* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
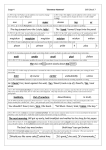
Download Exercise - Alien children`s Academy
Navajo grammar wikipedia , lookup
Ojibwe grammar wikipedia , lookup
Modern Greek grammar wikipedia , lookup
Old English grammar wikipedia , lookup
Georgian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Arabic grammar wikipedia , lookup
Udmurt grammar wikipedia , lookup
Modern Hebrew grammar wikipedia , lookup
Zulu grammar wikipedia , lookup
Portuguese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Macedonian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Chinese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Kannada grammar wikipedia , lookup
English clause syntax wikipedia , lookup
Italian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek grammar wikipedia , lookup
Esperanto grammar wikipedia , lookup
Lithuanian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Scottish Gaelic grammar wikipedia , lookup
Swedish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Serbo-Croatian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Latin syntax wikipedia , lookup
Yiddish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Icelandic grammar wikipedia , lookup
French grammar wikipedia , lookup
Malay grammar wikipedia , lookup
Spanish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Pipil grammar wikipedia , lookup
1. ALPHABETS Alphabets are a set or group of the letters. KIND OF ALPHABETS – (1) VOWELS – Total vowels are 5. They are – „ A , E , I , O , U‟ (2) CONSONANTS – Total consonants are 21. They are – „ B , C , D , F , G , H , J , K , L , M , N , P , Q , R , S , T , V , W , X , Y , Z‟ EXERCISE – Q.1 Define to the alphabets. _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ Q.2 a x Separate the vowels and consonants from the boxu m o I w e p q r v i n Vowels ___________________________________________________________________________________ Consonants _______________________________________________________________________________________ Q.3 How many vowels are in vocabulary? _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ Q.4 How many consonants are in vocabulary? _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ Composed by HEMRAJ JANGID E-mail - [email protected] Page 1 2. NOUN A noun is a naming word of person, place, thing, or group. eg- Lion, School, Delhi, Ram, Hemraj, Cow, Woman, Child etc. KIND OF NOUN – (1) A COUNTABLE NOUN- Proper noun – Proper noun is the name of a particular person or place. egRajesh, Jaipur, Geeta, Ram, Mumbai etc. (2) Common noun – Common noun is the name given to every person or thing of the same class or kind. eg- Man, River, Biscuit, Mountain, Country, Book etc. (3) Collective noun – Collective noun is the name of a group of people or things taken together. eg- a herd of cows, a bunch of grapes, a bouquet of flowers, a crowd of people, a suit of clothes, a swarm of bees, a troop of monkeys, a flight of pigeons, a bunch of keys, a deck of card, a knot of toads, a bask of crocodiles, a flock of sheep /goat / birds etc. B UNCOUNTABLE NOUN (4) Abstract noun - Abstract noun is the names of a feeling, quality, action or state rather than an object, person, animal or thing. egFeeling Quality Action State Happiness, Hatred Kindness, Goodness, Honestry Laughter, Obedience, Growth, Theft Childhood, Poverty, Slavery Abstract nouns are formed byfrom adjectives (quality) from verb (action) from common noun (state) (5) Material noun - Material noun is the name of substances or materials. eg- steel, wood, gold, iron, silver, water, aluminium etc. EXERCISE – Q.1 Separate to the proper and common noun- Ram, River, Woman, Delhi, Jaipur, Biscuit, Mountain, Ramayana, Geeta, Book, Man, Sohan, Krishan, Boy, Capital, Girl, USA, Mt. Everest Composed by HEMRAJ JANGID E-mail - [email protected] Page 2 Proper Noun _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ Common Noun _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ Q.2 Fill in these blanks with the correct collective nouns from the boxCollection, Gang, Herd, Bunch, Flock (a) A ………… of birds flew high in the sky. (b) The farmer has a ………… of cattle on his farm. (c) He ate a ……………… of grapes today. (d) The police arrested a ……………… of thieves last week. (e) Rajat showed me his a ………………… of stamps. (f) Q.3 I had lost a ……………… of keys last week. Write the abstract noun forms for the following wordsSad, Rich, Proud, Child, Adult, Brave, Grow, Young, Obey, Slave _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ Composed by HEMRAJ JANGID E-mail - [email protected] Page 3 3. PRONOUN Pronoun are that words which used in place of noun. eg- he ,she, they, it, you etc. Ram plays cricket so he goes to stadium daily. KIND OF PRONOUN – (1) Personal pronoun – Personal pronoun are divided into three classes on the following basis The first person is the person(s) speaking / speaker The second person is the person(s) spoken to / listener The third person is the person(s) spoken about eg- I want to speak to you about Mita. Here - I - First person You – Second person Mita – Third person The various forms of the personal pronoun are given below – (PERSON CHART) Name of Always use noun word after Possessive pronoun Subjective form Objective form Possessive form Reflexive form Vocative form Person Singular Plural Singular Plural Singular Plural Singular Plural Singula r Plural FIRST I We Me Us My Our My self Mine Ours SECOND You You You You Your Your Your self Him self Her self Our selves Your selves Yours Yours He Him His She Her Her Gender Mascul ine Femi nine Neu ter His Hers THIRD They It Them It Their Its Them selves Theirs It self Its Composed by HEMRAJ JANGID E-mail - [email protected] Page 4 (2) Relative pronoun – Relative pronoun shows the relation between two thing, person, or place. They are following Relative pronoun Usage Example Who Use only for people as a subjective form. If verb is after blank, put only „who‟ . It means always use verb after „who‟ The person who talk much is a liar. People who are honest are loved by all. Pooja who lives in Jaipur, is a brilliant student. I met the girl who topped the class. Whom Whose Use only for people as a objective form. If pronoun / noun is after blank, put only „whom‟. It means always use pronoun after „whom‟ Use only for people. If noun is after blank, put only „whose‟. It means always use noun after „whose‟ Which Use only for animal or things. The boy whom you teach is very intelligent. Ramesh whom the manager appointed is a clerk. This is the man whose father is a famous. Can you tell me the boy whose bag has been stolen? I lost the pen which I bought yesterday. The mangoes which are in the basket ate rotten. The present which my uncle sent me is very valuable. That Place on „which‟. Use for people, animal, or things. Keep the things that you have got. The dress that you gave me is very nice. The wolf that was man-eater has been killed. Unhappy is the man that is greedy. The book which / that is on the table is mine. Give me the pen which / that is there. The book which / that I bought yesterday was lost. EXERCISE – Q.1 Fill in the blanks with appropriate personal pronouns- (a) Marry and Cherry are happy. ……………… are playing at the moment. (b) Mr. and Mrs. Thatcher are teachers. ……………… teach English. (c) Daniel and you are bowlers. ……………… play for the school cricket team. Composed by HEMRAJ JANGID E-mail - [email protected] Page 5 (d) ………… am a student. (e) Bob is a painter. ……………… has painted a mosque. (f) This is Tom, and this is …………… father. (g) Peter and …………… family do not live in Kolkata. (h) Mum, have you seen ………… money box? (i) Please tell ………… (he / him) that ………… (I / me) have bought something from the market for him. (j) I remember that …………… (they / them) bought a lot of fruits for ……… (we / us ). (k) Please don‟t tell …… (she / her) about …………… (I / me). (l) I met Alice yesterday. ………… (she / her) invited …… (I / me) to her house. (m) Jane has a cat. ……… (she / her) likes to play with ………… (it / its). (n) My uncle works in a factory. ………… (he / him) says ………… (it / its) is a noisy place. Q.2 Fill in the blanks with appropriate relative pronouns(a) I know the man ………… stole your watch. (b) I lost the pen …………… I bought yesterday. (c) The answer …………… he gave is not correct. (d) The man …………… you met is my friend. (e) Give me the bat ……… is there. (f) This is the village ……………… I was born. (g) My father had left office ……… I reached home. (h) This is the man ………… father is a famous. (i) He knew …………… Ram is done it. (j) I gave her all the money …………… I had. (k) She was very happy ………… she found her lost purse. Composed by HEMRAJ JANGID E-mail - [email protected] Page 6 4. ADJECTIVE Describing words of the noun / pronoun are called adjective. Describing words show the size, colour, shape, taste, feel, age, appearance, material or number of a noun. eg- an honest boy, a clever fox, a wise woman, an old man a beautiful girl Adjectives are usually used before nouns. But sometime they are also used after them. eg- She is a beautiful girl. / The girl is beautiful. It is a sunny beach. / The beach is sunny. It is a cold ice cream. / The ice cream is cold. When two or more adjectives come before a noun, they are not usually separated by „and‟. eg- a large, oval vase. (not a large and oval vase) three green leaves. However, when the last two are adjectives of colour, they are usually separated by „and‟. eg- a black and white photo. a blue and red sparrow. There are two types of adjectives : adjectives of quantity and adjectives of quality. Adjectives of quantity tell us how much of a thing is being referred to. Adjectives of quality tell us the kind or quality of a noun. eg- Last evening, I had some ice cream. It was frosty. EXERCISE – Q.1 Rewrite these sentences so that the adjective come after the noun- (a) I have a beautiful dog. Composed by HEMRAJ JANGID ……………………………………………………………… E-mail - [email protected] Page 7 (b) I saw a tall tree. (c) It is a sharp pencil. (d) It is a dense forest. (e) I ate a tasty cake. Q.2 ……………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………… ………………………………………………………………… ………………………………………………………………… Identify the adjectives in this passage- Yesterday, my mother made a tasty cheese sandwich. It was really delicious! The bread was toasty, and the cheese was gooey. She had spread some butter on the bread too. Then she had put a thick slice of chicken on the spread. My father took a little bite from my sandwich. _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ Composed by HEMRAJ JANGID E-mail - [email protected] Page 8 5. ADVERB Describing words of the verb is called adverb. They tell us how, where, and when the action happen / took place. egTintin saved the cat bravely. The tortoise walks slowly. The man walks carelessly. He spoke to me rudely. He spoke to me angrily. Kevin sews neatly. I answered all the question easily. KIND OF ADVERB Adverb of Describe Example Manner Adverb of manner describe the manner in which an action takes place Carefully, loudly, neatly, beautifully, bravely, luckily, quickly, quietly Place Adverb of place tells where an action takes place. Here, there, everywhere Time Adverb of time tells when an action takes place. Today, yesterday, tomorrow, previous day, next day, last day Frequency Adverb of frequency tells how often an action takes place. Again, normally, generally, often, occasionally, sometimes, usually, never, ever, rarely, seldom, always, Certainty Adverb of certainty tells possibility of an action takes place. Maybe, perhaps, definitely, probably, certainly, surely, undoubtedly Adverb of Frequency - We use some adverb to describe how frequently we do an activity. These are called adverb of frequency and include - Frequency Adverb of Frequency 100% always I always go to bed before 11pm. 90% usually I usually have cereal for breakfast. 80% normally / generally I normally go to the gym. 70% often* / frequently I often surf the internet. Composed by HEMRAJ JANGID Example Sentence E-mail - [email protected] Page 9 50% sometimes I sometimes forget my wife's birthday. 30% occasionally I occasionally eat junk food. 10% seldom I seldom read the newspaper. 5% hardly ever / rarely I hardly ever drink alcohol. 0% never I never swim in the sea. Change adjective into adverbs Many adjective take –ly after them to change into adverbs. nice – nicely quiet – quietly quick – quickly egbeautiful - beautifully If an adjective ends in the consonant –y , change the –y to –i and add –ly. egeasy – easily If an adjective ends in –le, replace the letter –e with the letter –y. possible – possibly eg- However, don‟t drop the letter –e for other adjective ending in –e. Instead, add –ly to the adjective. eg- extreme – extremely supreme - supremely Exception : - true - truly If an adjective ends in –ic, add –ally to the adjective. eg- basic – basically, fantastic – fantastically, abnormal – abnormally, terrific – terrifically EXERCISE – Q.1 Underline the verbs and circle the adverbs in these sentences(a) He shouted loudly. (b) Meera ran quickly. (c) Anne writes neatly. (d) Lata is singing sweetly. Q.2 Complete these sentences by using the correct adverbs from the help box given below – loudly, badly, softly, brightly, quickly, bravely, quietly, slowly Composed by HEMRAJ JANGID E-mail - [email protected] Page 10 (a) The soldiers fought …………………………… (b) The monkey …………… climbed up the tree. (c) The sun shines …………………… (d) John whispered ……………………… (e) The teacher scolded you because you behaved ……………………… (f) The athlete ………………… ran towards the finish line to win the race. (g) The kids shouted ………… as they played their games. (h) The librarian asked the students to read their books ……………… (i) The turtle walked …………………… Q.3 Change these adjective into adverbsfresh, bold, lucky, noisy, possible, horrible, fine, lazy, neat, brave _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ Composed by HEMRAJ JANGID E-mail - [email protected] Page 11 6. VERB Doing word is called verb. Verb tell us about the action that noun perform. A verb have many forms such as V(s/es), V(1), V(2), V(3), V(ing). Different form of the verb is used to show different tense or condition. Eg- take , come, obey, say, look , cry etc. KIND OF VERB – Verbs are two types : (1) Helping Verb (2) Main Verb (1) Helping verb are also two types : Auxiliaries : - Auxiliaries verb change when the subject change. They are – Do, Does, Did, Is, Are, Am, Was, Were, Has, Have, Had, Will, Shall. Modals :- Modals verb don‟t change when the subject change. Always use V(1) after modals. They are – Can, Could, May, Might, Must, Will, Shall, Would, Should, Ought to, Dare to, Need to. (2) Main Verb : - The main verb generally names the action. Main verb are also two types. Transitive Verb : - When the object of the verb is present in the sentence, then the verb is called transitive verb. eg- The soldiers fought with the enemy. Intransitive Verb : - When the object of the verb is not present in the sentence, then the verb is called intransitive verb. eg- The soldiers fought fiercely. VERB FORM S.no. 1 2 3 4 5 6 Verb (V1) Play Cook Bake Try Take Give Means aaaa[ksyuk idkuk lsduk dksf‟k‟k djuk ysuk nsuk Composed by HEMRAJ JANGID Always write VERB form as the following- V(s/es) Plays Cooks Bakes Trys Takes Gives V2-form Played Cooked Baked Tried Took Gave E-mail - [email protected] V3-form Played Cooked Baked Tried Taken Given Ving-form Playing Cooking Baking Trying Taking Giving Page 12 Rule for make verbs form- Rule - 1 V(s/es) = by adding –s If “-i-“ is present among V(ing) = by adding –ing the verb then Eg- begin, drink, swim, ring, spring, sink etc. V(2) = remove –i and put –a V(3) = remove -i and put -u Rule - 2 Eg- If “-ind” is at the last then find, bind, wind, grind etc. V(s/es) = by adding –s V(ing) = by adding –ing V(2) = V(3) = remove –i and put –ou Rule – 3 If “-ee-” is among and “-p” or “-l” V(s/es) = by adding –s is at the last then Eg- V(ing) = by adding –ing sleep, weep, keep, sweep, creep, feel, kneel etc. Rule - 4 V(2) = V(3) = remove single – e and put –t at the last If “-ee-” is among V(s/es) = by adding –s V(ing) = by adding –ing and “-d” is at the Last then Eg- Rule – 5 V(2) = V(3) = remove single – e bleed, feed, breed etc. If “-d” is at the V(s/es) = by adding –s V(ing) = by adding – ing last then Egetc. send, build, spend, lend, But „spread‟ is not change Rule - 6 Eg- If “-ow” or “-aw” is at the V(2) = V(3) = remove – d and put -t V(s/es) = by adding –s last then V(ing) = by adding –ing know, throw, grow, flow, glow, blow, V(2) = remove –o and put –e draw etc. V(3) = by adding -n Composed by HEMRAJ JANGID bend E-mail - [email protected] Page 13 Rule – 7 If “-consonant +y” is at the last then Eg- carry, cry, fly, try, dry, reply, apply, supply, fry, study, Copy, marry, multiply, tally, magnify etc. Rule – 8 If “-vowel + y” is at the last then Eg- obey, play, display, pray, stay, employ, clay, spray, Bay, jay, enjoy, stray etc. V(s/es) = by adding –s V(ing) = by adding –ing V(2) = V(3) = remove –y and put – ied V(s/es) = by adding –s V(ing) = by adding –ing V(2) = V(3) = by adding –ed Rule - 9 If “-e” is at the last then V(s/es) = by adding –s Eg- die, agree, abuse, arrive, advise, bathe, V(ing) = remove –e and add –ing revise Believe, close, care, change, compare, trace, dare Hate, decorate, divide, injure, V(2) = V(3) = by adding –d invite, hospitalize, like, live, love, imagine, move, remove, promise, bake, prepare, receive, refuse, use, salute, save, solve, smile, seize, twice, notice, Noise, enable, delete, advantage, adventure, induce, inspire, provide, excite, estimate, evolve, involve, prove, traduce, issue etc. Rule – 10 If “-single vowel + single consonant” is at the last then Eg- beg, stop, quarrel, slip, travel, rob, top etc. V(s/es) = by adding –s V(ing) = double to consonant and add –ing V(2) = V(3) = double to consonant and add –ed Special Rule – V(s/es) = (1) if at the last ”ss, s, ch, a, o, I,u ” then Eg- act, plant, appear, ask, attack, Answer, arrest, call, clean, Collect, add –es complain, order, cook, cross, fail, (2) if at the last other letter then add-s Defeat, enter, pass, finish, grant, help, Join, kick, kill, need, open, V(ing) = by adding –ing present, press, pull, push, punish, reach, request, return, turn, Rain, V(2) = V(3) = by adding –ed remember, search, show, allow, borrow, start, succeed, talk, thank, touch, visit, wait, want, wash, watch, work, climb, water, look, clear, form, crop, plough, paint, claim etc. Composed by HEMRAJ JANGID E-mail - [email protected] Page 14 THERE ARE VERBS WHICH HAVE SECOND AND THIRD FORM SAME- eg- bring-brought, buybought, dig-dug, catch-caught, hear-heard, teach-taught, sell-sold, tell-told, say-said, seeksought, pay-paid, lay-laid, lie-lied, spend-spent, lift-left, leave-left, lie-lay-lain, learn-learnt, loselost, find-found, shoot-shot, make-made, sit-sat, stand-stood, have-had, fight-fought, think- thought, burn-burnt etc. THERE ARE VERBS WHICH HAVE FIRST,SECOND AND THIRD FORM SAME- eg- cut, put, shut, read, set, hit, cost, cast Some Special Verbs Form THERE ARE VERBS WHICH HAVE FIRST, SECOND AND THIRD FORM DIFFERENT- eg- see-sawseen, break-broke-broken, speak-spoke-spoken, steal-stole-stolen, drive-drove-driven, ride-roderidden, swear-swore-sworn, weave-wove-woven, give-gave-given, come-came-come, go-wentgone, run-ran-run, get-got-got(gotten), bite-bit-bitten, hide-hid-hidden, fall-fell-fallen, eat-ateeaten, beat-beat-beaten, do-did-done, fly-flew-flown, take-took-taken, choose-chose-chosen, write-wrote-written, tear-tore-torn etc. EXERCISE – Q.1 Circle the helping verb and underline the main verb of the given sentences- (a) They are walking. (b) Radha is singing a song. (c) You can go. (d) I must go to her. Q.2 What are the difference between auxiliaries verb and modals verb? _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ Q.3 Write the various form of the following verbsbake, take, cry, come, fry, listen, speak, write, cook, notice, answer, ask _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________ Composed by HEMRAJ JANGID E-mail - [email protected] Page 15 Q.4 Identify the transitive or intransitive verb form the given(a) Anne loves the ice cream. …………………………… (b) The gate opened. …………………………… (c) Mary found the ring. …………………………… (d) He writes poetry. …………………………… (e) The children play in the evening. …………………………… (f) The lamb died. …………………………… Composed by HEMRAJ JANGID E-mail - [email protected] Page 16 7. SENTENCE A sentence is a group of words that expresses a complete meaning, thought, or sense. A sentence must contain a verb. A sentence starts with capital letter and ends with full stop (.), question mark (?), or exclamation mark (!). The elements of the sentence are subject, verb, object and functional mark. eg- The sky is blue. My name is Monica. That‟s great! The boy threw a stone. The sun rises in the East. The dog is scared. What is your name? Every sentence has two parts : Subject and Predicate. The subject is the part of the sentence that performs the action of the verb. The predicate is the part of the sentence that tells something about the subject. The subject can be noun or pronoun. The predicate usually contains an object. eg- Tim He I bought a new bicycle last week. kicked the ball. He saw two beautiful goldfish. sat on the table. NOTE : Subject is in circle and predicate shows by underline. types. KIND OF SENTENCE :Sentence type depending on what we say and how we say it, sentences are of four 1. Declarative (Statement or Simple) – A statement starts with subject and ends with a full stop (.) eg- Mr Bean teaches us English. Statement are two type – (a) Affirmative (Subject + HV + Verb + Object + .) eg- He plays cricket. They were friend. The child is crying. (b) Negative (Subject + HV + Not + Verb + Object + .) eg- I don‟t play. We are not going. He is not playing. 2. Interrogative (Question) – An interrogative sentence asks a question and starts with Wh-word + HV or HV and ends with question mark (?) egHow are you? Did you play? Composed by HEMRAJ JANGID E-mail - [email protected] Page 17 3. Imperative – An imperative sentence gives a command or makes a request and starts with Don‟t + V(1) or V(1) or Please / Kindly + V(1) and ends with full stop (.) egTake your hands off. Close the door, please. Don‟t make a noise. 