* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit 3 - Concord Carlisle High School
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Catalytic triad wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Enzyme inhibitor wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
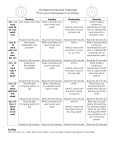
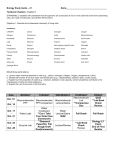
Intro Biology Unit 3: Enzymes And The Digestive System Name________________________________________ Date____________ block____ Unit Test: Tuesday Oct 25th – 100pts Corresponding Chapters: Sections 2.3, 2.4, 30.3 Essential Questions: 1. What is a chemical reaction? What is a reactant, what is a product? What do we mean when we say “chemical reactions rearrange, atoms, but do not destroy them”? 2. Which organic macromolecule are enzymes made out of? What does it mean to be a catalyst? 3. What is an active site? What is a substrate? Why is it important that the enzyme folds properly? What happens for a chemical reaction if the enzyme does not fold properly? 4. Explain how an enzyme works to catalyze a chemical reaction. Be sure to use the words “reactant”, “substrate”, “product”, “active site” in your answer. 6. How do pH and temperature affect enzymes? What does it mean for an enzyme to denature? 7. Name the structure and function of all organs of the digestive system. Which organs are of the alimentary canal? Which organs are “accessory organs”? What does it mean to be an “accessory organ”? 8. Where is salivary amylase made? Where does it function? Which organic macromolecule does it break down as a reactant, and what is the product? 9. Where is pepsin made? Where does it function? Which organic macromolecule does it break down as a reactant, and what is the product? 10. Where is bile made? Where is it stored? Where does it function? What does it do? 11. Where are trypsin, pancreatic amylase, and lipase made, and where do all three function? What does each one do? 12. Explain the difference between a bolus, gastric juice, and acid chyme. What does the sodium bicarbonate from the pancreas do to the acid chyme that enters in from the stomach? 13. How does the epiglottis help prevent us from choking? What is peristalsis? Why it is important? What are villi, and why are they important? What would happen if our large intestine didn’t absorb water? Monday Oct 10 Tuesday Oct 11 Wednesday Oct 12 Thursday Oct 13 Friday Oct 14 No School Columbus Day No h.w. day No h.w. day Section 2.4 textbook reading and google classroom homework due Enzyme lab due In google classroom Oct 17 Oct 18 Oct 19 Oct 20 Oct 21 Review worksheet due today Quiz today 30.3 reading and h.w. assignment Digestive system chart due “fate of the burger” essay due Oct 24 Oct 25 Oct 26 Oct 27 Essential questions due in google drive, 10pt h.w. assignment Test today 100pts Unit 4 Unit 4 Oct 28 Unit 4 Q1 ENDS All Q1 make-up work done by today Vocabulary: Unit 2 – Molecules of Life These are the main vocabulary words from the unit. It is not necessarily a complete list. If we use a term in class that you don’t know – add it to your vocabulary list! Section 2.3 (review) SPONCH elements monomer polymer carbohydrate (polysaccharide) starch cellulose sugar (monosaccharide) glucose protein amino acid organic macromolecule Section 2.4 chemical reaction reactant product activation energy catalyst enzyme substrate denature active site Polymer (reactant) monomer (product) Starch (carbs) lipid protein Sugar C6H12O6 glycerol+fatty acids amino acids Section 30.3 Mouth Salivary gland Salivary amylase saliva bolus epiglottis esophagus peristalsis stomach gastric juice stomach acid, HCl stomach mucus lining pepsin chyme pancreas sodium bicarbonate lipase pancreatic amylase trypsin small intestine liver bile gallbladder villi absorbtion large intestine rectum