* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Geometry: 3-1 Video Lesson Parallel line and Transversals
Duality (projective geometry) wikipedia , lookup
Analytic geometry wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
Riemannian connection on a surface wikipedia , lookup
History of geometry wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Perspective (graphical) wikipedia , lookup
Multilateration wikipedia , lookup
Euler angles wikipedia , lookup
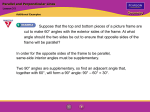
Geometry: 3-1 Video Lesson Parallel line and Transversals parallel lines: skewed lines: parallel planes: ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------transversal: interior angles: exterior angles: consecutive interior angles: alternate interior angles: consecutive exterior angles: alternate exterior angles: corresponding angles: Classify the relationship between each pair of angles as alternate interior, alternate exterior, corresponding, or consecutive interior angles. Identify the transversal. a. <10 and <16 b. <4 and <12 c. <12 and <13 d. <3 and <9 1 Geometry: 3- Video Lesson Angles and Parallel line If two line are parallel and cut by a transversal then the following relationships exist: Alternate Interior Angles Consecutive Interior Angles Alternate Exterior Angles Consecutive Exterior Angles Corresponding Angles Find the value of the variable(s) in each figure. Explain your reasoning 1. 3. 2. j is parallel to k. Find m<1, m<7 and m<8 m<1= (2x +5) ° m<4 = )x + 71) ° 1 5 2 6 3 7 4 8 j k Find x. (Hint: Draw an auxiliary line.) 4. 2 Geometry: Video Lesson 3-3 Slopes of lines What letter is used to represent slope? Slope is calculated two ways: 1. Rise Run 2. y 1- y 2 x 1- x 2 Find the slope of the following 1. 2. 3. Parallel lines and their slopes: Perpendicular lines and their slopes: 3 Determine whether line MN and line RS are parallel, perpendicular, or neither. Show your work! Graph the line that satisfies each condition. 1. passes through H(8, 5), perpendicular to line AG with A(−5, 6)and G(−1, −2) 2. passes through C(−2, 5), parallel to line LB with L(2, 1) and B(7, 4) 4 Geometry: Video Lesson 3-4 Equations of lines Slope intercept form of an equation: Point slope form of an equation: Write an equation in slope-intercept form of the line having the given slope and y-intercept or given points. 1. contains (2, 0) and (0, 10) 2. x-intercept is -2, y-intercept is -1 3. Write an equation in point-slope form of the line having the slope ½ through (3, -1) 4. Write an equation in slope intercept form for a line perpendicular to the line y=1/5x + 2 through (2, 0) 5 Geometry: Video Lesson 3-5 Proving lines are parallel Given the following information, determine which lines, if any, are parallel. State the postulate or theorem that justifies your answer. Find x so that l || m. Identify the postulate or theorem you used. 5. 6. M<3 = 2x + 12 & m<5 4x + 18 6 Geometry: Video Lesson 3-6 Perpendicular and Distance Distance From a Point to a Line When a point is not on a line, the distance from the point to the line is the length of the segment that contains the point and is perpendicular to the line. 1. 2. Distance Between Parallel Lines The distance between parallel lines is the length of a segment that has an endpoint on each line and is perpendicular to them. Parallel lines are everywhere equidistant, which means that all such perpendicular segments have the same length. Find the distance between a line containing points (4, 3) and (-2, 0) and point P (3, 10) 7 Find the distance between the parallel lines l and m with the equations y = 2x + 1 and y = 2x - 4, respectively. 8