4. Exclamatory – An exclamatory sentence expresses a strong feeling and ends with exclamation mark (!) egWhat a ! beautiful girl. Hurrah! we will win the match. Help! 5. Optative – An optative sentence expresses a strong wish and ends with exclamation mark (!) egMay you live long! Good morning, sir! May God bless you! Exercise – Q.1 Turn the negative sentence into an affirmative sentence and the affirmative sentence into a negative one(a) I am not studying. ………………………………………… (b) They played cricket. …………………………………………… (c) Ram prays. …………………………………………… (d) You are good. …………………………………………… (e) We go to temple. ………………………………………… (f) ……………………………………………… It is not fair. (g) They are quite. …………………………………………… (h) We did not want it. …………………………………………… (i) …………………………………………… He does not love her. Q.2 What are the elements of a sentence? _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ Q.3 Identify the subjects and the predicate (circle the subject and underline the predicate) (a) Four young soldiers led the troops into the battle. (b) We ate the entire cake in less than five minutes. (c) Jim bought a new bicycle last week. (d) I saw two beautiful goldfish fighting with each other into pond yesterday. Composed by HEMRAJ JANGID E-mail - [email protected] Page 18 (e) Manish and Rohit came to my house last evening. (f) Last week‟s, fire injured many people. (g) Rahul paints the wall. (h) The batsman played well. (i) The lion roared. (j) A troop of monkeys is coming. Q.4 Identify the type of each of these sentences(a) Why do you believe that? ______________________ (b) I want to know why you believe that. ______________________ (c) ______________________ How scary you look! (d) Oh, my shoe is on fire! ______________________ (e) Ask Neetu for the recipe. ______________________ (f) ______________________ Have you solved the puzzle? (g) Anne, hand me your coat. ______________________ (h) There are five apples in the refrigerator. ______________________ (i) We are on the wrong side of the road. ______________________ (j) Send her a nice gift. ______________________ (k) Stay in your seat. ______________________ (l) ______________________ (m) What a beautiful painting! I didn‟t have time to finish my homework last night. __________________ (n) Why didn‟t you come to school today? Composed by HEMRAJ JANGID ______________________ E-mail - [email protected] Page 19 8. PHRASES AND CLAUSES PHRASESA group of words that does not make complete sense by itself is known as phrases. eg- Bunch of roses, Some people of India, My mother, at home, a good student, can sing, very weak etc. KINDS OF PHRASES(1) NOUN PHRASE - The phrase that has a noun / pronoun as the main word is called a noun phrase. egmy mother, the cat , a good student. (2) VERB PHRASE – The phrase that has a verb or more than one verb as the main word is known a verb phrase. egcan sing, will do, is going (3) PREPOSITION PHRASE – The phrase that begins with a preposition is called a preposition phrase. eg- at home, in the room, on the table. (4) ADJECTIVE PHRASE – The phrase that has an adjective as the main word is known an adjective phrase. egvery poor, too difficult, extremely good etc. (5) ADVERBIAL PHRASE – The phrase that has an adverb as the main word is known as an adverbial phrase. eg- very quickly, quite well, quite happily etc. NOTE – (a) The main word of the phrase is a word that is necessary to understand the meaning of the phrase. (b) A clause must have a verb in it. (c) A phrase has not a verb leaving verb phrase. CLAUSESA clause is a group of words forming part of a larger sentence and contains a Subject and a Predicate of its own. eg- The sky looks blue in the morning. KINDS OF CLAUSES – (a) Main Clause OR Principal Clause OR Independent Clause – “Main clause has a subject and a predicate and expresses a complete thought. When a sentence contains two main clauses, the clauses are joined by a coordinating conjunction. If a conjunction is missing, the two clauses can be joined with a semicolon.” egComposed by HEMRAJ JANGID E-mail - [email protected] Page 20 1. Hard work is the secret of success. Subject (one clause) Predicate Main Clause 2. Wise men love virtue Sub Pred. whereas fools Coord. Conj. Sub Main Clause shun it. (two clauses) Pred. Main Clause (b) Subordinate Clause OR Dependent Clause – “A subordinate clause has a subject and a predicate but doesn‟t express a complete sense by itself. It depends on a main clause for its complete sense. It is introduced with a relative pronoun (who/whose/whom/which/that) or a subordinate conjunction (if/though/because) or a connective adverb (why/where/when/before/after)” 1. God Sub bless us Pred. when we Subord. Conj. Sub Main Clause 2. If you worship him. Pred. Subordinate Clause work hard Subord. Conj. Sub , you Pred. Sub will reach the goal. Pred. Subordinate Clause Main Clause IN THE SENTENCE (1) Simple Sentence – (A sentence which have only one main clause, is called simple sentence) I don‟t know how to operate a computer. Subject Predicate Main Clause Composed by HEMRAJ JANGID E-mail - [email protected] Page 21 (2) Compound Sentence – (A sentence that have two main clauses joint with conjunction, basically “and, or, but” is called compound sentence ) Man Sub. proposes Pred. and God disposes. Conj. Sub. Pred. Main Clause (3) Main Clause Complex Sentence – (A sentence that have one main clause and one subordinate clause joint with conjunction, basically “when, after, before”, is called complex sentence) student learns grammar Sub. Pred. Main Clause when she reads it. Conj. Sub. Pred. Subordinate Clause EXERCISE – Q.1 Identify the main clause and the subordinate clause in the following sentences(a) If you try, you will succeed. (b) He is playing while she is studying. (c) As soon as I reached school, the bell rang. (d) The patient had died before the doctor came. (e) I got up when the sun rose. _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ Q.2 Fill in the blanks with appropriate words given in the box – As, since, as though, so that, so long (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) You may go home …………………… you have finished your work. The old farmer nodded ………………… he understood every word. I worked hard ……………… I might win the gold medal. There will be no trouble …………………… as you keep your mouth shut. She is as pretty ………………… a doll. Q.3 Identify each of the following as phrases and clauses. Write P for phrases and C for clauses. (a) Shina talks very softly ………………… (b) those beautiful sunflowers ………………… (c) class VI students are learning about the clause ………………… Composed by HEMRAJ JANGID E-mail - [email protected] Page 22 (d) Suman dances very well (e) paper packages (f) these are a few of my favourite things (g) tied up with strings (h) Humpty Dumpty sat on a wall ………………… ………………… ………………… ………………… ………………… In the following sentences, phrases are underlined. Write the type of each phrase. (a) A captain is considered the leader of a team. (b) The painting in the Ajanta Caves are very beautiful. (c) Namrata can run very fast. (d) A rolling stone gathers no moss. _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ Q.4 Q.5 Identify in the following sentences as simple, compound and complex sentence(a) Ravi works very hard in order to perform well in the examination. ____________________________ (b) You can leave after you finish writing. ____________________________ (c) Babar is the founder of the Mugul Empire in India. ____________________________ (d) Ali will call me when his flight lands. ____________________________ (e) Kaushiki, who is my sister, is a great dancer. ____________________________ (f) Ram is very excellent boy. ____________________________ (g) This book is costly but it is very fantasting. ____________________________ (h) God bless us when we worship him. ____________________________ (i) Hard work is the key of success. ____________________________ (j) Ram is a god boy and Sita is a good player. ____________________________ Composed by HEMRAJ JANGID E-mail - [email protected] Page 23 9. TENSE There usage is an important area of learning a language. The word TENSE stands for a „verb‟. Verb used to express some „time relation‟. It shows two things – (1) Time of an action (2) Its degree of completeness. There are mainly three tense – Present, Past, and Future. KIND OF TENSE : - (1) PRESENT TENSE : (a) SIMPLE PERESNT TENSE - This tense is used to express habitual action, universal truths, to make general statements, desire statement, and with certain adverb such as – always, never, usually, generally, often, sometimes, on Sunday ……, in time clauses as „when, whenever, as soon as, and also uses for express the conditional sentence in the future time (open condition). Helping verb do, does Pattern Subject + V(s /es) + Object. Rules : V(1) _ form is used for plural subjects or I and You. V(s /es) - form is used for singular subjects. Do - is used for plural subjects or I and You. Does - is used for singular subjects. always use „do / does + V(1) eg- I play. They play. He plays. Ravi plays. Fish lives in water. Rain falls from clouds. Oil floats on water. Two and two make four. I always go for a walk in the morning. Cats drink milk. It is very hot day. Whenever it rains, he goes out for picnic. I want a cup of tea. I love my mother. Your answer seems correct. He usually takes coffee. If you work hard, you will pass. (b) PRESENT CONTINUOUS TENSE – This tense is used for action which progress (continue) at time of speaking or writing and with certain adverb of time such as – now, still, at this moment, these days, today etc. It also shows define arrangement in near future. Helping verb is, are, am Pattern Subject + HV + V(ing) + Object. Rules : Is - is used for singular subjects. Are - is used for plural subjects. Am - is used for I. eg- It is raining now. Children are playing cricket. I am reading book. All guests are watching TV. Some guests are coming tonight. I am leaving this place tomorrow morning. I am seeing a bird. I am hearing a song. He is writing. (c) PRESENT PERFECT TENSE – This is used for action which took place (completed) in the present up to time of (till) speaking or writing and with certain adverb such as – just, already, yet, recently, etc. Helping verb has, have Pattern Subject + HV + V(3) + Object. Composed by HEMRAJ JANGID E-mail - [email protected] Page 24 Rules : Has - is used for singular subjects. Have - is used for plural subjects or I and You. eg- You have already meet her. We have bought a TV. haircut. The police have arrested criminals. I have seen you just your (d) PRESENT PERFECT CONTINUOUS TENSE – This tense is used for an action which began in the past and is still continuing. In this tense, time phrase is added „since and for‟. Helping verb has been, have been Pattern Subject + HV + V(ing) + Object + Since/for + Time. Rules : Since - is used for (to indicate) a point of time. For - is used for (to indicate) a period of time. eg- I have been making sausage rolls for the party all the morning. The radio has been playing since 7am. Her phone has been ringing for ten minutes. She has been learning computer for six months but she hasn‟t leant much yet. (2) PAST TENSE : (a)SIMPLE PAST TENSE – This tense used for action which took place in past at the time of speaking or writing and with certain adverb of past tense such as – yesterday, last day……, ago, once, one day, previous day……, that day etc. This tense also uses „used to + V(1)‟ for express past habit and also uses to express the imaginary condition. Helping verb did Pattern Subject + V(2) + Object. Rules : always use „did + V(1)‟ eg- The water in the pond froze last night. India got freedom in 1947. I left home at 8am and got back at 12noon yesterday. They got back very late last night. He used to go to Landon. If you asked me, I would help you. (b) PAST CONTINUOUS TENSE – This tense used for past action which continued for some time in the past. This tense doesn‟t tell us when the action began or ended in the past. Past continuous is often found in compound sentence with another action in simple past tense. In this way past simple tense is used for complete action and past continuous for action still in progress in the past. It also has adverb clauses beginning with „when, while, and as‟. Helping verb was, were Pattern Subject + HV + V(ing) + Object, (+ adverb clauses) Rules : Was - is used for singular subjects and I. Were - is used for plural subjects and You. eg- When I arrived home, Rekha was talking on the phone. While the guests were dancing, thieves broke a window in the house. When I first met him, he was painting a Composed by HEMRAJ JANGID E-mail - [email protected] Page 25 picture. As we were coming here, a police man stopped us, While he was learning to drive, he had twenty five accidents. While he was making speech, the minister suddenly fell faint. (c) PAST PERFECT TENSE - This tense used for action which had completed in the past time. Past perfect tense is often found in compound sentence with another action in simple past tense. In such cases earlier (first) action is expressed in the past perfect tense and later (second) action is expressed in simple past tense. „Before, after, and when‟ are often used as connectives. This tense uses also to express the impossible condition. Helping verb had Pattern Subject + HV + V(3) + Object, (+ adverb clauses) eg- The robbers had run away before the police came. The fire brigade arrived after the villagers had put out the fire. The teacher had marked attendance before I entered the class. On reaching the examination center, Gopal found that he had forgotten to bring his admission card. The students had solved all the sums before the bell rang. We had already taken breakfast when you got up. The crops had dried before the rain came. If you had run fast, you would have caught the train. (d) PAST PERFECT CONTINUOUS TENSE – This tense is used for action which began in the past and was still continuing in the past. In this tense time phrase is added „since or for‟. Helping verb had been Pattern Subject + HV + V(ing) + Object + Since / for + Time. eg- He had been playing cricket in national ground for two hours. The children had been weeping / reading in the class room since 9 am. We had been discussing about it for two hours. Her telephone had been ringing for ten minutes. (3) FUTURE TENSE : (a)SIMPLE FUTURE TENSE – This tense is used for action which will complete in future. In English language, there are two principal ways of expressing the simple future – By using the auxiliaries „shall and will‟ By using the „be (is, are, am) + going to‟ It is also used certain adverbs such as – tomorrow, next day…… etc. Helping verb will, shall Pattern Subject + HV + V(1) + Object. Rules : Shall - is used for only I and We. Will - is used for other person. In fact, „will and shall‟ replace by „is, are, am + going to‟ eg- I shall see you tomorrow. We shall invite them to dinner. I shall be fifty on my next birthday. It will rain tonight. Kavita is going to buy a new car next month. The plane is going to land in half an hour. I shall tell you a secret. The police will be very strict with bad drivers in future. Composed by HEMRAJ JANGID E-mail - [email protected] Page 26 (b) FUTURE CONTINUOUS TENSE – This tense is used for action which will be going on at some time in the future. Helping verb will be, shall be Pattern Subject + HV + V(ing) + Object. eg- I shall be traveling at this time tomorrow. After dinner at 8 pm, we shall be watching „National Reporter‟ on star news channel. They will be assembling at the club this evening. (c) FUTURE PERFECT TENSE – In this tense the action is sure to be completed in the time mentioned. In this tense „By‟ is used with time. Helping verb will have, shall have Pattern Subject + HV + V(3) + Object + By + Time. eg- I shall have completed my course by December 2018. My mother will have washed all the clothes by now. My mother will have saved a lot of money by next year. We shall have finished this work by Sunday evening. They will have reached Delhi by 10 pm (d) FUTURE PERFECT CONTINUOUS TESE – This tense is used for an action which began in the past and will be still continuing. Helping verb will have been, shall have been Pattern Subject + HV + V(ing) + Object + Since / for + Time. eg- He will have been waiting for me since 2 pm. They will have been playing cricket in National ground for 9 am. TENSE CHART : S.No 1. Name of Tense Simple Present 2. Present Cont. 3. Present Perfect 4. Present Per. Cont. 5. Simple Past Keywords always, never, usually, generally,often, normally, sometimes, on Sunday … now, still, at this moment, these days, today just, already, yet, recently, By + present time Since, for, all + time (or second clause must be in present tense) yesterday, last day.., ago, once, one day, previous day…, that day Composed by HEMRAJ JANGID Helping Verb Do, does Pattern of Sentence S + V(s /es) + O Is, are, am S + HV + V(ing) + O Has, have S + HV + V(3) + O Has been, have been S + HV + V(ing) + O + since / for + Time Did S + V(2) + O E-mail - [email protected] Page 27 6. when, while, as Past Cont. 7. Past Perfect Was, were S + HV + V(ing) + O Had S + HV + V(3) + 0 Had been S + HV + V(ing) + O + since / for + Time Will, shall Or (is, am, are) + going to Will be, shall be Will have, shall have Will have been, shall have been S + HV + V(1) + 0 V(2) Or Did + V(1) Was/ were + V(ing) Before, after, when, by + past time V(2) Or Did + V(1) Had + V(3) Since, for + time (or second clause must be in past tense) Tomorrow, next day…… 8. Past Per. Cont. 9. Simple Future 10 Future Cont. 11. Future Perfect Tomorrow at this moment By + future time 12 Future Per. Cont. Since, for + time (or + on/by + time) S + HV + V(ing) + O S + HV + V(3) O S + HV + V(ing) + O + since / for + Time EXERCISE : Q.1 Fill in the brackets with correct form of the verb- (a) My mother ……… food before I reached home. (cook) (b) Patient had died before doctor ………… (reach) (c) She had gone to school after Pareek ………… tea. (take) (d) Mohan ………… his work before I come. (do) (e) Mira …………… clothes after Gopal had gone to the office. (wash) (f) Normally it ……… in July in India. (rain) (g) Ram usually …………… me on Sundays. (visit) (h) He …………… to the radio at this moment. (listen) (i) They …………… a book now. (read) (j) Ravi ……………… just ……… to school. (go) (k) They ………………… already ……………… their homework. (finish) (l) (m) I …………… just ……………… dinner. (take) He ……………… recently …………… from America. (return) Composed by HEMRAJ JANGID E-mail - [email protected] Page 28 (n) They ……………… not ……………… their work yet. (finish) (o) Anurag ………………… to Jaipur last week. (go) (p) I …………… a letter yesterday. (write) (q) Geeta ………………… to Agra tomorrow. (go) (r) Next week we ……………… for America. (leave) (s) When she met me, I …………… tea. (take) (t) She ………………… always when she was a child. (complain) (u) When I entered the class, the teacher ……………… students. (teach) (v) She …………… in her room when the thief entered the room. (sleep) (w) When I reached school, the bell …………… (ring) (x) Vimla …………………… for two hours. (sleep) (y) Sita ……………… food since morning. (cook) (z) She …………… rice for one hour and now she is reading. (cook) (aa) My father …… in Bikaner since 1998 but he has not left the house yet.(live) (bb) He ……… for the train for two hours when it came. (wait) (cc) It …… all night and the roads were flooded. (rain) (dd) The girls …… in this theatre for four years by the end of next month.