying to be persuasive by trying to get people to do what you want them to. Opinions and emotions can be considered tools What is bias, and why should I know about it? When your personal opinion is used in a commercial, ad, news story, or other area of the media When an opinion is used, the facts can be overlooked. Propaganda Techniques: Methods that people use to make what they say or write more convincing Can be used on purpose to appeal to emotion Can also be called “fallacies” or flaws in logic Kinds of propaganda techniques/fallacies: Bandwagon: Everyone else is doing it, so I should too. Kinds of propaganda techniques/fallacies: Testimonial: Uses a famous person to try and influence you to do or buy something. Review: Testimonial or Bandwagon? The pop singer Nelly declared, “I support the workers!” Testimonial Children across the nation are helping the homeless. Bandwagon Kinds of propaganda techniques/fallacies: Loaded Words: Using emotionally charged words (tone words) to produce strong positive or negative feelings. EXAMPLE: Cheaters are lowdown and dishonest people. Kinds of propaganda techniques/fallacies: Broad Generalization: Making a broad statement that something is true about all members of a group. EXAMPLE: “Everyone says that learning French is for losers.” Review: False Analogy and Appeal to Tradition Why would you support a law that would hurt poor, hardworking moms and dads that make America strong? Loaded Words Ellen is a poor student because she got a bad grade on her paper. Broad Generalization Kinds of propaganda techniques/fallacies: Novelty: The mistaken assumption that an idea is good just because it is new. Kinds of propaganda techniques/fallacies: False precision: The attempt to support an idea with math that may be tough to prove. EXAMPLE: “Our product is 25% better than the national leading brand.” Review: Novelty and False Precision: Try Cheerios today; you will love the new and improved taste! Novelty Kids like the taste of chocolate crunchies 30% more over the leading brand. False precision