(work) (ee) Raju …… English for eight years on 10 March, 2010. (teach) (ff) They ……… for three hours by 7 o‟clock this evening. (play) (gg) By the end of this year he ……… English for two years. (study) (hh) Babita …………… tea by 8 am. (take) (ii) She …………… Jaipur by this time. (reach) (jj) She …………… from England by 2018. (return) (kk) The guests ……………… here by tomorrow. (reach) Composed by HEMRAJ JANGID E-mail - [email protected] Page 29 10. SUBJECT – VERB – CONCORD (AGREEMENT) In English language, a rule for write correct sentence according to grammar in which subject has correct relation with verb is called subject-verb-concord. HERE SOME BASIC TIPS- Rule – 1 If subject is singular – verb is singular And subject is plural – verb is plural Anu plays, A girl is singing, They are reading, If two or more subject joint with „and‟ – verb is plural Rule - 2 You and I are classmates, Rule - 3 Cow has four legs Two and two make four If two or more subject joint with „or‟ – verb is according to subject that is after „or‟ Either you or he has stolen the water. Neither the chairman nor the directors are present. He or I am a doctor. Rule - 4 They or you are going to Agra. If two or more nouns joint with „and‟ and give only single message – verb is singular The leader and speaker is sitting on the stage. The poet and philosopher is dead. Fish and meat is the food of the Bengalis. Milk and bananas is my favourite food. Rule - 5 Slow and steady wins the race. The horse and carriage has come. If above every nouns have article (a, an, the) – verb is plural The manager and the principal have come. Composed by HEMRAJ JANGID E-mail - [email protected] Page 30 Rule - 6 If subjects joint with „each, every, either, neither, everyone, one of, none of, anyone of, each of, the number of , a pair of, a chain of, a species of , a team of, a land of, a herd of, a crowed of , a flock of, a variety of , an army of, a bunch of, a set of, a couple of, a gang of etc „ - verb is singular Each of them is good natured. Neither of these roads leads to hospital. Either of the brothers is at fault. Rule - 7 None of them is a teacher. a lot of, a great deal of , a plenty of , some of , most of if above show quantity --- singular verb if above show number --- plural verb Note:- a number of --- plural verb A lot of work was finished till evening. A lot of candidates have applied for this job. A number of girls were dancing. Rule - 8 „The + adjective‟ make a noun - plural verb The young are strong. The honest never tell a lie. The rich are not always happy. Rule - 9 committee, gentry, poultry, cattle, people , police, crew, army, ---- The cattle are grazing in the field. plural verb People are waiting for you. Rule - 10 if the sentence starts with „there‟ , verb use according to subject that is after „there‟ There are five books on the table. Composed by HEMRAJ JANGID There is no pen on the table. E-mail - [email protected] Page 31 Rule - 11 If subject of the verb is relative pronoun (who, which, that,) then use the verb according to number of antecedent person. It is he who is to blame. The books which are on the table is mine. NOTE :- But in case of „whom‟ the verb is used according to after person. The boy whom you have sent a present is my friend. Rule – 12 If the plural nouns show a special number or quantity ---Use singular verb Sixty miles is not a long distance. Fifty thousand rupees is a large sum. Rule – 13 Nine hundred rupees is not much for this cow. Some nouns visual as plural but their means singular ---- Use singular verb (Physics, Maths, Economics, wages, news, means, assets, alms, innings, mammals, politics, billiards, etc) This news is false. Politics is a game of liars. Maths is my favourite subject. EXERCISE – Q Fill the correct form of the verb according its subject (a) Two and two ………………… (make / makes) four. (b) This news ………………… (is / are) true. (c) There …………… (is / are) seven fruits in box. (d) A number of boys ……………… (were / was) dancing. (e) Slow and steady ………………… (win / wins) the race. Composed by HEMRAJ JANGID E-mail - [email protected] Page 32 11. ARTICLES There are mainly three articles. They are – A , An ,The USE OF „A‟ : - „A‟ is used before the words which have starting sound of consonants. eg - A gentleman is talking to our headmaster. A cat can kill a rat. A cow gives milk. He is a good teacher. She is a doctor. Other example – a man, a boy, a girl, a university, a useful book, a European, a one rupee coin, a B.A. degree, a B.Sc. degree USE OF „An‟ : - „An‟ is used before the words that have starting sound of vowels. eg- An elephant has a trunk. Her father is an engineer. Other example – an apple, an egg, an hour, an honest man, an inkpot, an MLA, an umbrella, an old man, an MP, an NCC officer, an M.A. degree, etc. USE OF „The‟ : - „The‟ is used before – Before the name, noun, or thing that is only single (one) in the world. Before the repeated noun in the sentence or paragraph. Before the superlative degree‟s word. Before the special event, moment, battle, revolutions. eg- the sky, the Earth, the weather, the Ganga, the Himalayas, the Indian ocean, the Ramayana, the Bible, the Times of India, the Indian Express, the Tajmahal, the Red fort, the Rajadhani Express, the Hindus, the Muslims, the Sikhs, the French Revolution, the battle of Panipat, the Green Revolution, etc. Other example - His car struck a tree. You can still see the mark on the tree. EXERCISE : Q. 1 Use correct article (a, an, the) in the blanks – (a) There is …………… University of Rajasthan. (b) He is ………… honest boy. (c) Rajan has lost his …………… one rupee coin. (d) ………… Ganga is a holy river. (e) Ram is …………… wisest boy in the class. Composed by HEMRAJ JANGID E-mail - [email protected] Page 33 12. DEGREES OF COMPARISON Degree of comparison makes from adjective words. Degree of adjective is three type(1) Positive (2) Comparative (3) Superlative POSITVE DEGREE - This degree show general degree of noun. It use in the sentence two type – egRita is tall. Sushmita is as tall as Smita. COMPARATIVE - In this degree be comparison between two nouns. egRicha is wiser than Anuradha. SUPERLATIVE - In this degree, be comparison among more than two nouns. egDivya is the shortest girl in her class. FORMATION OF COMPARATIVE AND SUPERLATIVE DEGREES OF COMPARISON : Most adjectives take –er to make the comparative form and –est to make the superlative form. egsweet – sweeter – sweetest, If an adjective ends in –e, then add –r to make the comparative form and –st to make the superlative form. egbrave – braver – bravest If an adjective end in –y, then change –y into –i and add –er to make the comparative form and –est to make the superlative form.eghappy – happier – happiest Some adjectives ending in a consonant, double their last letter and take –er to make the comparative form and –est to make the superlative form. egbig – bigger - biggest Some adjectives also take more to make the comparative form and most to make the superlative form. egbeautiful – more beautiful – most beautiful Some adjective‟s form are different. egbad – worse – worst good – better - best INTERCHANGE IN DEGREES : - (FORMULAS) TYPE – 1 P.D. C.D. Note eg - Noun (1) + V + not + as / so + PDA + as + Noun (2) Noun (2) + V + not + CDA + than / to + Noun (1) Don‟t make superlative degree from this form. And in P.D., if „not‟ is present than in C.D. don‟t use „not‟ and its opposite one. C.D. Iron is more useful than Gold. P.D. Gold is not as useful as Iron. TYPE -2 Composed by HEMRAJ JANGID E-mail - [email protected] Page 34 P.D. C.D. S.D. eg- P.D. C.D. S.D. No other / very few + Noun (1) + V + as /so + PDA + as + Noun (2) Noun (2) + V + CDA + than /to + any other / most other + Noun (1) Noun (2) + V + one of the / the + SDA + Noun (1) No other island in the world is as large as Australia. Australia is larger than any other island in the world. Australia is the largest island in the world. EXERCISE :- Q.1 Change the following sentence into comparative and superlative degree(a) No other state of India is as big as Rajasthan. _______________________________________________________________________________________ (b) Very few players are as good as Sachin. _______________________________________________________________________________________ (c) No other poet of India is as great as Kalidas. _______________________________________________________________________________________ (d) Very few Indian leader were as great as Gandhi. _______________________________________________________________________________________ (e) No other peak in the world is as high as Everest. _______________________________________________________________________________________ (f) Very few men are as learned as Dr A.P.J. Abdul Klam. _______________________________________________________________________________________ (g) No other son of Kunti was as strong as Bhīma. _______________________________________________________________________________________ Q.2 Format the following words into comparative and superlative formWise, great, rich, tall, pretty, small, scary, hot, lazy, fine, delicious, frosty, cold, good _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________ Composed by HEMRAJ JANGID E-mail - [email protected] Page 35 13. NUMBERS (SINGULAR AND PLURAL NOUN) When a noun talks about one person, place or thing, then it is said to be singular. egbook, temple, he, monkey, apple etc. When a noun talks about more than one person, place or thing, then it is said to be plural. egbooks, temples, they, monkeys, apples etc. FORMATION OF THE SINGULAR NOUNS INTO PLURAL NOUNS :- For most nouns, the plural is formed by adding –s to the singular. toy – toys, bag – bags, girl – girls, boy – boys, egdoll – dolls Nouns ending in –s, -ss, -sh, -ch, -x form their plural by adding –es to the singular noun. egass – asses, dish – dishes, church –churches, box –boxes, class – classes brush – brushes, watch – watches, fox – foxes Noun ending in –o form their plural by adding –es to the singular noun. egmosquito – mosquitoes, hero – heroes, mango – mangoes, buffalo – buffaloes Nouns ending in –y, with a consonant before it , form their plural by changing –y into –i and adding –es. egcity – cities, story – stories, baby – babies, lady – ladies Nouns ending in –f or –fe form their plural by changing –f or –fe into –ves. egwolf – wolves, knife – knives, calf – calves, wife – wives, leaf – leaves, elf – elves, thief – thieves, loaf – loaves. Some nouns form their plural by changing the vowels within the nouns. egman – men, woman – women, foot – feet, tooth – teeth, goose – geese Some nouns form their plural differently. eg- ox – oxen, child – children, mouse – mice, louse – lice, person – people Some nouns have similar spellings for both their singular and plural forms. egsheep – sheep, deer – deer, aircraft – aircraft EXERCISE : Q. 1 Change these singular nouns into plural nouns – Composed by HEMRAJ JANGID E-mail - [email protected] Page 36 tree, potato, photo, pony, elf, dwarf, handkerchief, mouse, deer, ox, child, foot, fish, person, aircraft, rope, hunter, tong, scissor, glass, trouser, secretary, fox, goose, man _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________ Q.2 Separate the following nouns as singular and plural Bees, men, children, leaves, mango, bags, sheep, lice, person, geese, cars, ass, brushes, calf, people, fish, dolls, foot, knife, heroes, elves Singular ___________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________ Plural ___________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________ Composed by HEMRAJ JANGID E-mail - [email protected] Page 37 14. DETERMINERS Determiners are words which signal to us that noun is Uncountable (U), Singular countable (SC), Plural countable (PC). They are few, a few, the few, little, a little, the little, some, any, much, many etc. Few and Little group – „Few‟ group 1. few, a few, the few 2. use before countable plural noun. 3. use for only numbers. 4. use for plural nouns. „Little‟ group 1. little, a little, the little 2. use before uncountable singular noun. 3. use for only quantity. 4. use for singular nouns. Few or little – is used to show hardly any and it shows negative. egFew boys would help you. Few friends can help me. I have little money. There is little chance of his success. He takes little interest in his work. Few books are left here. There is little water in the pitcher. A few or a little – is used to show some but not nil or zero, not many or much but still some. egI am in need of a few friends. Would you like a little tea. Go and bring a little milk. A little knowledge is dangerous thing. I want a few books. He takes a little interest in other things. A few students came to my class. The few or the little – is used to show some but all. egThe few books he had were very thrilling. The little money she had was spent. Don‟t spoil the little milk you have.I gave the beggar the little money I had. The few words he spoke were full of wisdom. The little money she had was stolen. The few friends he has are honest and sincere. The few books, I had I have given to my brother. Some and Any : - Some 1. use in affirmative sentence. 2. to show request, command, invitation. 3. use for countable and uncountable nouns (numbers or quantity). Composed by HEMRAJ JANGID Any 1. use in negative and interrogative sentence. 2. use for select one from a group. 3. use for countable and uncountable nouns. 4. here some negative words :hardly, scarcely, never, rarely, seldom, forbid, prohibit, impossible. E-mail - [email protected] Page 38 eg- There is some milk in the pot. Some children are making a noise in the class. There is some oil on the road. Will you please give me some money? There is not any milk in the bottle. Are there any mangoes in the basket? Have you any pen? Take any pen you like. There is hardly any water in the tank. Much and Many : - Much 1. Used to show large quantity of. 2. use before uncountable singular nouns. Many 1. used to show large number of . 2. use before countable plural nouns. eg – There is much water in the tank. There are many books in the library. EXERCISE : - Q.1 Fill in the blanks with correct word from the box – few, little, a few, a little, the few, the little, some, any, many, much (a) There were ………… people at the meeting. (b) He is a man of …………… words. (c) I have ……………… time for playing. (d) We cann‟t do anything with this ………… money. (e) Only ……………… boys passed in English. (f) He died only ………… days ago. (g) …………… knowledge is a dangerous thing. (h) There is ……………… milk in the pot. (i) …………… oranges which were lying in the basket were rotten. (j) …………… milk which was in the pot was drunk by the cat. (k) …………… boys are playing there. (l) (m) Please give me …………………… more milk. I don‟t think there is ………… doctor in the village. (n) Have you got ………… money. (o) There are ……………… books for sale. (p) He has ………………… water to supply in the colony. Composed by HEMRAJ JANGID E-mail - [email protected] Page 39 15. FRAME AND TAG QUESTIONS TAG QUESTIONS :- Tag questions are question attached to the end of a statement. A positive statement takes a negative tag and a negative statement takes a positive tag. Pattern of the tag question Positive tag Negative tag HV + Subjective pronoun + ? (HV)n‟t + Subjective pronoun + ? An imperative sentence usually takes „will you? or won‟t you? or can you? or can‟t you?‟ Everybody, everyone, someone, somebody are treated as plurals and remove by „they‟ in tag question. here some negative words :- little, few, hardly, scarcely, never, rarely, seldom, forbid, prohibit, impossible. These words make negative to the sentence. (HV)n‟t form write as – HV + not Do + not Did + not Am + not Was + not Has + not Had + not Shall + not Could + not Would + not May + not Short form Don‟t Didn‟t Aren‟t Wasn‟t Hasn‟t Hadn‟t Shan‟t Couldn‟t Wouldn‟t Mayn‟t HV + not Does + not Is + not Are + not Were + not Have + not Will + not Can + not Must + not Should + not Might + not eg - You don‟t work hard, do you? She likes music, doesn‟t she? Let‟s try to forget it, shall we? None of us liked to stay there, did we? Short form Doesn‟t Isn‟t Aren‟t Weren‟t Haven‟t Won‟t Can‟t Mustn‟t Shouldn‟t Mightn‟t Few people knew the answer, did they? Everybody likes money, don‟t they? Come and have a cup of tea, will you? Please keep quiet, should you? FRAME QUESTIONS :- Question can be framed mainly by two ways – (1) By using „HV‟ (2) By using „Wh–word‟ often, pattern of the question is – Wh-word + HV + Subject + V + Object + ? 1st pattern complete show 2nd pattern NOTE – In question first person change into second person Composed by HEMRAJ JANGID E-mail - [email protected] Page 40 By using HV :- „Yes or No‟ are removed in question. After using question pattern, make a question. eg – Ans – Yes, I have visited Agra. Q – Have you visited Agra? Ans – No, I will never do it again. Q – Will you do it again? Ans – Yes, I am going to give away the prizes. Q – Are you going to give away prizes? By using Wh-word :- Firstly we have to need to understand the usages of „Wh-word‟. So „Wh-word‟ table is given to understandWh-word Usage / Remove from the answer Who To show the person that is subject in the sentence. WHO is only used when referring to people. (= I want to know the person) To show the person that is object in the sentence. To show the relation between the person. „whose‟ always puts before the noun. For animal, things. WHICH is used when a choice needs to be made. (= I want to know the thing between alternatives) Whom Whose Which Where To show place / name of the place. WHERE is used when referring to a place or location. (= I want to know the place) To show time, WHEN is used to refer to a time or an occasion. (= I want to know the time) When Why To show reason of the action. WHY is used to obtain an explanation or a reason. (= I want to know the reason) How To show method of the work or action. HOW is used to describe the manner that something is done. (= I want to know the way) How much To show the quantity of. How much – refers to a quantity or a price (uncountable nouns) How many To show the number of. How many – refers to a quantity (countable nouns) How long How far To show the length of To show the distance of. How far – refers to distance How often How often – refers to frequency What eg - To use general asking. WHAT is used to refer to specific information. (= I want to know the thing) (a) Q : What have you taken in your breakfast? Ans : I have taken two slices of bread with butter in my breakfast. (b) Q : Whose smile did you be fond? Ans : I was fond of her smile. (c) (d) Q : Q : Who caused many problem to his neighbor? Ans : Dinesh caused many problem to his neighbor. Whom did you like very much? Composed by HEMRAJ JANGID E-mail - [email protected] Page 41 (e) Q : Ans : I liked my daughter very much. How does she talks? Ans : She talks in elegant manner. EXERCISE : - Q.1 Frame the question of the following answers(a) Ans : We eat to live. Q : Why ………………………………… ? (b) Ans : I am cooking rice for you. Q : What ………………………………… ? (c) Ans : No, we didn‟t know her name. Q : ………………………………………… ? (d) Ans : I am going to Udaipur for five days. Q : How many ………………………… ? (e) Ans : We are going to library. Q : Where ………………………………… ? (f) Q : When ………………………………… ? Ans : I get up early in the morning . (g) Ans : They are sitting under a tree. Q : Where ………………………………… ? (h) Ans : He broke the window and entered the room. Q : How ………………………………… ? (i) Ans : I like a banana most. Q : Which fruit ………………………… ? (j) Ans : I want fifty rupees. Q : How much money ……………… ? (k) Ans : Agra is fifty five kilometer from Bharatpur. Q : How far …………………………… ? (l) Ans : They came by bus. (m) Ans : They are all visitors. (n) Ans : Those are Ram‟s book. Q : How ………………………………… ? Q : Who ………………………………… ? Q : Whose ………………………………… ? (o) Ans : Sunita reads „Rajasthan Patrika daily. Q.2 Q : What / which paper ………… ? Tag the question of the given statements- (a) Bacteria live all around us, ……………………………… ? (b) I am going to Jaipur, ……………………………… ? (c) You will come, ……………………………………… ? (d) I don‟t play cricket in the morning, …………………………… ? (e) Pass me the book, ………………………… ? (f) Sit down, ……………………… ? (g) Stand up, ……………………… ? (h) She never sees pictures, ………………………………… ? (i) We hardly believe ghost stories, ……………… ? (j) A little progress has been made, ……………………… ? (k) Someone removed the picture, ………………………… ? Composed by HEMRAJ JANGID E-mail - [email protected] Page 42 16. A SHORT RESPONSE A short response is only for questions that begin with HV. It is a short answer of the question. KIND OF SHORT RESPONSE : – POSITIVE SHORT RESPONSE – In this way, an answer is given in positive. The pattern of the positive response is “Yes, + Subject + HV” NEGATIVE SHORT RESPONSE – In this way, an answer is given in negative. The pattern of the negative response is “No, + Subject + (HV)n‟t” eg – 1. Do you like music? Positive Response – Yes, I do. Negative Response – No, I don‟t. 2. Are prices coming down? Positive Response – Yes, it is. Negative Response – No, it isn‟t. 3. Is that right? Positive Response – Yes, that is. Negative Response – No, that isn‟t. EXERCISE : - Q. 1 Give the positive and negative short response for the following questions(a) Will you attend the marriage ceremony? _____________________________________ (b) Should I consult this doctor? _____________________________________ (c) Are you going to Japan? _____________________________________ (d) Did you unlock the almirah? _____________________________________ (e) Does she go to temple daily? _____________________________________ Composed by HEMRAJ JANGID E-mail - [email protected] Page 43 17. PASSIVE-VOICE (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) Rule for change into passive form – STATEMENTS-NEGATIVES-QUESTIONS If in the sentence, following given HV + MV is Object subject Suitable form of ‘BE’ Put V(3) form Use ‘by’ (to or at) Subject object Then use right form of BE V(1), V(s/es), Do/Does+ V(1) is/are/am V(2), Did + V(1) was/were Is/are/am/was/were + V(ing) same + being Has/have/had + V(3) same + been Will / shall / can / could / may / Might / must / should / would / Had to / dare to / ought to / Need to / used to / (is/are/am +going to) + V(1) same + be ALWAYS Use V(1) after „to‟ Use HV before subject in question sentence Write always „not to‟ form „Who‟ convert into „by whom‟ in passive form Don‟t write „everyone, somebody, anybody etc. in passive form as a subject. Use „HV + not‟ in negative. Use HV according to the subject. Some negative words are – nobody, seldom, never, little, few, forbid, too-to, neither-nor etc. EXERCISE – (1) This book contains 120 pages. _________________________________________ (2) Trees give us shade in summer. _________________________________________ (3) Trees provide wood as fuel. _________________________________________ (4) We don‟t allow smoking in the office. ________________________________________ (5) Nobody can solve your problem. _________________________________________ (6) The bank is going to open a new branch in Jaipur. Composed by HEMRAJ JANGID E-mail - [email protected] Page 44 _________________________________________________________________________________ (7) Who taught you English? _________________________________________ (8) Have you posted my letter? _________________________________________ (9) When did you receive the letter? _________________________________________ (10) Can anybody ask any question about match? _________________________________________________________________________________ IMPERATIVE SENTENCE – (V1 + Object OR Don‟t + V1 + Object OR Please/kindly + V1 + Object) (a) You are asked/requested to (b) Put sentence as to as NOTE – Requested = Please/kindly, Not to = don‟t (After remove) OR Let + Object + Should /+Be + V(3) Eg- Open the door fire Please give me your pen Don‟t waste your time or money Should = please/kindly after remove please sit down please allow me to go don‟t speak lie never speak a lie _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ EXERCISE – Complete the following sentences using the correct passive form of the verbs given in the brackets. 1. When we went to visit the factory, we ______________ (provide) with a map showing us where each building was. We ______________ (take) round the factory by guide. 2. This book _______________ (give) to me by my friend. He said that it ____________ (find) on the table in my room. Composed by HEMRAJ JANGID E-mail - [email protected] Page 45 3. I told my teacher that a story book ________________ (read) by me at that moment. This book _____________________ (give) to me my father. 4. I am sad because my watch ___________________ (lose) last night. I think it ___________________ (steal) when I was not at home. 5. Yesterday I bought a bat from your shop. But the bat you gave me __________________ (find) broken. Now it ____________________ (replace) or I shall go to the consumer forum. 6. Today tea ____________ (export) by India every year to many countries. Tests and experiments _______________ (conduct) to produce the best quality of tea. 7. When I went to the fields I ____________ (surprise) to see that every inch of the five acres of land _______________ (dig) up. 8. The seeds ________________ (grow) in small beds. When they are 6 to 8 inches tall, they _______________ (transplant). In two years‟ time, they are ready to be plucked. 9. Onam ____________ (celebrate) in the memory of Mahabali, a great king, who ruled the earth long ago. His kingdom was in a happy state. Theft, robbery, murder or any other crime _______________ (not know). 10. This year my birthday ________________ (celebrate) on July 1st with my grand parents. We went to their house in Jaipur. I ____________ (give) a beautiful watch by my grandfather. 11. He stole his neighbor‟s gold so he _____________ (arrest). 12. I know that he ______________ (send) to Canada for higher education next year. HELP ZONE – is exported, were provided, should be replaced, was given, was arrested, was found, will be sent, was stolen, were taken, was not known, was lost, was being read, had been dug, is celebrated, are grown, was given, are transplanted, was celebrated, was found Composed by HEMRAJ JANGID E-mail - [email protected] Page 46 18. DIRECT-INDIRECT HERE SOME BASIC RULES FOR CHANGE A SENTENCE INTO INDIRECT SENTENCE – According to 1. RULE FOR CHANGE OF PERSON First person change according to subject Second person change according to object Third person no change (1 2 3) ∞ (S O N) Right person will be on 2. RULE FOR CHANGE OF VERB (TENSE) – V(1/s,es) ∞ V(2) Do/does + V(1) ∞ V(2) Is / are /am ∞ Was /were Has / have ∞ had V(2) or Did + V(1) ∞ Had + V(3) Will /shall ∞ Would Was / were + V(ing) ∞ Had been +V(ing) Can ∞ Could May ∞ Might Other verbs no change If reporting verb is in present/future tense or Reported part has universal truth, then no change in verb of the reported part. 3. RULE FOR CHANGE OF TIME and DISTANCEThis ∞ That These ∞ Those Today … ∞ That day… Before Thus ∞ So day… Here ∞ There Now / Just ∞ Then Ago ∞ Tomorrow/ Next day… ∞ The following Yesterday / Last day… ∞ The previous day… HERE SOME BASIC CONCEPT- My father said to me, “ I have bought a new car for you.” Reporting part (Reporting-Verb) Composed by HEMRAJ JANGID E-mail - [email protected] Reported part (Reported-Verb) Page 47 HERE SOME RULES FOR DIFFERENT SENTENCE – FOR SIMPLE SENTENCE Say (s/v2) ∞ Say (s/v2) Say (s/v2) to ∞ Tell (s/v2) Commas That ∞ FOR QUESTION SENTENCE Say(s/v2) or Commas Say (s/v2) to ∞ If ∞ Ask (s/v2) (if reported part starts with HV ) Same Wh-word (if reported part starts with wh-word) Note:- question sentence converts into simple sentence by following method HV + Subject ∞ Subject + HV FOR IMPERATIVE SENTENCE Say(s/v2) Commas or ∞ Say (s/v2) to ∞ Order, Advise, Request, Ask, Forbid , Suggest (s/v2) To ,That (in case of Let) Note:- Use “ Request” if sentence starts with please or kindly , “ Forbid” if sentence starts with don‟t and “Suggest” if sentence starts with let . At last remove „please , kindly , don‟t and let‟ . In case of LET , use „should‟ before verb FOR EXCLAMATORY SENTENCE Say(s/v2) or Say (s/v2) to Sorrow (alas, oh) Commas ∞ ∞ Exclaim (s/v2) with Surprise (what a, how), Joy (hurrah), That FOR OPTATIVE SENTENCE Say(s/v2) Commas or ∞ Say (s/v2) to ∞ Wish, Pray, Curse (s/v2) That Composed by HEMRAJ JANGID E-mail - [email protected] Page 48 EXERCISE 1. They said to me, “Let us go to a movie.” _______________________________________________________________________________________ 2. My friend said to me, “Please lend me your bicycle for while.” _______________________________________________________________________________________ 3. He said to her, “Did you go to your brother‟s house yesterday?” _______________________________________________________________________________________ 4. Sudha (on mobile) , “ Yes, you will have to wait for half an hour.” _______________________________________________________________________________________ 5. Sharda (on phone), “No, I can‟t attend your party” _______________________________________________________________________________________ 6. Sita said to Ram, “How shall I spend my days without you?” _______________________________________________________________________________________ 7. “Don‟t sit on my hat” , he shouted. _______________________________________________________________________________________ 8. The old man said, “Don‟t leave me alone. I am dying.” _______________________________________________________________________________________ 9. She said to me, “Oh God! I have lost my purse.” _______________________________________________________________________________________ 10. Rinku said, “What a beautiful scene!” _______________________________________________________________________________________ 11. Ritu said to me, “Who is that girl and where does she live?” _______________________________________________________________________________________ 12. She said to Atul, “Do you know me and my house?” _______________________________________________________________________________________ 13. The collector said to the servant, “Don‟t let anybody come in without my permission” _______________________________________________________________________________________ 14. Vimla said, “Thank you Ramesh for coming to my house.” _______________________________________________________________________________________ 15. She said, “Sir, I want to go home.” _______________________________________________________________________________________ 16. The teacher said, “I shall not teach you, boys.” _______________________________________________________________________________________ 17. She said to her friend, “Good Morning.” _______________________________________________________________________________________ 18. She said to her friend, “Good Morning. How are you?” _______________________________________________________________________________________ 19. A old lady said to me, “May you live long!” _______________________________________________________________________________________ 20. The mathematician said, “The sum of the angles of a triangle is always 180 degrees.” _______________________________________________________________________________________ Composed by HEMRAJ JANGID E-mail - [email protected] Page 49 21. Sita : You are going to Jaipur. Mohan : Yes. _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ 22. Rohan : How are you? Surbhi : I am well. _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ 23. Anjali : Aunty, I want to know something about the computer. Aunty : Do, you know what is a calculator? _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ 24. Radha : Where did you go this morning? Mohan : I went to the grocer to buy things. _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ 25. Mother : Go to the market and bring vegetables. Son : I can‟t go now because I have to complete my homework. _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ 26. Meera : Tell me what you did today. Sohan : Didi, I read two lessons of Geography today. _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ 27. The judge : Why did you break into the house? The thief : I broke into the house because the door was locked. _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ 28. Rakesh : What does your father do? Manvi : My father works in a factory. _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ Composed by HEMRAJ JANGID E-mail - [email protected] Page 50 19. NON-FINITES Form of the verb that is not affected / changed by subject or tense, is called nonfinites. TYPE OF NON-FINITES – (1) INFINITIVES (2) GERUNDS (3) PARTICIPLES INFINITIVES – Infinitives is made by “To + V (1)” . Infinitives work in sentence as subject, object and complement. eg- To take exercise daily is good habit. (as subject) He forgot to bring the bat. , He wants to study abroad. My target is to succeed. (as object) (as complement) IT + INFINITIVE - When the subject of a clause is an infinitive, then it doesn‟t usually come at the beginning of the sentence. We generally begin with the Preparatory subject „IT‟ , followed by the infinitive clause. egIt is fun to travel over the weekend. It is good habit to take exercise daily. It was the time to leave the house for the station. It is easy to book tickets online these days. It is your task to practise the subject regularly. QUESTION WORD + INFINITIVE The structure „question word + infinitive‟ is often used in indirect speech. It often corresponds to a direct question with should. eg- Grandmother : who should I invite? Grandson : she asked me who to invite. Another Example : - How to improve your grammar. , How to be a millionaire. I don‟t know how to do it. I don‟t know what to do. I don‟t know where to go. I don‟t know when to leave. I don‟t know who to blame. No one told me how to start the engine. NOTE : - We don‟t usually use „why‟ with infinitives. Composed by HEMRAJ JANGID E-mail - [email protected] Page 51 FOR + OBJECT + INFINITIVE – eg- There is nothing for the children to eat. I can‟t wait for her to finish eating. I have arranged for you to meet the Prime Minister. I‟m anxious for the party to be success. It‟s time for you to learn it. This is the pen for you to write with. GERUNDS – Gerunds are nouns that are formed from verbs. The form of a gerunds is „VERB + ing‟. eg - Smoking is bad habit. , Jogging isn‟t exhausting. , Exercising is good for health. (as subject) I like swimming. (as object) My hobby is gardening. (as complement) To make a gerund negative, add „not‟ before the gerund. Eg - Not exercising can be unhealthy. Use the singular form of the verb after a gerund. Eg - Walking is good for you. A gerund can be used after a preposition. Eg - She believes in working hard. PARTICIPLES – Present Participle – This participle qualify to the noun / pronoun as adjective. egI met a little weeping boy. , Hearing the noise, the thief ran away. Past Participle - This participle qualify to the noun / pronoun as adjective. eg- I saw a fallen tree. , The injured patient was taken to hospital. Perfect Participle - This participle qualify to the subject of reference. The form of „Having + V(3)‟ is called perfect participle. eg- Having finished his work, he went to home. Having taken food, he goes to school. Composed by HEMRAJ JANGID E-mail - [email protected] Page 52 EXERCISE – Q.1 Write sentences about yourself. Complete these sentences using „it + infinitive‟(a) …………… your teeth after dinner. (good habit, clean) (b) ……………… on a diet. (part of daily routine, go) (c) ………………… away from children. (medicine, keep) (d) …………………… before the exam. (necessary, complete, revision) (e) …………………… as quickly as possible. (your task, complete) Q.2 Complete these sentences using the „for + object + infinitive‟ form. Use the set of words given in brackets. (a) I have …………………… (arrange / you / meet) the chairman of the company. (b) It is difficult ……………………… (me / do / the task). (c) It took minutes …………………… (me / reach / station). (d) There is …………………… (nothing / children / eat). (e) I can‟t wait ………………… (her / finish) talking. Q.3 Write sentences with the „question word + infinitive‟ form using the sets of words given. (a) …………………………………………………… (no one / tell me / unlock / door). (b) …………………………………………………… (I / teach / make / coffee). (c) …………………………………………………… (don‟t / know / do). (d) …………………………………………………… (did / you / just / ask / me / open / drawer). (e) …………………………………………………… (no one / tell me / start / engine). (f) …………………………………………………… (rules / specify / who / emergency). (g) …………………………………………………… (do / know / do). (h) …………………………………………………… (I / forget / put / screw). Q.4 Read these conversation and rewrite each of B‟s responses using „ for + object + infinitive‟. (a) A : If I clear the test, do I still need to memorise the periodic table? B : Yes, it is time that you know it by heart. It is time ……………………………………………………………………………………………… (b) A : When can we see the Himalayan range? B : They are usually seen in autumn and winter. It is usual ……………………………………………………………………………………………… (c) A : How will Rajat feel about Mita coming? B : Rajat will be delighted to hear that. It will delight ………………………………………………………………………………………… Composed by HEMRAJ JANGID E-mail - [email protected] Page 53 (d) A : When has Anne asked for the designs? B : Anne wants the designs by Friday. Anne has asked …………………………………………………………………………………… Q.5 Identify and circle the gerunds in the sentences below. (a) I love reading thrillers by Brandon Massey. (b) Travelling is exciting. (c) Walking alone is boring. (d) Not knowing how to solve a sum is irritating. (e) Being with naughty kids all day is tiring. Q.6 Complete these sentences with suitable gerunds from the box. looking, working, playing, swimming, meeting, talking (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) She is good at …………………………… He is mad about ………………………… I don‟t like ……………………………… cards. They are afraid of ………………………… in the sea. The prime minister called an emergency …………………… to discuss the issue. He is interested in ………………………… friends. Q.7 Define to the each participle giving example. ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________ Composed by HEMRAJ JANGID E-mail - [email protected] Page 54 20. PREPOSITION A preposition is a word that shows the relation noun or pronoun to other noun or pronoun. Structure - Noun / pronoun Preposition Other Noun / Pronoun Prepositions are short words (on, in, to) that usually stand in front of nouns (sometimes also in front of gerund verbs). Even advanced learners of English find prepositions difficult, as a 1:1 translation is usually not possible. One preposition in your native language might have several translations depending on the situation. There are hardly any rules as to when to use which preposition. The only way to learn prepositions is looking them up in a dictionary, reading a lot in English (literature) and learning useful phrases off by heart (study tips). The following table contains rules for some of the most frequently used prepositions in English: Group wise study – 1st Group – on, over, above, onto, upon, up, upto Preposition Usage ON Before days of week, date, festival name, ceremony, and being on a surface (touching position) OVER Covered by something else, show up side at perpendicular without touching and running position, show end of ABOVE Higher than something else, show great in post, show up side without perpendicular and touching ONTO / UPON movement to the top of something (show up –down position) UP UPTO To show getting upside, with „climb‟ To show last limit Composed by HEMRAJ JANGID These preposition show up side. Example She comes to me on Diwali. There was a function on his birthday. He will return on 10th March of 2019. Ajay is sitting on chair / carpet. Your pen is on the table. Many pictures are hanging on the wall. I spread the cloth over the table. Apply this cream over affected area. The sky is over our heads. We hold an umbrella over our heads when it rains. Stop writing, time is over. When the show /film was over, she went home. A field marshal is above a general in rank. There is fan above my chair. The birds were flying above the trees. A rat jumped onto / upon the table. A mouse jumped upon / onto the lion‟s body. He climbed up the tree. They were climbing up the hill. I can teach upto 8th class in English medium. Upto 5km who come, stopped here. E-mail - [email protected] Page 55 2nd Group - in, for, at, since These preposition show time. Preposition Usage Example IN We use in for specific months, years, seasons, and parts of the day, show about a thing that is already inside, before language, show period of time (don‟t use in perfect continuous tense), before cities, towns, country I normally go on holiday in February. I was born in 1972. We can go skiing in winter. I go to the gym in the morning. There is tea in the pot. My book is in the bag. He writes his letters in English. There are no clouds in the sky. The train leaves in 5 minutes. He will return in two hours. She lives in Nagpur. AT To show point of time (don‟t use in perfect continuous tense) , meaning next to, near, by an object, show rate of interest, show direction, before the small town / city FOR Show period of time in perfect continuous tense, before the words that get something, meaning „for‟ SINCE Show point of time in perfect continuous tense, I start work at 9 o‟clock. I get up at 7 o‟clock. I find it difficult to sleep at night. I left the party at midnight. The train starts at 10 pm. She was standing at the gate. He looked at me. The child threw a stone at the dog. He asked me to meet him at the post office. She lives at Kishangarh in Ajmer. I have been teaching here for five years. The train left for Delhi at 10 pm. I go for walk everyday. This house is for sale. The water is for drinking. We should save some money for future. It is a machine for washing clothes. Vijay has been playing since 5 am. She has been writing since morning. from, of, with, by, to These preposition show relation. 3rd Group – Preposition Usage Example FROM To show starting point of time, place, show cause of, show different, who gave it, in sense of where from, before the thing which made of (not appearing) Examination will start form 7th April. He is suffering form fever. A lion is different from a cat. Apples come from Kashmir. Many birds come from Siberia. Butter is made from milk. Bread is made from flour. OF To show relation, who / what does it belong to, what does it show, before the thing which made of (appearing) WITH Before the weapons, instrument that is using, in the company of, in the possession of, meaning „with‟ Neera is going to school with her brother. I left my luggage with the station master. He murdered his wife with a knife. I beat him with stick. I always write with a pen. BY By way of, in passive form, show the agent of the action, rise or fall of something, travelling (in which sit inside), who made We always travel by train. He went to Mumbai by air. Ravi came and sat by me. Jane is standing by the car. Her house is by the bank. It is composed by Alien school. My father sent me a book by post. He gets his salary by cheque /cash. Composed by HEMRAJ JANGID My cap is made of wool. These shoes are made of leather. Tajmahal is made of marble. Table is made of wood. Give me a sheet of paper. Rahul is member of this club. I need a piece of paper. She is proud of her beauty. He died of cancer. (in case of died) He is a master of Arts. E-mail - [email protected] Page 56 it, to be left or right of somebody or something, in the sense of at the latest up to a certain time, for swear / oath / promise solemnly TO To show lack of time (telling time), to compare, before going / destination place, before last point of time 4th Group – show place. Prices have been risen by 10 percent. I will be back by 6 o‟clock. By 11 o‟clock, I had read 5 pages. Godan was written by Munshi Prem Chand. By you, by god, by mother. It is quarter to nine (8:45), He sent a present to his wife. He goes to temple daily. The teacher teaches us from 7 am to 9 am. below, under, through, across, beside, along Preposition Usage It is ten to ten (9:50) These preposition Example BELOW Lower than something else but above ground, show lower in post / rank The fish are below the surface. Your answer is below standard. I wrote my name below his name. A post of principal is below the M.D. of school. UNDER On the ground, lower than (or covered by) something else, less in comparison, to show work processing The bag is under the table. Rekha is under forty. The road is under repair. The house is under construction. The road was under water. Some cows were sitting under the tree. You should keep your legs under the table. THROUGH To make a hole or passage in, Something with limits on top, bottom and the sides Drive through the tunnel. They were passing through the jungle. The thief came through the window. It rained through the night. ACROSS Getting to the other side, to show second side of the something “Across = a + cross” There is a bridge across the river. There was a road across the garden. Our school is across the main road. The boat will carry you across the river. BESIDE To be left or right of somebody or something, “Beside = be + side” BESIDES – to mean additional to or apart from Ramesh sat beside the Jane. The hut was beside a river. Your argument is beside the point. Besides sita all the students were present. There was nothing in the room besides a chair. ALONG Meaning „edge to edge‟, to be together “Along = a + long” There are many trees along the road. The railway track is along the National Highway. The runner will run along the road. She ran along the railway line. We walked along the road. OTHER RULES -Composed by HEMRAJ JANGID E-mail - [email protected] Page 57 Prepositions – Time Preposition Usage Example on days of the week, We use ON for specific days and dates. at We use AT with specific times (hour / minutes for night for weekend a certain point of time (when?) in We use IN for specific months, years and seasons since ago before from a certain point of time (past till now) over a certain period of time (past till now) a certain time in the past earlier than a certain point of time to past to / till / until till / until telling the time telling the time marking the beginning and end of a period of time in the sense of how long something ten to six (5:50) ten past six (6:10) from Monday to/till Friday by in the sense of at the latest up to a certain time I will be back by 6 o‟clock. By 11 o'clock, I had read five pages. for is going to last I will return it to you on Wednesday. They got married on Friday the 13th. We get paid on the 20th of every month. I drank too much on New Year's eve. at night, at the weekend, at half past nine, I get up at 7 o'clock. My English classes starts at 10am. She finishes work at 6.15 I left the party at midnight. My birthday is in January. (I don't mention the date, just the month) My grandmother was born in 1927. The river near my house is dry in Summer since 1980 for 2 years 2 years ago before 2004 He is on holiday until Friday. Prepositions – Place (Position and Direction) Preposition Usage in at on by, next to, beside under below over room, building, street, town, country, book, paper etc. car, taxi, picture, world meaning next to, by an object for table for events place where you are to do something typical (watch a film, study, work) attached for a place with a river being on a surface for a certain side (left, right) for a floor in a house for public transport for television, radio left or right of somebody or something on the ground, lower than (or covered by) something else lower than something else but above ground covered by something else meaning more than getting to the other side (also across) overcoming an obstacle Composed by HEMRAJ JANGID E-mail - [email protected] Example in the kitchen, in London in the book, in the car, in a taxi, in the picture, in the world at the door, at the station at the table at a concert, at the party at the cinema, at school, at work the picture on the wall London lies on the Thames. on the table on the left on the first floor on the bus, on a plane on TV, on the radio Jane is standing by / next to / beside the car. the bag is under the table the fish are below the surface put a jacket over your shirt over 16 years of age walk over the bridge climb over the wall Page 58 above across through to into towards onto from higher than something else, but not directly over it getting to the other side (also over) getting to the other side something with limits on top, bottom and the sides movement to person or building movement to a place or country for bed enter a room / a building movement in the direction of something (but not directly to it) movement to the top of something in the sense of where from Other important Prepositions Preposition a path above the lake walk across the bridge swim across the lake drive through the tunnel go to the cinema go to London / Ireland go to bed go into the kitchen / the house go 5 steps towards the house jump onto the table a flower from the garden Usage Example from who gave it a present from Jane of who/what does it belong to a page of the book what does it show the picture of a palace by who made it a book by Mark Twain on walking or riding on horseback on foot, on horseback entering a public transport vehicle get on the bus in entering a car / Taxi get in the car off leaving a public transport vehicle get off the train out of leaving a car / Taxi get out of the taxi by rise or fall of something prices have risen by 10 percent travelling (other than walking or horse riding) by car, by bus at for age she learned Russian at 45 about for topics, meaning what about we were talking about you EXERCISE – 1. Exercise on Prepositions – Time (Fill in the correct prepositions) (a) Peter is playing tennis Sunday. (b) My brother's birthday is (c) My birthday is the 5th of November. May. (d) We are going to see my parents (e) (f) the weekend. 1666, a great fire broke out in London. I don't like walking alone in the streets (g) What are you doing Composed by HEMRAJ JANGID night. the afternoon? E-mail - [email protected] Page 59 (h) My friend has been living in Canada (i) I have been waiting for you (j) I will have finished this essay two years. seven o'clock. Friday. 2. Exercise on Prepositions –– Place (choose the correct preposition) (a) We live London. (at, in, on) (b) Would you like to go the cinema tonight? (at, in, to) (c) the cinema yesterday. (at, into, to) No, thanks. I was (d) We are going holiday next week. (in, on, to) (e) There is a bridge (f) the river. (across, through, outside) The flight from Leipzig to London was (g) Frankfurt.(about, along, via) my wall, there are many picture postcards. (at, on, onto) (h) Who is the person this picture? (at, in, on) (i) Come the sitting room, we want to watch TV. (at, in, into) (j) Munich lies 530 meters sea level. (above, across, past) 3. Exercise on Prepositions – Place (Complete the exercise according to the picture) (a) the picture, I can see a woman. (b) The woman is sitting (c) She is sitting a table. a chair. (d) There is another chair (e) Her feet are (f) (g) the table. The woman is holding a cup her hands. the table are a laptop, a paper, a calculator, an appointment calendar, two pens and a muffin. (h) The woman is looking (i) the woman. The woman's bag is Composed by HEMRAJ JANGID her laptop. the table. E-mail - [email protected] Page 60 4. Exercise on Prepositions – Place (Complete the exercise according to the picture) (a) the picture, there are four people. (b) A couple is sitting (c) the table. They are sitting (d) The drinks are chairs. the table. (e) One woman is standing (f) the table. her is a man who is barbecuing. 5. Exercise on Prepositions – Place (Complete the exercise according to the picture) (a) the picture, there are three kids. (b) The girl is standing (c) the two boys. The boy with the green shirt is (d) He has a gameboy the right. his hands. (e) The kids are looking his gameboy. 6. Exercise on Prepositions – Place (Complete the exercise according to the picture) (a) the picture, I can see Santa Claus and a girl. (b) Santa is sitting (c) a chair. The girl is standing Santa. (d) Santa and the girl are looking (e) The girl has a present (f) each other. her hands. the girl, there is a Christmas tree. (g) There are more presents the tree. (h) Santa's big bag is lying the floor. 7. Exercise on Prepositions – Time (a) What are you doing (choose the correct preposition) the weekend? (at, in, on) (b) I don't know yet. Maybe I'll go to the cinema (c) Saturday.(at, in, on) That's interesting. I haven't been to the cinema since) (d) We could go there together Composed by HEMRAJ JANGID so many years. (for, the afternoon. (at, in, on) E-mail - [email protected] Page 61 (e) That would be great. But I would prefer to go there visiting my grandma (f) (h) It lasts (i) (j) Saturday. (at, in, on) / (at, in, on) That's okay. The film starts (g) I can pick you up on) / (to, past) the evening. I am half eight o'clock. (at, in, on) seven. How long does the film last? (at, in, two hours and forty-five minutes. (for, to, until) eight a quarter eleven. (before, by, from) / (for, past, till) / (for, past, to) That's right. But I must hurry home home the film. I have to be eleven o'clock. (after, before, past) / (by, since, until) Composed by HEMRAJ JANGID E-mail - [email protected] Page 62 21. MODALS Modals : can, could, may, might, will, shall, would, should, must, ought(to), used(to), need and dare. There are negative form of the modals auxiliariesModal Full negative form Short negative form Can Can not Can‟t Could Could not Couldn‟t May May not Mayn‟t Might Might not Mightn‟t Shall Shall not Shan‟t Will Will not Won‟t Should Should not Shouldn‟t Would Would not Wouldn‟t Must Must not Mustn‟t / musn‟t Ought to Ought not to Oughtn‟t to Used to Used not to Usedn‟t to Need Need not Needn‟t Dare Dare not Daren‟t Modals have three common characteristics. They are – (1) Always use bare infinitive (1st form of the verb) after modals. (2) Modals don‟t have infinitive (to shall, to must etc) or participle form (maying, canning, mayed, shalled etc), so these are called defective verbs. (3) Modals don‟t affected by subject. eg – I can do it. She can do it. Composed by HEMRAJ JANGID They can do it. E-mail - [email protected] Ram can do it. Page 63 Uses of the modals – Modal Can Or Can‟t Could Or Couldn‟t May Or Mayn‟t Might Or Mightn‟t Will Won‟t And Shall Shan‟t Keywords Examples Can use in present tense to show future ability, capability, permission (giving), suggestion, allow (on asking), possibility, power, prohibition, puzzlement or impatience (less than „may‟) Pat form (tense) of can, polite request She can left 100kg weight at a time. Can you guide me, brother? Anybody can make mistake. What can he mean? If you request, he can help you. I can‟t left it. He went late so he can‟t have caught the bus. You can‟t drink in public places. Present probability, more possibility, guess, wish, hope, permission (formal), allow(without asking), wish, likely, purpose, uncertainty, guess, formal etc Past form (tense) of may, remote or least possibility, suggestion, proposed etc I could learn fast when I was young. We could attend the meeting. If I had more money, I could buy a bunglow. He could be very rough. We couldn‟t attend the meeting. He couldn‟t type fast when he was in job. May I come in, Sir? You may come in. The clouds are dark so it may rain. They may be at home now. May live long! May this news be true! May God bless you! She may obtain good marks as she is working hard. If you try, you may reach the goal. It mayn‟t rain tonight. She went early so she mayn‟t have missed the train. There are very few clouds so it might rain. The road might be blocked for the VIP. You might post these for me. What you say might be true. The last bus has gone so he might come now. Willingness, intention, threat, command, promise, consult, determination, legal notice, request, polite request, habitual activity, duty, lest, prediction, invitation, (Note :- always use „will‟ with I or we and „shall‟ with another) Would Or Wouldn‟t Past habit, polite request, to denote wish, promised, insistence, enquire, past of „will and shall‟ Should Or Shouldn‟t Advice, duty, responsibility, obligation, logical necessity, suggestion, to express purpose and desire, lest Composed by HEMRAJ JANGID We will not surrender to the enemy. Will I write this essay? They shall sell this house. Every citizen shall have right to live. Trespassers shall be punished. He shall buy a car. You shall be punished if you do it again. India shall be a world super power by 2025. Shall you take a cup of tea, please? Shall you mind your business? I will help you. You shall not tease the girl again. I will present you a gift if you get the 1st rank. He would bring me a watch. Would you like to go Jaipur? You would help me. I would like to call Mr Obama. We would sit on the hilltop in childhood. Would you please convey my message / regards. Would that I was a bird! It‟s your fault; you would pay the penalty. You should work hard. You should respect the elders. We should defend the nation. Be careful lest you should catch infection. I did not like that my son should join the army. We should attend our classes regularly. Children should be careful while crossing the road. You shouldn‟t help him. E-mail - [email protected] Page 64 Must Or Mustn‟t Compulsory, urgent, need, requirement, necessary, obligation, duty, inevitability, prohibition, essential, strong possibility, Ought to Or Oughtn‟t to Moral duty, moral obligation, moral responsibility, advisability, logical necessity, disapproval (if „to‟ is after blank, then use „ought‟ although use „should‟) Need Or Needn‟t Dare Or Daren‟t Compulsory, urgent, need, required, necessary, absence of necessity, Absence of courage, courage Past habits, to be accustomed to, Used to Or Usedn‟t to We must study English. We must eat. You must do the homework. You mustn‟t enter the office. All men must die. We mustn‟t smoke in the class, bus and public places. You mustn‟t spit here. We must inform the police about the accident. You must have a licence to drive a vehicle. You ought to help the poor. Everyone ought to obey the olders. They ought to start at once. You oughtn‟t to eat too many breads. She oughtn‟t to have gone in the rains. We ought to pay our taxes regularly. You needn‟t work so hard. He needn‟t go there. You needn‟t come on Sunday. He daren‟t touch me. He daren‟t tell a lie. The USA daren‟t attack China. I used to exercise daily in young age. She used to swim one hour daily in childhood. We are now used to work without electricity. I am now used to exercise daily. EXERCISE – Q.1 Fill in the blanks the correct modal using the word(s) as indicators given in brackets. (a) He ……………… do this work easily. (ability) (b) You …………………… go to the cinema today. (allowed) (c) You …………………… help your brother. (moral duty) (d) You ……………… respect your teachers. (duty) (e) You …………… enter the office without permission. (prohibited) (f) She ……………… dance well when she was young. (capability) (g) I ……………… help your sister in her work. (h) There are clouds in the sky. It ………… rain at night. (possibility) (i) She …………………… to help her old mother. (moral duty) (j) The students insulted the teacher. He ………………… punish them. (determine) (k) They …………… help one another with the homework. (past ability) (l) (promise) When Evelyn plays the xylophone, she ………… sense the sound. (present capacity) (m) Bishmillah Khan ………… sit practicing throughout the day. (past habit) Composed by HEMRAJ JANGID E-mail - [email protected] Page 65 (n) The headmaster predicted that Einstein …………… never make a success at anything. (prediction) (o) I don‟t believe the story is true and yet you …………… learn a lesson. (more possibility) (p) Prashant ………… help the orphaned children. (suggestion) (q) A single bomb ……………… destroy the whole port. (remote possibility) (r) Students …………… play in the classroom. (prohibited) (s) You …………… park your car here. (not allowed) Q.2 Rewrite the following sentences using the suitable modal. (a) He has no courage to tell a lie. _______________________________________ (b) He was in the habit of smoking. _______________________________________ (c) It is necessary for us to study of grammar. _____________________________________ (d) You are prohibited to enter the office. _______________________________________ (e) Isn‟t it urgent for us to work hard? _______________________________________ (f) He promised to bring me a watch. _______________________________________ (g) I am determined to get 1st division. _______________________________________ (h) It was possible to rain yesterday. _______________________________________ (i) He was able to run fast. _______________________________________ (j) You are allowed to go. _______________________________________ Composed by HEMRAJ JANGID E-mail - [email protected] Page 66 22. CONNECTORS / CONJUNCTIONS / SYNTHESIS / LINKERS Connectors are that words which join together words, phrases, clauses, nouns, pronouns, ideas or things. eg- Breakfast and lunch are served to all guests. (here „and‟ is conjunction) FUNCTIONS OF CONJUNCTION – (type of conjunction) Conjunctions are used to add similar things to form a group to contrast two different elements, ideas or things to logically derive something 1. conjunction of addition The conjunction and is used to join: two or more things, ideas, or elements of similar type. egShakespeare, Milton, Shelley and Keats are great English poets. You and I can go together. two sentences. egA. Preety wants to visit London. + She wants to visit Rome. = Preety wants to visit London and Rome. B. I opened the door. + I found you. = I opened the door and found you. 2. conjunction of contrast The conjunctions but, although, though, and still are used to join: A. The rabbit was fast. + The tortoise was steady. = The rabbit was fast but the tortoise was steady. B. It is raining. + The weather is very hot. = It is raining; still the weather is very hot. = Though (although) it is raining, the weather is very hot. 3. conjunction of choice The conjunctions or and otherwise are used to join: A. Study well. + You will fail if you don‟t. = Study well otherwise you will fail. B. This work can be done by you. + This work can also be done by me. = This work can be done by you or me 4. conjunction of condition The conjunctions if and unless are used to join: if for positive sentences unless for negative sentences eg- 5. You‟ll do well in the examinations. + You need to study hard for that. = You‟ll do well in the examination if you study hard. = You won‟t do well in the examination unless you study hard. conjunction of reasoning and logical deduction The conjunctions because, so, and therefore are used to join: Composed by HEMRAJ JANGID E-mail - [email protected] Page 67 eg- I won‟t be able to go to school. + I am unwell today. = I won‟t be able to go to school today as I‟m unwell. = I won‟t be able to go to school today because I‟m unwell. = I‟m unwell so I won‟t be able to go to school today. = I‟m unwell, therefore I won‟t be able to go to school today. 6. eg- 7. eg- 8. eg9. conjunction of relation The conjunctions who, whom, whose, which, and that are used to join: Ram is an intelligent boy who gets always 1st rank in the class. (Ram, He) Sita is a doctor whose father is teacher. (Sita‟s , Her) Laxman is a great brother whom everybody likes. (Him) This is the chair which I got yesterday. (It) The wolf that was man-eater has been killed. conjunction of oppose The conjunctions yet, however, and else are used to join: He is very poor. + He is honest. = (He is very poor yet honest) He is intelligent. + He is simple. = (He is intelligent, however he is simple) A worker must remain disciplined. + He will face expulsion. = (A worker must remain disciplined else he will face expulsion.) conjunction of time limit The conjunctions till and until are used to join: Wait for me here until I come back. Don‟t leave till I arrive. conjunction of time, place, method When Where How What Wait until the rain stops. If in the sentence time or time showing word / clause is given then use only „when‟ If in the sentence place or place showing word / clause is given then use only „where‟ To show method of action or work. To ask common things. The train had gone when I reached the station. The boys had stand up when the teacher came This is the village where I was born. Put it where you found it. He died where he was born. I don‟t know how this work has been completed. I don‟t know what he means to say. 10. other conjunction Both …… and (always use plural verb) Not only ………… but also (use verb according noun / pronoun which is after „but also‟) Either ………… or (in positive sentence, use verb according noun / pronoun which is after „or‟) Neither …… nor (in negative sentence, use verb according noun / pronoun which is after „nor‟) So that (use at the last of first clause and before the second clause) Too ……… to (in negative sentence, use „too‟ before adjective and „to‟ before verb) Example – Composed by HEMRAJ JANGID E-mail - [email protected] Page 68 A. B. C. D. Both Ram and Shyam were found guilty. He is good at both English and Hindi. Not only Ram but also Mohan got a prize. Not only December but January is also very cold. Either you or Ram was sleeping on the bench. The boy was either reading or doing something. My brother lost either his purse or pen. He has neither a TV nor a Radio. You are neither intelligent nor hard working. E. He works hard so that he may succeed. He often comes to me so that he may seek my help. F. He is very old. He can‟t walk. (He is too old to walk) He is very proud. He can‟t talk to the poor. (He is too proud to talk to the poor.) EXERCISE : Q.1 Connect the following sentences using the connectors given in brackets. (a) It is very cold. We can‟t go out. (too ……… to) ________________________________________________________________________________ (b) He is too poor boy to pay his fees. (so that) ________________________________________________________________________________ (c) This mango is big. This mango is sweet. (not only ………… but also) ________________________________________________________________________________ (d) Give me a story book. Give me a newspaper. (either ……… or) ________________________________________________________________________________ (e) He is good in Hindi. He is good in Maths. (both ……… and) ________________________________________________________________________________ (f) I don‟t have a ticket. I don‟t have money to buy a ticket. (neither …… nor) ________________________________________________________________________________ Q.2 Join the following pairs of sentences with appropriate conjunctions. (a) I want to sing. I want to dance. _________________________________________________________________________________ (b) Raju is naughty. He is not disobedient. _________________________________________________________________________________ (c) Pay attention to what your teacher says. You won‟t understand the lesson without it. _________________________________________________________________________________ (d) I went to your house twice. I was not able to meet you. _________________________________________________________________________________ (e) The rain must stop. The whole area will be flooded. _________________________________________________________________________________ (f) Mahatma Gandhi was a great national leader. He led a very simple life. _________________________________________________________________________________ Composed by HEMRAJ JANGID E-mail - [email protected] Page 69 (g) I was afraid. It was very dark outside. _________________________________________________________________________________ (h) We should all be together. We want to make rapid progress. _________________________________________________________________________________ (i) You must not leave the classroom. You must finish your work before you leave. _________________________________________________________________________________ (j) You must register online. You won‟t be allowed to take the test. _________________________________________________________________________________ Q.3 Fill in the blanks with the proper sentence connectors given in brackets: (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) We waited under a shady tree ________ the rain stopped. (then / just / until) The accident took place ________ he was walking along the GT Road. (then / while / since) The mice will play ________ the cat is away. (while / when / before) I‟ll light the fire ________ it gets cold. (as / until / when) I‟ll e-mail you _________ I arrive. (as soon as / while / as) Composed by HEMRAJ JANGID E-mail - [email protected] Page 70 23. PUNCTUATION Punctuation marks help us read and understand a written passage clearly. OR Punctuation marks such as the full stop, comma, quotation marks, capital letters, etc. , are used in the written language. The principal punctuation marks that we use for writing are – 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Capitalization Full stop (.) Comma (,) Semicolon (;) Colon (:) Capitalization 6. 7. 8. 9. A sentence begins with a capital letter. letters. Interrogation / question mark (?) Exclamation mark (!) Single inverted commas ( „ ‟ ) Double inverted commas ( “ ”) Proper nouns also begin with capital Full stop The full stop represents the longest pause. at the end of an assertive or imperative sentence. after abbreviations and initials. (but current English usages doesn‟t require full stops for abbreviations and initials ) egAmit is a skilled mechanic. M.A. S.P. Sharma Mr (mister), Dr (doctor), Mrs (mistress), Ms (miss), St (street and saint), Pt (pandit) Comma The comma indicates the shortest pause. to separate three or more words of the same part of speech (nouns, verbs, adjectives, and adverbs) eg- Aziz bathed, ate, dressed, and went out. to avoid the repetition of a verb eg- Richa is an engineer and Rishi, a technician. to separate the subordinate clause of any kind that comes before the principal clause eg- If it rains, the match will have to be cancelled. to mark off phrases in apposition eg- Gandhiji, the Father of the Nation, preached non-violence. Semicolon The semicolon indicates a longer pause than the comma. It is usually followed by conjunction like “and, but, or” . to separate the clauses of a compound sentence, when they contain a comma Composed by HEMRAJ JANGID E-mail - [email protected] Page 71 eg him. eg - Our teacher was a simple, modest, unassuming person; but we all respected to separate sentences which are closely connected in thought, where a full stop would denote a much longer break Reading makes a full man; conference a ready man; writing an exact man. Colon The colon indicates a much longer pause than the semicolon. to introduce a quotation, list, explanation eg Our teacher says: „ Hard work is the key to success.‟ These are the things we need to take with us: a torch, a flask of coffee, some biscuits, sandwiches and sweets. Question mark The question mark is used after a question. egHave you completed your assignment? Exclamation mark eg- The exclamation mark is used only after real exclamation. Oh dear! Alas! Hello! What a terrific idea! Inverted commas The inverted commas is used to suggest direct speech, that is, to enclose the actual words of a speaker or a quotation. egShe said, “I will see what I can do about it.” Or She said, „I will see what I can do about it‟ EXERCISE Q.1 Punctuate the following sentences appropriately. (a) what is that father asked miranda in wonder. _________________________________________________________________________________ (b) on new year‟s day we went on a picnic to golconda fort. _________________________________________________________________________________ (c) i am sorry i interrupted you said the teacher please go on with your explanation. _________________________________________________________________________________ (d) the sun is one of the countless stars in the sky or to put it differently most of the stars are at least as big as the sun. _________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ Composed by HEMRAJ JANGID E-mail - [email protected] Page 72 (e) pt jawharlal nehru the first prime minister of independent india is known as chacha nehru to children india celebrates his birthday as children‟ day on 14th of November every year. _________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ (f) trees help to support human life by supplying the atmosphere with oxygen essential for life moreover forest soil has a way of quickly absorbing water this helps to prevent sudden floods. _________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________ Composed by HEMRAJ JANGID E-mail - [email protected] Page 73 24. VOCABULARY There are different types of words in all languages. Some are similar in meaning, some have the opposite meaning and some sound similar. SYNONYMS Synonyms are different words or phrases in a language that have a similar meaning. eg- Words Synonyms Words Synonyms Almost Nearly Answer Reply Arise Occur Away Absent Awful Terrible Backbone Spine Brave Courageous Comic Funny Complete Finish Contrary Opposite Defective Faulty Disclose Reveal Dull Stupid Eager Keen Business Trade Chiefly Mainly Clever Intelligent Collect Gather Commence Begin / Start Especially Particularly Evaluate Assess Exactly Precisely Fantastic Great Question Enquire Big Large Composed by HEMRAJ JANGID E-mail - [email protected] Page 74 ANTONYMS - Antonyms are words that have opposite meanings. Antonyms Words Antonyms Words Polite Rude Clean Dirty Ugly Beautiful Win Lose Excellent Lousy Left Right Hard Soft Holy Unholy Bad Good Liquid Solid Up Down Right Wrong Large / Big Small Happy / glad Sad / sorrow Light Dark / Heavy Gentle Rough Wet Dry Old New Hot Cold Foul Mean / fair Foolish Intelligent / dumb Usual / interesting Extraordinary / boring Dead Alive / lively Decent Ugly / indecent Refuse Decline / accept Same Different Harmony Symphony / discord Crazy Insane / sane Day Night White Black Possible Impossible Proper Improper Complete Incomplete Discipline Indiscipline Regular Irregular Literate Illiterate Understand Misunderstand Use Misuse Vegetarian Non-vegetarian Painful Painless Useful Useless Obey Disobey Like Dislike Known Unknown Honour Dishonour Unusual Usual Careful Careless Forward Backward False True Save Spend Famous Notorious Ahead Behind Export Import Poor Rich Composed by HEMRAJ JANGID E-mail - [email protected] Page 75 Perfect Imperfect Warm Cool Healthy Unhealthy Come Go Buy Sell Lend Borrow Exhale Inhale Masculine Feminine Employment Unemployment Deposit Withdrew Debit Credit Loss Profit Composed by HEMRAJ JANGID E-mail - [email protected] Page 76 HOMOPHONES Homophones are different words which are pronounced in a similar way / sound. These words may or may not have the same spellings, but have completely different meanings. Words - Meanings Aid (V) – to assist Aide (N) – an assistant Ail (V) – to be sick Ale (N) – a type of beer Ascent (N) – the act of climbing up Assent (N) – agreement Ate (V) – past tense of „eat‟ Eight (N) – the number after seven Bare (Adj) – naked Bear (N) – a wild animal Beach (N) – an area of sand along the sea Beech (N) – a type of tree Bean (N) – a legume Been (V) – past tense of „be‟ Be (V) – to exist Bee (V) – an insect Bell (N) – an object that makes a ringing sound Belle (N) – beautiful woman Berth (N) – a place to sleep on a ship or train Birth (N) – the process of being born Blew (V) – past tense of „blow‟ Blue (N) – a colour Bold (Adj) – brave Bowled (V) – knocked over Born (V) – came into being Borne (V) – past participle of „bear‟ Peace (N) – a situation without violence Piece (N) – a single item Doe (N) – a female deer Dough (N) – a mixture of flour and water Fair (Adj) – just Fare (N) – money paid for travel Find (N) – to locate to have to pay as Fined (V) – punishment Incite (V) – to provoke Insight (N) – understanding Hear (V) – to listen Here (Adj) – at this location Scent (N) – aroma Sent (V) – dispatched Hole (N) – a round opening Whole (Adj) – full or complete Flew (V) – past tense of „fly‟ Flu (N) – short form of influenza Composed by HEMRAJ JANGID Words - Meanings Air (N) – the mixture of gases we breathe Heir (N) – one who will inherit Altar (N) – a holy structure found Alter (V) – in religious places to change Allowed (V) – permitted Aloud (Adv) – in a loud voice Bard (N) – a port Barred (V) – enclosed with bars or poles Eye (N) – the organ of sight I (N) – oneself Band (N) – a group Banned (V) – forbidden Beat (V) – to hit Beet (N) – an edible red root Boar (N) – a wild pig Bore (N) – someone or something interesting Board (N) – a plank Bored (Adj) – not interested Bread (N) – a loaf Bred (V) – past tense of „breed‟ Broach (V) – to raise a subject Brooch (N) – an ornament fastened to clothes Cast (V) – to throw Caste (N) – social class Cereal (N) – grains Serial (Adj) – in sequence Cite (V) – refer to, Sight (N) – vision Site (N) – a place or sitting of something Higher (Adj) – comparative form of „high‟ Hire (V) – to employ Cue (N) – a signal Queue (N) – a waiting line Flea (N) – an insect Flee (V) – to run away Foul (Adj) – grossly offensive or bad Fowl (N) – domestic hen or cock Cell (N) – a small room Sell (V) – to exchange something for money Him (Pronoun) – third person singular, masculine Hymn (N) – a religious song Feat (N) – an accomplishment Feet (N) – the part of the leg below the ankle Know (V) – to be aware of No (Adj / Det) – used to show negation E-mail - [email protected] Page 77 Made (V) – prepared Maid (N) – a young woman Groan (N) – a long, deep sound of anger, pain, or pleasure Grown (Adj) – became big Hart (N) – a deer Heart (N) – organ in the chest that pumps blood Heal (V) – to cure a disease Heel (N) – the back part of the foot Lead (N) – a heavy metal Led (V) – guided Hour (N) – a period of sixty minutes Our (Det) – possessed by us Knight (N) – a chivalrous man Night (N) – the period of darkness between one day and another Knot (N) – a fastening in a cord Not (Adj) – used to show negation Composed by HEMRAJ JANGID Buy (v) – to purchase By (Prep) - near Bye (N) – word used to bid farewell Meat (N) – flesh of animals Meet (V) – to come together and talk One (Det) – the first number Won (V) – was victorious Plain (Adj) – not fanciful Plane (N) – a surface Holy (Adj) – connected with god or religion Wholly (Adv) – completely Mail (N) – letters Male (Adj) – one who belongs to the masculine gender Loan (N) – something borrowed Lone (Adj) – without others E-mail - [email protected] Page 78 GENDERS – These words show to male and female (One for male and other for female) Masculine Gender Feminine Gender Masculine Gender Feminine Gender Brother Sister Father Mother Son Daughter Uncle Aunt Husband Wife King Queen Sir Madam Gentleman Lady Man Woman Nephew Niece Hero Heroine Horse Mare Bull Cow Dog Bitch Actor Actress Tiger Tigress Hunter Huntress Traitor Traitress Lion Lioness Prince Princess Host Hostess Poet Poetess Emperor Empress Master Mistress Mr. Mrs. God Goddess Man-servant Maid-servant Grandfather Grandmother Landlord Landlady Peacock Peahen Headman Headwoman Hen Cock His Her Composed by HEMRAJ JANGID E-mail - [email protected] Page 79 ONE WORDS 1. A person who makes furniture etc. Carpenter 2. A Person who makes and repairs made of iron. Blacksmith 3. A person who makes gold ornaments. Goldsmith 4. A person who robs someone else‟s property. Robber 5. A person travelling on foot. Pedestrian 6. A worker whose job needs strength. Labourer 7. A person who looks after students in a hostel. Warden 8. A person who is receiving medical treatment. Patient 9. A person who washes other‟s clothes. Washerman 10. A person who hunts wild animals. Hunter 11. A person who is in charge of soldiers. Commander 12. A person who brings our letters. Postman 13. The place where things are bought and sold. Market 14. One who travels by bus/train/aero plane. Passenger 15. A person who grows crops. Farmer 16. The person who lives near one‟s house. Neighbours 17. The person who treats patients. Doctor 18. One who cannot see. Blind 19. One who cannot hear. Deaf 20. One who cannot speak. Dumb 21. A place where Hindus go to worship. Temple 22. A place where Muslims go for worship. Mosque 23. A place where kings and queens live. Palace 24. A garden with a lot of fruit trees in it. Orchard 25. The son of a king. Prince 26. The daughter of a king. Princess 27. The art of using the bow and arrows. Archery 28. The mark to be shot at. Target 29. Showing readiness to give help, money etc. Generosity 30. A member of an army. Soldier 31. One who steals something. Thief 32. A strong rope for beating. Whip 33. Mother and father. Parents 34. A place where aeroplanes can land and take off. Airport 35. A place where traveller‟s belongings are searched when leaving of entering a country. Customs 36. A motor vehicle for carrying the sick or the wounded people especially to a hospital. Ambulance 37. An area of water by a coast to shelter ships safely. Harbor 38. A person who works on a telephone switchboard. Telephone operator 39. A person employed to carry traveller‟s bags at railway stations, airports etc. Porter Composed by HEMRAJ JANGID E-mail - [email protected] Page 80 40. 41. 42. 43. 44. 45. 46. 47. 48. 49. 50. 51. 52. 53. 54. 55. 56. 57. 58. 59. 60. A violent man, especially a criminal. Terrorist An entertainer who performs magic tricks. Magician A person who selects articles for the newspaper. Editor A person who collects news items and sends them to the editor. Correspondent The head of the country. President A person who works in a science. Scientist A small group of trees. Grove A tool with a curving blade to cut grain or grass. Scythe The place where patients are treated. Hospital A place where tourists can stay and take meal. Hotel Unwanted or unpleasant sound that causes discomfort. Noise An instrument for showing direction. Compass An instrument to see distant things. Binoculars Famous and admired. Eminent A path across rough country made by passing of people or animals. Trail Land that is soft and wet. Marsh A place where dead persons and buried. Graveyard A small restaurant where light meals and drinks are served. Café Hard portion at the end of legs of animals. Hoof An infectious disease causing fever and red spots on the body. Measles A large tightly tied mass of soft material. Bale Composed by HEMRAJ JANGID E-mail - [email protected] Page 81 PHRASAL VERB - (Phrasal verb is made by adding preposition after verb) PHRASAL VERB 1- BREAK Break-down Break-off Break-out Break-into Break-with Break-in Break-up Break-away 2- BRING Bring-about Bring-down Bring-out Bring-in Bring-up Bring-forth Bring-forward Bring-round Bring-on Bring-over Bring-under 3- CARRY Carry-on Carry-off Carry-out Carry-over Carry-away Carry-through 4- COME Come-along Come-about Come-across Come-off Come-out Come-round Come-at Come-in for Come-into Come-to Come-by Come-up Come-up to Come-upon 5- GET Get-along Get-up Get-on Get-away MEAN HINDI MEAN To be defected To stop suddenly To circulate suddenly To enter with forcedly To break relation To discipline To disperse, to dissolve To flee [kjkc gks tkuk vpkud #d tkuk vpkud QSyuk tcjnLrh ?kqluk LakcaÄ rksMuk vuq’kklu cukuk lekIr gksuk Hkkxuk To make, to happen To abate, to lose power To appear, to launch a new product To earn To look-after, to care To produce, to give birth to To bring in notice To convert to thought To lead, help to produce To bring in favour To subdue cukuk ?kfVr gksuk de djuk izxV gksuk dekuk ykyu ikyu djuk mRiUu djuk tUe nsuk tkudkjh esa ysuk lksp cnyuk iSnk djuk i{k es ykuk neu djuk ’kks"k.k djuk To keep regular, to continue To take away with forcedly To work according guideline To stop To charm, to attract To complete, to support to the end tkjh j[kuk cyiwoZd ys tkuk funsZ’kkuqlkj dk;Z djuk LFkfxr djuk yqHkkuk iwjk djuk To come with To happen To meet sudden To be, belong to To declare result, to come out To improve to disease To reach To receive, to get To inherit Amount to, to regain consciousness To get To raise According to, to be equal to To find by chance fdlh ds lkFk vkuk /kfVr gksuk vpkud feyuk gksuk ifj.kke fudyuk ckgj vkuk chekjh ls Bhd gksuk igq¡puk izkIr djuk mrjkfÄdkj ds #i esa izkIr djuk ds cjkcj gksuk gks’k esa vkuk izkIr djuk mBuk ds vuqlkj la;ksx ls To live with To awake, to stand up To do manage To run lkFk jguk tkxuk [kMk gksuk O;oLFkk djuk Hkkxuk Composed by HEMRAJ JANGID E-mail - [email protected] Page 82 Get-by Get-through Get-over Get-on with Get-about Get-at / get-to Get-into Get-down / get-off Get-out Get-out of 6- PUT Put-on Put-off Put-out Put-up/ Put-away Put-down Put-in Put-by Put-into Put-up with Put-forth 7- TURN Turn-away Turn-down Turn-on Turn-off Turn-out Turn-to Turn-up Turn-about Turn-aside 8- GIVE Give-away Give-up Give over/ give out Give up on 9- Take Take on Take against Take away(from) Take down Take off Take out Take over To get To get success To get health To live as friendship To move about, to walk To reach To be involved in Alight To remove Escape from izkIr djuk lQyrk izkIr djuk fBd gksuk fe=rk iwoZd jguk pyuk igq¡puk Qal tkuk mrjuk gVkuk nwj djuk cp fudyuk To wear, to dress To remove cloths, to stop To douse To put, to adduce To nip To invest money To save To drag into To endure To abstract, to experiment iguuk mrkjuk fLFkfxr djuk cq>kuk izLrqr djuk j[kuk nck nsuk Äu yxkuk cpkuk /klhVuk lgu djuk fudyuk iz;ksx esa ykuk To send back To neglect, not to accept To open, to depend To close To prove, to involve To attention To come To move back side To deviate okil Hkstuk vLohdkj djuk [kksyuk fuHkZj djuk can djuk fl) djuk ’kkfey djuk ?;ku nsuk vkuk foijhr ?kqeuk fopfyr gksuk To distribute To leave To stop doing something To stop having faith or belief in ckVuk NksMuk jksduk fo’okl mBuk Become very upset Begin to dislike Detract from/ to carry Write down spoken words Become successful Kill, destroy, disable Assume control of, responsibility for ijs’kku gksuk ukilan djuk ys tkuk fy[kuk lQy gksuk u"V djuk ftEesnkjh ysuk Composed by HEMRAJ JANGID E-mail - [email protected] Page 83 25 SUFFIX AND PREFIX A prefix is a group of letters added before a word and a suffix is a group of letters added after a word. When we add a prefix or suffix to a word the meaning of the word change. Root, Prefix or Suffix Meaning Examples a, ac, ad, to, toward, near, in addition to, by aside, accompany, adjust, adverb, apolitical, atheist -able, -ible Adjective: worth, ability solvable, incredible acu sharp acute, acupuncture, accurate -acy, -cy Noun: state or quality privacy, infancy, adequacy, intimacy, supremacy -age Noun: activity, or result of action courage, suffrage, shrinkage, tonnage -ance, -ence Noun: action, state, quality or process resistance, independence, extravagance, fraudulence, reference, eminence -ancy, -ency Noun: state, quality or capacity vacancy, agency, truancy, latency, emergency anti, ant against, opposite antisocial, antiseptic, antithesis, antibody, antinomies, antifreeze, antipathy, antigroup, antibiotic -ation Noun: action, resulting state specialization, aggravation, alternation aut, auto self automobile, automatic, automotive, autograph, autonomous, autoimmune cent hundred centennial, century, centipede com, con fully complete, compel, conscious, condense, confess, confirm dis not, opposite of, reverse, separate, deprive of, away dismiss, disallow, disperse, dissuade, disconnect, disproportion, disrespect, distemper, disarray eco- household, environment, relating to ecology or economy ecology, economize, ecospheres, ecomanagement -ed Verb: past tense dressed, faded, patted, closed, introduced -en Verb: to cause to become, Adjective: material, to make verb from the noun lengthen, moisten, sharpen, golden, woolen, silken, encircle, enrichment, end- inside, within endorse, endocardial, endergonic, endoskeleton, endoscope, endogenous -er, -ier, -or Noun: person or thing that does something flyer, reporter, player, member, fryer, collector, concentrator, happier -es, -ies Noun: plural of most nouns ending in -ch, -s, -sh, -o and -z and some in -f and -y passes, glasses, ladies, heroes -ess female actress, goddess, poetess -est, -iest Adjective or Adverb: superlative latest, strongest, luckiest, lyingest ex- out of, away from, lacking, exit, exhale, exclusive, exceed, explosion, ex- Composed by HEMRAJ JANGID E-mail - [email protected] Page 84 former mayor for, fore before forecast, fortune, foresee -ful Noun: an amount or quantity that fills, Adjective: having, giving, marked by Mouthful, fanciful, meaningful, beautiful -fy, -ify make, form into falsify, dandify, classify, indentify -gon birth, race, produce Pentagon, polygon, octagon hyper over, above hyperactive, hypertensive, hyperbolic, hypersensitive, hyperventilate, hyperkinetic in, im, il, ir not illegible, irresolute, inaction, inviolate, innocuous, intractable, innocent, impregnable, impossible, imposter -ing Noun: material made for, activity, result of an activity, to make gerunds flooring, swimming, building, depicting, cohering inter between, among international, intercept, interject, intermission, internal, intermittent, -ity, ty Noun: state or quality lucidity, novelty, naughty, acidity -less Adjective: without, missing motiveless -ly Adverb: in the manner of fluently main strength, foremost mainstream, mainsail, domain, remain mega great, million megaphone, megaton, megaflop, megalomaniac, megabyte, megalopolis ment mind mental, mention, management, Mid In Centre Midway, midnight, midwife, etc micro small, millionth microscope, microfilm, microcard, microwave, micrometer, microvolt mill, kilo, milli Thousand, thousandth millennium, kilobyte, kiloton, millisecond, milligram mis wrong, bad, badly misconduct, misinform, misinterpret, mispronounce, misnomer, mistake, misogynist multi many, much multifold, multilingual, multiped, multiply, multitude, multipurpose, multinational mono one monopoly, monotype, monologue, mononucleosis, monorail, monotheist, -ness Noun: state, condition, quality kindness non not nonferrous, nonsense, nonabrasive, nondescript per through, intensive persecute, permit, perspire, perforate, persuade photo light photograph, photoelectric, photogenic, photosynthesis, photon post after, behind postpone, postdate, postman re back, again report, realign, retract, revise, regain, reuse, reduce, recycle, recover Composed by HEMRAJ JANGID E-mail - [email protected] Page 85 scope see, watch telescope, microscope, kaleidoscope, periscope, stethoscope semi half, partial semifinal, semiconscious, semiannual, semimonthly, semicircle sub under, below, from, secretly, instead of submerge, submarine, substandard, subnormal, subvert super over, above superior, suprarenal, superscript, supernatural, superimpose, supercede, superman -wise Adverb: in the manner of, with regard to timewise, clockwise, bitwise with against withhold, without, withdraw, forthwith trans across, beyond, change transform, transoceanic, transmit, transportation, transducer, transplant, transport, translate tele distance, far, from afar telephone, telegraph, telegram, telescope, television, telephoto, telecast, telepathy, telepathy EXERCISE – Q.1 Find the suffix or prefix from the following wordsRegiment monopoly flooring , incredible disobey richest useful wisdom really played readmission _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ Q.2 Define to the suffix and prefix giving examples. _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ Q.3 Make five - five words using “anti, sub, re, post, end, dis, in, a” prefix. _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ Composed by HEMRAJ JANGID E-mail - [email protected] Page 86 Q.4 Make five – five words using “able, acy, ance, ful, ify, less, ness, ly, wise” suffix. _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ Composed by HEMRAJ JANGID E-mail - [email protected] Page 87 26. WRITING - COMPOSITION NOTE :1. ½ Mark is deducted if the student exceeds / crosses the word limit. 2. ½ Mark is deducted if grammatical, spellings, or punctuation mistake are made by student. 3. ½ Mark is deducted or awarded for writing scale. 4. 1 Mark is award for format. 5. Remain marks are awarded for content. 26-A NOTICE A Notice is a very short piece of writing which is formal in style and is used by individuals and organizations to announce events and celebration, inaugurations, or sales, to issue public instructions and to make appeals as well as to extend invitations. AN EFFECTIVE NOTICE – An effective notice includes the following points – Draw a box for 50 words. Name of the Organization or Institution or Office in capital letter. Date of issuing the notice. „NOTICE‟ A suitable heading in capital letter. Purpose of writing the notice, i.e., meeting or appeal etc. In case the notice is about an event the details of schedule like – date, time, venue, program, duration etc. are given. Signature, name and designation of the person issuing the notice. Style and tone of the language, i.e. formal or informal. Ensure the word limit and check grammar and language. EXERCISE – Q.1 Suppose you are Arpit Goel, the Head Boy Scout of Alien Children‟s Academy, Mahalan. The Scout leader wants to hold a meeting of all the Boy Scouts in order to give them important instructions for the Boy Scout Camp to be held next month. Write the notice in not more than 50 words and put it in a box. (MEETING) ALIEN CHILDREN‟S ACADEMY – MAHALAN NOTICE July 20, 20xx MEETING OF BOY SCOUTS All the Boy Scouts are informed that a meeting of Boy Scouts will be held on 1st August 20xx, during the break period at the Assembly Hall. The Scout leader will give important instructions for the Boy Scout Camp to be held next month. Attendance is compulsory Arpit Goel (ARPIT GOEL, Head Boy Scout) Composed by HEMRAJ JANGID E-mail - [email protected] Page 88 Q.2 Suppose you are Ghanshyam Sharma, the Head Alien Children‟s Academy, Mahalan. In the memory of a great poet, Wordsworth, your school is organizing a Poem Recitation Competition, for the students of classes VI to VIII. Invite the students to take part in the competition. Draft a notice. (EVENT) ALIEN CHILDREN‟S ACADEMY – MAHALAN NOTICE July 20, 20xx POEM RECITATION In memory of the great poet Wordsworth, a Poem Recitation Competition will be held for the students of Classes VI to VIII on 25th July in the School Auditorium from 9.30 a.m. to 12.30 p.m. Budding poets, willing to participate may submit their names, to their class monitors latest by 22th July 20xx. The winners will be given awards by our esteemed Hindi Poet, Dr Ashok Chakardhar. Don‟t miss the golden opportunity. Shakshi Mahajan (SHAKSHI MAHAJAN, Head Girl) Q.3 You are Amit, the Head Boy of Alien Children‟s Academy, Mahalan. Your school is organizing a Science – Exhibition. Write a notice not exceeding 50 words inviting the students of classes VI to VIII to take part in the exhibition. (TOUR / FAIR / EXHIBITION) ALIEN CHILDREN‟S ACADEMY – MAHALAN NOTICE July 20, 20xx SCIENCE EXHIBITIN You will be pleased to know that our school is organizing a Science Exhibition on 28th August 20xx. The students interested in participation are requested to submit their names to the respective subject teachers, latest by 25th July 20xx along with the topics of your modals and projects. The best work will be awarded. Amit (AMIT KHOJI, Head Boy) Q.4 Niharika is a student of class VII in Alien Children‟s Academy, Mahalan. She attended a meeting with the Principal and teachers at which it was decided to collect donations for orphans. Later, she decides to write a notice for the school notice board asking students to donate liberally for this cause. Write the notice. (APPEAL) ALIEN CHILDREN‟S ACADEMY – MAHALAN NOTICE July 20, 20XX APPEAL FOR DONATION Our school has decided to help orphans who are cared by some organizations. We appeal to the students to donate generously for this noble cause. Please deposit your contribution with Miss Rekha Jain in the School Reading Room from 9:00 am to 5:30 pm. Don‟t miss the golden opportunity to get blessings. Niharika (NIHARIKA ARORA, Head Girl) Composed by HEMRAJ JANGID E-mail - [email protected] Page 89 Q.5 You are Chirag Mathur, the Head Boy of Alien Children‟s School, Mahalan. You have been asked to draft a notice announcing that a boy of class VI has lost his spectacles somewhere in the school premises. Put the notice on the Lost Found notice board of your school, requesting the finder to return the same to him.(LOST) ALIEN CHILDREN‟S ACADEMY – MAHALAN NOTICE July 20, 20XX SPECTACLES LOST A brand new spectacles were lost in the school premises on 18th July i.e. Tuesday. The frame is silver and the glass lenses are of „esslor‟ company. They are safely kept in a plastic – case, and the words „vision care‟ is written on the box. If found please return them to the undersigned. Chirag (CHIRAG MATHUR, Head Boy) Q.6 You are Pallavi Ghosh, the Head Girl of Alien Children‟s Academy, Mahalan. You have been asked to write a notice informing that an umbrella was found in the school bus. (FOUND) ALIEN CHILDREN‟S ACADEMY – MAHALAN NOTICE July 20, 20XX AN UMBRELLA FOUND An umbrella has been found lying unclaimed in the school bus. Anyone who has lost it or left it by mistake can identify and claim it from the „Lost Property Room‟ during the activity period within ten days of this notice. Pallavi (PALLAVI GHOSH, Head Girl) Composed by HEMRAJ JANGID E-mail - [email protected] Page 90 26-B MESSAGE Message is a short piece of information, news, or request meant for someone. It can be verbal or written. The reader is provided with such a conversation. He / she is expected to read, understand and interpret the conversation and convert it into a message for a third person. The main points of the conversation should be expressed accurately and precisely. AN EFFECTIVE MESSAGE – An effective message includes the following points – MESSAGE A brief salutation is given, i.e., Sir / Madam / Dear… Time and Date are mentioned. Name of the person for whom the message is written may be written at the top. Entire content should be put in a box. Only the important points should be written. Put the Senders Name / Signature at the end of the message. Abbreviations, symbols and contracted forms can be written. The message should not exceed 50 words. Message should be written in a box. EXERCISE – Q.1 Compose a message by help conversation between Ashu and Riya (Ashish‟s Sister). Ashu to Riya : “Would you mind giving a message to Ashish. Actually, I wanted to request him to bring my science report tomorrow, which he had borrowed last Tuesday. I have to show it to the science teacher tomorrow.” MESSAGE July 21, 20XX 4:30 PM ASHISH Riya called up to ask for his science report, which you had borrowed last Tuesday. He needs it urgently for he has to show it to the science teacher tomorrow, definitely. Ashu Q.2 Compose a message by help conversation between Nitin and Akshay (Arjun‟s Brother). Nitin to Akshay : “Please tell Arjun that, I have got two tickets for the World Cup Cricket Series Test. There is a flight on Monday morning and we are going to Hyderabad. I already have booked the air bus seats and a room in a hotel there. So, please don‟t forget and get prepare for the flight.” Composed by HEMRAJ JANGID E-mail - [email protected] Page 91 26-C SMS (Text Message) Text messages are necessarily the most abbreviated form of communication; most mobile-phone networks restrict users to around 160 characters per message and the handset does not facilitate the composing of lengthy messages. Although many users develop their own codes, there are basic principles that govern the formation of abbreviations: Certain words or syllables can be represented by letters or numbers that sound the same but take up less space. For example, „U‟ sounds the same as „you‟ and „C‟ sounds the same as „see‟ (e.g. CU = see you), while the number „8‟ can be substituted wherever the sound /-ayt/ occurs in a word (e.g. GR8 = great, L8R = later) Words are shortened by simply omitting certain letters, especially vowels (e.g.MSG = message) Abbreviations are formed from the initial letters of familiar fixed phrases, such as BFN „bye for now‟ or TTYL „talk to you later‟. These principles, and the abbreviations themselves, are also found to a lesser extent in conversations in chat rooms and in email. A fuller list of SMS abbreviations is given below. There are some of the more established abbreviations used in all types of electronic communication are listed below : AFAIK - as far as I know AFK - away from the keyboard ASL - age, sex, location ATB - all the best B - be BAK - back at the keyboard BBL - be back late(r) BCNU - be seeing you BFN - bye for now B4 - before BRB - be right back BTW - by the way C - see CUL8R - see you later F2F - face to face F2T - free to talk FWIW - for what it‟s worth FYI - for your information GAL - get a life GR8 - great HAND - have a nice day H8 - hate HSIK - how should I know? HTH - hope this helps IANAL - I am not a lawyer, but (as a disclaimer) IMHO - in my humble opinion KWIM - know what I mean? L8R - later LOL - lots of luck/laughing out loud MOB - mobile MSG - message Composed by HEMRAJ JANGID TTYL - talk to you later TX - thanks U - you WAN2 - want to W/ - with WKND - weekend WU - what‟s up? X - kiss XLNT - excellent XOXOX - hugs and kisses YMMV - your mileage may vary (i.e. your experience may differ) YR - your 2 - to, too 2DAY - today 2MORO - tomorrow 2NITE - tonight 3SUM - threesome 4 - for M – am F9 – fine IMU – I miss you GM – good morning GE – good evening GN – good night GD – good day V – we PPL - people R - are ROTF(L) - rolling on the floor (laughing) SIT - stay in touch SOM1 - someone E-mail - [email protected] Page 92 MYOB - mind your own business NE - any NE1 - anyone IMO - in my opinion IOW - in other words JIC - just in case JK - just kidding KIT - keep in touch NOYB - none of your business NO1 - no one OTOH - on the other hand SPK – speak PCM - please call me PLS - please EXERCISE : Q.1 Write short sms to your friend about 50 characters telling him congratulation on his great success. Congratulation frnd on your gr8 success. It is result of your hardworking and regular study. Now u‟ve to achieve your goal. GM Composed by HEMRAJ JANGID E-mail - [email protected] Page 93 26-D E-MAIL E-mail or electronic mail is the process of exchanging messages electronically using computers or mobile. E-mails allow users to communicate with each other in less time and at nominal costs. Any form of data like text, graphics, sound, or video can be sent through e-mail. E-MAIL ADDRESS – An e-mail address is divided into two part, namely the username or the user ID and the identity of the mail server. The two parts are separated by the @. The Structure of an e-mail address is given below – [email protected] For examples [email protected] [email protected] E-MAIL FORMAT – E-mail Format Date : …………………………………………………………………………………… From : …………………………………………………………………………………… To : …………………………………………………………………………………… Subject : …………………………………………………………………………………… Attachment : …………………………………………………… (browsing file) Message Box : send save The e-mail is immediately sent to the specified address and a message is displayed informing that your e-mail has been sent. EXERCISE – Q.1 You have just read a news in a newspaper that the state Government is planning to reduce the fees in the University. Write an e-mail to your friend who lives in Delhi and is planning to do B.Ed. after his graduation. Your friend‟s e-mail address is „[email protected]‟ . Composed by HEMRAJ JANGID E-mail - [email protected] Page 94 E-mail Format Date : ……………… 19-12-20XX ………………………… From : ……… [email protected] …………… To : ……… [email protected] ……… Subject : ……… A good chance to continue your education …… Attachment : …… Newspaper cutting image …… (browsing file) Message Box : Dear Ramanuj You told me that you‟re interested in doing B.Ed. from Rajasthan. You‟ll be glad to know that State Government is planning to reduce the fees in the University. There are about 38 Universities in Rajasthan out of which 15 Universities. You can easily get into any of these Universities. In this way you can continue your education and even your dream to do your B.Ed. can easily be fulfilled. The Government has plans to encourage number of students to get their education to fulfill the dreams and brighten their future by providing them better-equipped and quality education. I hope you will consider it. Raj Sinha send save Composed by HEMRAJ JANGID E-mail - [email protected] Page 95 26-E DIARY Diary entry is very personal form of writing having no hard or fast rules. It reflects our creativity, imaginations, expression etc. AN EFFECTIVE DIARY – An effective diary includes the followings points: Day, date, and time of entry. Descriptive heading. Expressive beginning. Contents of the diary entry – your thoughts and feelings. EXERCISE – Q.1 You have topped in your school in the final Examinations and feel happy and excited. Write a page in your diary expressing and sharing your feelings. Monday, 15th March, 20XX, 9:30 p.m. Topped in Final Examinations Today was the happiest day in my life. My result was declared early in the morning for which I was anxiously waiting. What a jump! The Final Examination results were declared today, in the morning. I topped the list of successful candidates in the school. I am the luckiest student in the school to have achieved full marks in all the subjects. No doubt I have done very well in the examination and such a superb achievement was beyond my expectations. How jubilant I felt today when the Principal along with the entire staff congratulated me. They said that they were proud of the Honour I had brought. My family was very happy. Today‟s memories will never, never fade from my mind. Composed by HEMRAJ JANGID E-mail - [email protected] Page 96 26-F LETTER A letter is a written message the writer sends others through post / couriers / e-mail. Letters enable us to communicate thoughts, needs, feelings and information to others when we can‟t express them verbally or directly. Personal letters help us to be in touch with our friends, relatives and dear ones. Official letters are written to convey official requests or suggestions as well as to serve as a record. CLASSIFICATION – LETTER WRITING FORMAL INFORMAL (Official - Business) (Personal) (a) Includes letters and applications to the editor of newspaper, official letters, letters from and to companies, government departments. (b) Language and Tone is objective, business-like to communicate message. (a) Personal / informal letters are written to relatives and friends. (b) Language and Tone is easy, relaxed and conversational style. LAYOUT OR LETTER FORMAT – FOR INFORMAL LETTERS - Composed by HEMRAJ JANGID E-mail - [email protected] Page 97 Sender‟s address Date Salutations (never use Dear Friend. always write a name) (Body of the letter) (This space is for the body of the letter containing all the information the sender wants to convey ) Closing of the letter (leave taking expression) (eg- convey my best regards to …… and love to …… See you. Bye) Subscription (yours sincerely, your loving …… ,) Name of the person writing the letter N.B. – In personal letters, we don‟t write the recipient‟s address in the letter but on the envelope. Subscription for personal letter – 1. Yours ever 2. Yours lovingly 3. Yours affectionately 4. Yours FOR FORMAL LETTERS - Sender‟s address Date Receiver‟s name, address, designation The theme (Subject) Salutations (Sir) (Body of the letter) (Body of the formal letter divide into three parts: ) [PARA – I (who you are and why are you writing)] [PARA – II (body of the letter, detail of the issue / topic)] [PARA – III (what would you like the reader to do)] Closing of the letter (Thank you!) Subscription (yours truly) Sender Signature, Name and Designation Subscription for official letter – 1. Yours faithfully 2. Yours sincerely 3. Yours obediently 4. Yours truly 5. Sincerely EXERCISE – (a) You are suffering from flu. You can‟t go to school for the next few days. You need to inform the principal of your school about your illness and ask for leave of absence from the school. (b) You have received a wonderful watch as your birthday gift from your uncle who lives in Gohati. You feel very happy that your uncle remembered your birthday as Composed by HEMRAJ JANGID E-mail - [email protected] Page 98 much as he remembered how much you wanted to buy that watch. You want to thank him for the gift. (c) Poor water and electricity supply have created problems in your area. You strongly feel that students like you can bring the attention of the city government towards such problems. Write a letter to the Editor of the Hindustan Times highlighting the problem and appealing to the government to pay attention. (d) You are Anne, a student of VIII standard of Alien Children‟s Academy, Mahalan. Write a letter / application to the class teacher requesting him / her to issue you a duplicate ID card as you have lost the original one. (e) You are Pradeep, living in hostel of your school, Alien Children‟s Academy. Write a letter to your father telling him your hostel life. (f) Your friend has got 1st rank in secondary board examination. Write a letter to your friend congratulating him / her on his / her great success. OR Your cousin took part in the NCC flying selection wing in Jaipur and was selected as the best cadet. Write a letter congratulating him / her on his/her achievement. (g) You are wholesaler. You have shorted some books of Mathematics. Write a letter to Oxford Press Pvt. Ltd. New Delhi, to send short books as soon as possible. Composed by HEMRAJ JANGID E-mail - [email protected] Page 99 26-G NEWSPAPER REPORTS It is an authentic account of an event, which is precise and specific in details and objective in style. METHOD OF WRITING A NEWS REPORT – Write a report in a practical and business manner providing necessary information clearly. Most relevant information is included in the report. The heading should be clear and factual. Well-structured report begins with a heading and runs into small paragraphs. NEWS REPORT FORMAT – Heading (By ……………………………………………, ……… designation …………) …… Location …… , …… date …… , ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- (Contents) ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- EXERCISE – (a) Suppose you are Neha Arha, the Staff Correspondent of The Hindustan Times, Jaipur. You have been asked to cover an accident which took place at Harmada near Jaipur. On reaching the spot, you have gathered the following information: Location : Harmada near, Jaipur Date / Time : Friday, August 18, 20xx , 9:00pm Killed (5) : Sheetal, Anisha, Anne, Firoj, and Kasim Injured : 12 Tempo – Trax : Proceeding to Laxmangarh from Jaipur Bus : From opposite direction 5 KILLED, 12 INJURED IN ROAD ACCIDENT NEAR JAIPUR (By Neha Arha, Staff Correspondent) Jaipur, August 18, 20xx, Five Persons were killed and 12 other, including two children, injured when the vehicle in which they were travelling collided head on with a private bus at Harmada near the state capital, police said. All the victims were travelling in Tempo – Trax and they were proceeding to Laxmangarh from Jaipur to pay obeisance at the „Baba‟s Mosque‟ near Sikar when the bus approaching from the opposite direction collided with it. The deceased have been identified as Sheetal, Anisha, Anne, Firoj, and Kasim. Immediately, the police rushed the injured persons to the SMS Hospital in Jaipur. The condition of two of the injured is stated to be serious. Composed by HEMRAJ JANGID E-mail - [email protected] Page 100 (b) Such as another exercise on – 1. A house on fire. 2. A serious train accident. 4. Serial bomb blast in Jaipur. Composed by HEMRAJ JANGID 3. Bank robbery 5. Attack on white house E-mail - [email protected] Page 101 26-H POSTER WRITING A poster is a very useful means of making an announcement, issuing a notice, advertising a product or bringing about awareness on any issue of public interest. A poster is always easily readable and is visually attractive. Posters are mainly used by political parties, film maker, advertisement agencies, different government departments etc. AN EFECTIVE POSTER – Is prepared with a particular audience in mind. Mentions the theme of the notice. Appeals for awareness, a warning or a caution. Takes the form of an invitation for sales, fashion shows exhibitions etc. FORMAT – A poster has no fixed format. But it incorporates the various points like theme / event, occasion, date, time and place, a message of appeal or caution or warning, slogans and captions and the name of the organization issuing it. Visuals enhance the impact of a poster. Ideally one full page should be used for writing a poster. The poster is prepared in about 50 words and is put in a box. EXERCISE – (a) Create a thought provoking poster in about 50 words inspiring people to grow more trees. Put the poster in a box. (b) Design a poster announcing a POLIO DROP weak in your city, encouraging people to bring their children to the camp „arranged in their locality‟, organized by the „Health Ministry‟. Put the poster in the box. (c) Such as another exercise on – 1. BLOOD DANATION CAMP 2. FREE MADICALE CHECK UP CAMP 3. OPPOSE RALLY 4. BENEFIT OF SOLAR ENERGY 5. WATER HARVESTING 6. CONSERVATION OF NATURE Composed by HEMRAJ JANGID E-mail - [email protected] Page 102 26- I PARAGRAPH / ESSAY WRITING MORNING WALK Morning time is the golden time of the day. It is the best and light form of exercise. It is a natural tonic. There is saying- “ Early to bed and early to rise, makes a man healthy, wealthy and wise” and “ A healthy mind in a healthy body” It is equally good for the old, young and children. It is easy but valueable. It keeps the body healthy and strong. It refreshes our mind and makes us smart. It makes our lungs and heart strong and keeps away illness. In the morning time, we come into close touch with nature. The air is cool and pleasant. Noble(good) ideas come to our mind. I get up early in the morning to go on a morning walk. Nature is full of peace and beauty. I see that birds are singing. I forget my worries. I feel that God is really a big artist. The scene of rising sun has its own charm(beauty). Looking at the rising sun improves our eye-sight. It gives us the wealth of health. In short I can say that morning walk is a boon. So I like morning walk. MY HOBBY Hobby is a work which we do in our leisure for our pleasure. It is a tonic to our dull and dry life. Different people have different hobbies. Photography, swimming, games, singing, dancing, painting, hunting, reading, fishing, boating, gardening are some of popular common hobbies. My hobby is gardening. It teaches is to work hard with our own hands. In gardening me study “The Book of Nature”. We learn about plant life. It gives us mental peace. Gardening adds to the beauty of the house. I have always a love for nature. I have made a small garden behind my house. I have planted some fruit plants, flower plants and grow vegetables. I work my garden for one hour. It saves money because we do not have to buy vegetables. Gardening is not a costly hobby. THE IMPORTANCE OF NEWSPAPERS Newspaper is a mirror which reflects the political, the economics and the social conditions. Newspaper tries to give us the latest news about the country and the world. We can know how things are going on. The government programs and policies are made public through newspapers. Everybody wants to read a newspaper. They are published in English, Hindi, Urdu and in almost all other regional languages in great number. Newspapers are eyes and ears of the government and politicians. They can know the public opinion. They ring awakening among people against social, economic and political ills. There are separate sections for business, sports and local news. It is a link between the people and the government. There are many advertisements. They help trade and business. They bring the sellers and the buyers closer. They increase our general knowledge. They have educational value. Composed by HEMRAJ JANGID E-mail - [email protected] Page 103 AN EDUCATIONAL TOUR Students get bored by doing the same king of study. So it is necessary to break the daily routine by doing something different. An educational tour one of the way of bringing some change in the students life. Our school decided to go an educational tour during Deepawali holidays. About eighty students of my school were ready to go. We were to go to Mount Abu. At about 11 am, we started for tour. We were in a happy mood on the way. On the way some friends were talking, singing and laughing loudly. Our teachers guided us. We reached there at 11pm at night. We went to a inn and got comfortable room. In the morning we got ready and went to see important places. We stayed there for two days. Then we want to Udaipur and saw important places and lakes there we came back to our home happily. We were tried but our hearts were happy. A PICNIC We get bored by doing the same kind of work daily. So it is necessary to break the daily routine by doing something different. Picnic is one of the way of bringing some change in the daily routine. Last Sunday it was a rainy day. My friends came to me and we decided to go on a picnic. At keoladev Ghana birds sanctuary. The weather was very fine. The sky was covered (filled) with dark clouds and the air was cool. At about 11a.m. we started for picnic. We were in a happy mood. On the way some friends were talking, singing and laughing loudly. We reached there at 9 o‟clock. Chirping of birds welcomed us. Most of migratory birds had come. We started visiting the place. We spread our carpet by the bank of a lake and took our lunch. After lunch and rest we started on our visit again. At about 6 p.m. we came back to our home happily. We were tried but our hearts were happy. A VISIT TO A HISTORICAL PLACE There are many famous historical places in India. Such as Chittorgarh fort, Tajmahal, Haldi Ghati etc. They gives us knowledge of history. Last Sunday my father took us to Agra. My father bought five tickets and we entered the Taj-Mahal and visited the Taj-Mahal. The Taj- the crown of the world-is at the Yamuna in Agra. Shah Jehan, the great Muslim emperor, got it built. It is made of white marble on the grave of his dear wife Mumtaz. He loved her very much. It is a token of love and sorrow of a great emperor. It was built about three hundred years ago. It was built in about twenty one years. The gateway is made of red stone. There are green lawns and beautiful flower beds. Flower plants add to its beauty. There is a very big platform made of marble. The main building is made on it. There is the Hall of Death. Sayings from the Holy Quran are written almost on every wall. There are four big „minars‟. Really it is a wonderful building. A VISIT TO A ZOO Zoo is a practical means to increase our knowledge. Books give us the second-hand knowledge while a zoo gives us first-hand knowledge. Composed by HEMRAJ JANGID E-mail - [email protected] Page 104 Last Sunday my father took us to the zoo. My father bought five tickets and we entered the zoo. It has two sections-„Animal Section‟ and „Bird Section‟. First of all we saw the animal section. We saw elephants, giraffe, zebra, lions, tigers, bears, stags, deer, rabbits, chimpanzee, alligators, rhinoceroses etc. In bird section we saw swallow, owl, wood-pecker, pigeon, raven, eagle, vulture, bat, dove, drake, ostrich, crane, parrot, swan, falcon etc. At last we talked to animal keepers. They gave us interesting information that increases our knowledge. Thus, this visit gave us amusement and education. IMPORTANCE OF TREES – We can‟t live without trees. Trees is a great gift of nature to man. No living being can exist on this earth if there are no trees. Trees give us the vital gas oxygen for breathing. Threes absorb the harmful gases like carbon dioxide, which we breathe out. Trees maintain the gases balance and moderate our climate. Trees control the pollution. Trees help in rain. Trees stop soil erosion. Trees maintain up the level of soil water. Forests are also shelter for birds and animals. Forests protect the wild animals. They also give us fader fuel, timber, rubber, drugs, spices fruits, gums etc. In short we can say that benefits of trees are endless. Trees give us direct and indirect benefits. So we should save trees and stop cutting of trees. A VILLAGE FAIR – Fair is a large crowded of people that come there to buy, to sell something and to enjoy. Fair is a memorable of folk God, God or Goddess and people worship them. It is way to meet to each other. In Rajasthan many fairs fall such Baba Ramdev, Tejaji, Khatushyam Ji, Pushkar, Dashehara, Jugal Ji etc. I live in a village. There are three words for villagers that describe their life – simple, pure, and fresh. Last Sunday I went to see the fair of Jugal Ji with my family. Hundreds of men, women and children were there. People were going and coming here and there in groups. Some singers were singing songs. There were many stalls of toys, clothes, sweets, juice and many other things. There were some magic show and chakries. There were some scouts and police men to help the people. We went into the temple. There was a long queue of people. After some time we had „Dharshan‟ of Jugal Ji. Then we came back to our house. I was very happy. I cann‟t forget this fair. WONDERS OF SCIENCE – We live in the age of science. Science has given us many wonders. Science is a blessing. Science has given legs to the lame and eyes to the blind. X-ray is a window through which we can see inside the body. X-ray has done much in finding out many diseases. Vaccination has almost rooted out small pox, cholera etc. Plastic surgery is the latest development in surgery. Now germs die, men live. Today man can live a longer and healthier life. Now man flies in sky like a bird and swim in oceans like a fish. Ships, aeroplanes, trains, motors have been invented. Electricity is another wonder. In the field of industry machines are very important. Cinemas, radios, television give us recreation. Computer and robots are wonders. Man has reached the moon. Composed by HEMRAJ JANGID E-mail - [email protected] Page 105 Science has given birth to many evils. It has invented various war weapons. Atom and hydrogen bombs, rockets, missiles, are the examples. Science has shaken our faith in God, religion and nature. Science has given us wealth but not happiness. MY FAVOURITE FESTIVAL – India is a country of festivals. There are many festivals fall in a year such Deepawali, Holi, Onam, Eid, Mohram, Rakshabandhan, Teej, Dashehara, Janmashtmi, Christmas etc. There are some festivals for Hindus, some for Muslims and some for others. My favourite festival is Deepawali. Deepawali generally falls in last week of October or first week of November and Hindi month it falls on Amavshiya of Kartik month. It is called light of festival. This festival to be celebrates on grove of Lord Rama. On this day Lord Rama returned to Ayodhiya from forest after fourteen years. This festival is victory of light on dark. Before week people clean white wash and paint their houses and shops. They decorate them. On this day people put on (wear) new dresses and say each other „Happy Diwali‟. They worship Laxmi – goddess of wealth. Children and grownups burnt fire crackers. All are very happy. Composed by HEMRAJ JANGID E-mail - [email protected] Page 106 27 COMPREHENSION HOW TO SOLVE THE PASSAGE IN BEST (METHOD TO SOLVE THE PASSAGE) Read the passage carefully least three times. Try to understand the passage message / theme / body. Try to understand the meaning of every word that is given in passage. Find the VOCABULARY of important words such as Antonyms(opposite), Homophones(same sound word / rhyming word), Synonyms(similar word, same meaning word), Gender, One word. Read the question carefully and understand what question is asking you. Now answer the question. EXERCISE – Q.1 Read the following passage carefully and answer the questionsWhen Namita went into her room, she saw a strange man was fast asleep in an armchair. She left the house immediately and went to the police station. She soon returned home in a police jeep with six policemen. But it was now too late. The man had disappeared. She went to her dressing table. She smiled with relief when she saw that the only thing the man had taken was an imitation diamond necklace which she had purchased for twenty rupees. (a) What thing had the man taken from the house? ………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ………………………………… (b) How many police men came with Namita? ………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ………………………………… (c) Find the word from the passage that mean Came back ……………………… Bought …………………………… Q.2 Read the following passage carefully and answer the questionsTrees help conserve soil and water. In open country, trees act as wind breaks and keep the wind from blowing away top soil. Their roots prevent soil from being washed away by heavy rains. Trees roots also help store water in the ground. In mountain regions, forests prevent sliding snow from causing avalanches. Forests also provide shelter for wild life and recreation areas for vacationists. Trees help preserve the balance of gases in the atmosphere. (a) In which regions do forests prevent sliding snow from causing avalanches? ………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ………………………………… (b) Who maintain the balance of gases in the atmosphere? ………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ………………………………… (c) Find the word from the passage that opposite is Top ……………………… Light …………………… Composed by HEMRAJ JANGID E-mail - [email protected] Page 107 Q.3 Read the following passage carefully and answer the questionsIt was late evening when he wrote the first letter. He did not have postage stamps and time was late. He went to bed and could not post the letter. (a) When did he write the first letter? ………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ………………………………… (b) Why could he not post the letter? ………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ………………………………… (c) Find the word from the passage that opposite isMorning ……………………… Last …………………………… Q.4 Read the following passage carefully and answer the questionsThe Ganga is a holy river to the Hindus. The Hindus call it „Mother Ganga‟. Every Hindu wishes to die on the banks of the holy Ganga so that he may reach heaven. It is one of the biggest rivers in India – about sixteen hundred miles in length. It rises in the Gangotri mountains in the Himalayas. At Haridwar, it leaves the mountains and enters the plains. Its speed is slower in the plains. At Allahabad, the Jamuna also joins it and the confluence is known as Triveni. After flowing through Uttarakhand, Uttar Pradesh, Bihar and West Bengal, it flows into the Bay of Bengal. The Ganga is very useful for the country. It brings with it rich soil from the mountains and spreads it on the land to make it very fertile. The fields in this area produce two crops a year. The Ganga is also very useful in other ways. Many saints and holy persons live on its banks and we can learn much from their teachings and wisdom. (a) In which Indian states does the Ganga flow through? ______________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________ (b) How is the Ganga useful for our country? ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ (c) Pick out from the passage the word which is the opposite of – Barren ______________________ Hell _______________________ Q.5 Read the following passage carefully and answer the questionsAt school, pupils are helped at every step by their teachers. At the university, the students listen to lectures and read books and they have to make notes for themselves. In order to take notes in the classroom, it is necessary to have a good ear, a quick mind and mastery over the written language. A good ear helps the students hear what the lecturer says. If the student has a quick mind, he can decide what the important points in the lecture are. Mastery over the written language enables him to take down notes while attending to the lectures. To make notes from books, it is necessary to have an understanding of the subject and the ability to decide what important is. In doing this, the student doesn‟t have to worry about time. He can read a page again. Most students find that the making notes from books help them make their own ideas clear and understand the subject better. (a) What is necessary to understand the subject? ____________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ Composed by HEMRAJ JANGID E-mail - [email protected] Page 108 (b) How can one make one‟s ideas clear? ____________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ (c) Pick out from the passage the word which is– Unnecessary (opposite of) _______________ Write (similar spelling of) _________________ Q.6 Read the following passage carefully and answer the questionsOne day George Washington was riding along a road. On his way, he saw some soldiers trying to lift a heavy beam. The corporal was giving them orders. The beam was too heavy to move without help. They needed only one man more. The corporal, however, would not help them. He thought, he was too big an officer to come down to the level of the soldiers. Washington watched for a minute and then asked the corporal why he didn‟t help the soldiers. The corporal at once turned round and said, “Don‟t you know sir, that I am an officer?” Washington replied, “I beg your pardon, Mr Corporal, I didn‟t know that you were such a great man.” Then he at once dismounted, took off his coat, rolled up his sleeves and pulled at the beam with all his might. The beam came up at once. Washington then mounted his horse again and said to the office, “Mr corporal, if in future you need the help of another man, send for your General.” Washington, the first President of America was a great man, indeed. (a) What did Washington see along the road? ____________________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ (b) How many persons did they need for their help? ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________ (c) Find out from the passage the word which means – Climbed down ____________________ Really __________________ Q.7 Read the following passage carefully and answer the questionsHelen Keller was aged two when an illness took away her sight and hearing. Since she was deaf, she also lost the ability to speak, for we learn to speak by imitating what we hear. So as a child she lived in a dark and silent world. At first it seemed impossible that he would even understand others or be understood by them. Hers was thus a very lonely world. She was helped by a wonderful teacher called Miss Sullivan who had herself been blind as a child but recovered her sight after an operation. Miss Sullivan volunteered to help Helen and taught her to speak, read and write. Helen, later, went to a university and even gained a degree. She then spent the rest of her life working to help the blind and the deaf. She has written many books. Her own book „The Story of My Life‟ is very famous. (a) What was impossible for Helen Keller at first? ____________________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ (b) What did Helen Keller do in the rest of her life? ____________________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ (c) Pick out from the passage the word which is the antonym of – Noisy __________________________ Possible __________________________ Composed by HEMRAJ JANGID E-mail - [email protected] Page 109 Q.8 Read the following passage carefully and answer the questionsIt is very easy to acquire bad habits, such as eating too many sweets or too much food or drinking wine or smoking. The more we do a thing the more we like doing it. If we do not continue to do it, we feel unhappy. This is called the „force of habit‟ and this force of habit should be fought against. Things may be very good, when only done from time to time. But these too become very harmful when we do them too often and too much. This applies even to such good things as work or rest. Some people form a habit of too much rest, while others form a habit of too much work. But „excess of everything is bad‟. In India, use of wine is not at all necessary and should be given up. Its regular use creates mischief in the various organs of the body. It affects the liver and weakness the mental power. (a) How does a man become used to bad habits? ___________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ (b) When do good habits change into bad habits? ___________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ (c) Pick out from the passage the word which is the opposite of – Harmless ________________ Acquire _________________ Q.9 Read the following passage carefully and answer the questionsThe ornament of woman is her character, her purity. Metal and stones can never be real ornaments. The names of women like Sita and Damayantri have become sacred to us for their unsullied virtue, never for their jewellery, if they wore any. Several sisters have told me that they feel all the better on getting rid of their jewels. I have called this an act of merit in more ways than one. No man of woman is entitled to the possession of wealth, unless he or she has given a fair share of it to the poor and the helpless. It is a social and religious obligation and has been called a sacrifice by the Bhagavad Gita. He who does not offer this sacrifice has been called a thief. The Gita has enumerated many forms of sacrifice, but what greater sacrifice can there be than to serve the poor and the needy. For us, today, there can be no sacrifice higher than to forget the distinctions of the high and the low and to realize the equality of all men. (a) What is a social and religious obligation? _______________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ (b) What is the real ornament of a woman? _______________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ (c) Pick out from the passage the word which is opposite of – Remember __________________ Distinction __________________ Composed by HEMRAJ JANGID E-mail - [email protected] Page 110 PRONUNCIATIONS Pronunciations are not given for ordinary, everyday words such as bake, baby, beach, bewilder, boastful, or budget, since it is assumed that native speakers of English do not, as a rule, have problems with the pronunciation of such words. In the Concise Oxford English Dictionary, the principle followed is that pronunciations are given only where they are likely to cause problems for the native speaker of English, in particular for foreign words, scientific and other technical terms, rare words, words with unusual stress patterns, and words in which the standard pronunciation is disputed. For example, full pronunciations are given for the following words: baba ganoush, baccalaureate, beatific, bijouterie, bucolic, and buddleia. The International Phonetic Alphabet (IPA) is used in representing the standard accent of English as spoken in the south of England (sometimes called Received Pronunciation or RP). It is recognized that, although the English of southern England is the pronunciation given, many variations are heard in standard speech in other parts of the Englishspeaking world. The symbols used for English words, with their values, are given below. Consonants The following have their usual English values: b, d, f, h, k, l, m, n, p, r, s, t, v, w, and z. Other symbols are used as follows: g get x loch D this j yes tS chip N ring S she dZ jar T thin Z decision introduction Vowels short vowels long vowels diphthongs triphthongs (; indicates length) a cat A; arm VI my VI@ fire E bed E; hair aU how aU@ sour @ ago @; her eI day I sit i; see @U no i cosy O; saw I@ near Q hot u; too OI boy V run U@ poor U put (@) before /l/, /m/, or /n/ indicates that the syllable may be realized with a syllabic l, m, or n, rather than with a vowel and a consonant, e.g. /"bVt(@)n/ rather than /"bVt@n/. (r) indicates an r that is sometimes sounded when a vowel follows, as in drawer, cha-chaing. Stress The mark " before a syllable indicates that it is stressed. Secondary stress is shown by the mark % before a syllable. Foreign pronunciations Foreign words and phrases, whether naturalized or not, are always given an anglicized pronunciation. The anglicized pronunciation represents the normal pronunciation used by native speakers of standard English when using the word in an English context. However, it is difficult to show the typical pronunciation of some commonly used French words by means of standard English vowel symbols, and for that reason the following nasalized vowels have been used: ë au gratin í bouffant ì chanson Composed by HEMRAJ JANGID E-mail - [email protected] Page 111 ï frisson Composed by HEMRAJ JANGID E-mail - [email protected] Page 112